The exact cause and pathology of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) are unknown; however, several factors are linked to a higher risk of the condition or worsened symptoms, known as triggers.
These triggers typically cause mild scarring of the lung tissue in the initial changes but can create significant damage over time, leading to changes in the function of the lungs in the delivery of oxygen to the body.
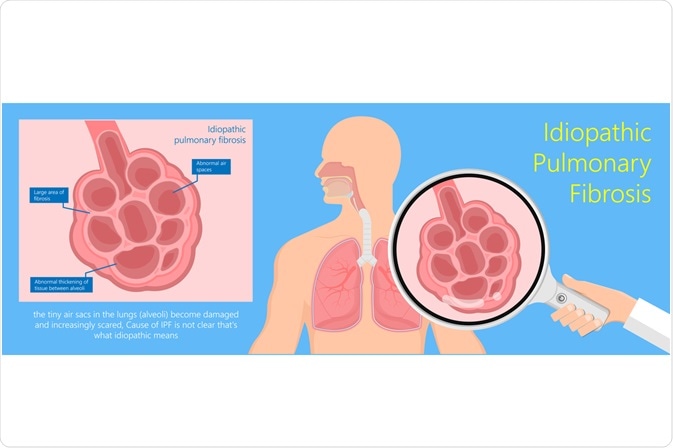
Image Credit: rumruay / Shutterstock.com
Exposure to irritants
Environmental factors play a large role in the pathology of IPF and can trigger the scarring of lung tissue that causes the condition. In particular, exposure to irritants such as certain dust or fumes can be pivotal in the development of IPF.
Some occupations are associated with greater exposure to these irritants and are hence linked to a predisposition to the condition. These jobs may include:
- Farmers
- Hairdressers
- Textile workers
- Stone workers
- Metal workers
Individuals working in these fields are more likely to be regularly exposed to irritants in the air, which they breathe in and trigger the pathogenesis of the condition. It appears that chronic exposure over time is most likely to cause damage to the lung tissue.
Smoking history
Individuals who currently smoke or have smoked in the past are at a higher risk of suffering from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis than other individuals, suggesting that smoke may be involved as a trigger.
This is likely to be similar to exposure to irritants, in that chronic exposure over a long period of time is most likely to cause severe damage.
Associated health conditions
Some health conditions are also linked to an increased risk of IPF and may be involved in triggering the condition, although it is not clear if they are causative of the disease. Some of these associated health conditions include:
- Epstein-Barr viral infection
- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GORD)
- Hepatitis C
- Pneumonia
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Scleroderma
- Tuberculosis
Additionally, chronic aspiration of food, drinks, or saliva as a result of another health condition may lead to the development of lung tissue damage and IPF.
Related medications
Some medications that are used in the treatment of other health conditions may also trigger IPF, as a result of damage to the lung tissue. These medications may include:
- Cytotoxic drugs (e.g. methotrexate or cyclophosphamide)
- Arrhythmic drugs (e.g. amiodarone or propranolol)
- Antibiotics (e.g. nitrofurantoin or sulfasalazine)
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Bills Story
Other risk factors
Although not classified as triggers, there are some risk factors for IPF that should be considered. The most important of these are gender and age.
A higher incidence of IPF has traditionally been observed in men, suggesting a gender susceptibility to the condition. However, the rates of women with the disease are currently increasing and this difference may be dissolving.
Age is a considerable risk factor for the condition, with the majority of patients diagnosed over the age of 60. Likewise, it is rare for an individual to be diagnosed with IPF before the age of 40. This is likely to be associated with the effect of chronic exposure to the irritant over time, which slowly damages the lung tissue and eventually leads to the symptoms and subsequent diagnosis of IPF.
Familial pulmonary fibrosis
Some patients may be genetically susceptible to IPF due to the inheritance of a gene from their parents, resulting in the condition running in family lines. However, in this case, it is no longer classified as idiopathic, without a known cause, and is instead referred to as familial pulmonary fibrosis.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Mar 11, 2023