Transform the production of oral solid dosage forms in the pharmaceutical industry with L.B. Bohle.
L.B. Bohle supports companies with their machines and processes in adopting Continuous Manufacturing. Whether a company is transitioning from a batch process or introducing a new product, L.B. Bohle offers the best solutions and applications.
L.B. Bohle provides fully integrated QbCon® production lines for transforming powder into coated tablets through various continuous manufacturing methods, including:
- Wet Granulation
- Dry Granulation
- Direct Compression
Additionally, it offers "bin-to-bin" solutions and individual components (modules) tailored for continuous manufacturing.
The stand-alone machines for continuous production include the following process steps:
- Twin-screw granulation
- Continuous drying
- Dry granulation
- Tablet coating
The definition of continuous manufacturing
Continuous manufacturing vs. batch manufacturing
Continuous manufacturing is a method in the pharmaceutical industry where products are produced in an uninterrupted, seamless flow from beginning to end.
Unlike batch manufacturing, which requires materials to be transported from one process to the next, with subsequent testing and re-feeding, continuous manufacturing integrates all testing, feeding, and processing in-line. This sophisticated approach leverages analytical technologies to guarantee in-process quality.
Continuous manufacturing within the pharmaceutical industry, particularly for oral solid dosage forms, presents significant advantages such as enhanced quality, cost reduction, increased flexibility, improved operator safety, and benefits for research and development. It allows for 24/7 processing.
These substantial advantages have prompted the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to actively support the development and adoption of continuous process concepts in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Continuous manufacturing – Process
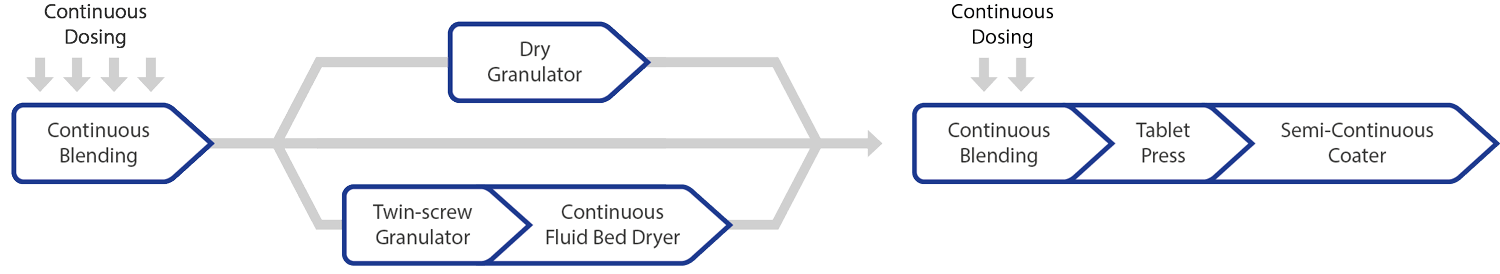
Image Credit: L.B. Bohle Maschinen und Verfahren
Continuous manufacturing with QbCon®– Advantages of continuous manufacturing
- PAT (Process Analytical Technology) ensures the highest quality and process control
- Integrated processes - multiple plants in one integrated plant
- Shorter production times
- Faster research and development cycles with no scale-up issues
- Customizable manufacturing allows for real-time release and customizable batch sizes
- Reduced GMP space requirements
- Higher operator and environmental safety
- Potential savings in:
- Resource consumption
- API consumption
- Personnel/working costs
- Energy consumption
The definition of batch manufacturing
All ingredients are charged before the process begins and discharged at the conclusion of each individual phase. A batch refers to a specific quantity of a product designed to maintain uniform character and quality within predefined limits. It is produced according to a single manufacturing order within the same manufacturing cycle.
Furthermore, a batch indicates the quantity of material and does not describe the method of production. The product is collected after each unit operation and must be transported to the next step. After processing, the finished product is examined in offline laboratories; therefore, processing timeframes can vary from days to weeks.
Batch manufacturing – Process
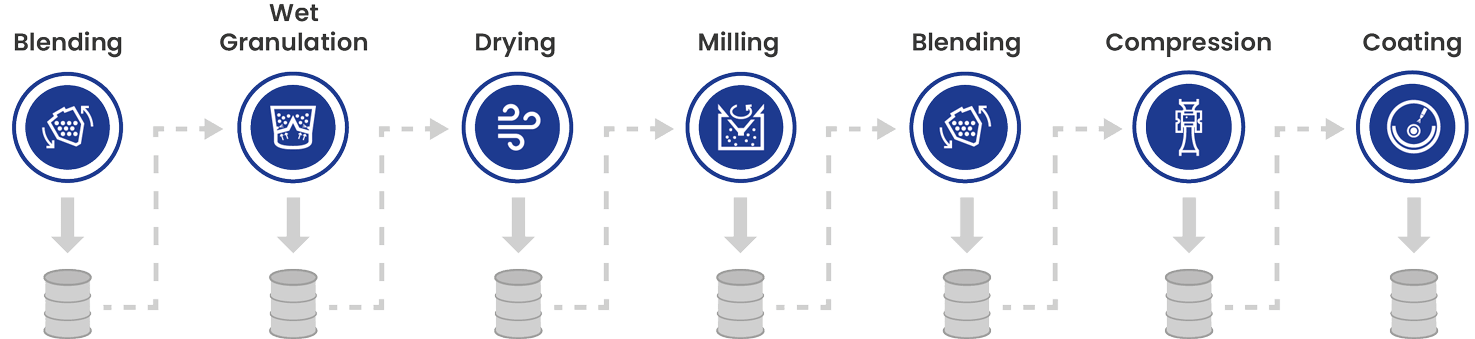
Image Credit: L.B. Bohle Maschinen und Verfahren