The limbic system is defined as the brain networking system responsible for controlling emotional drives and memory formation. There exists no universal agreement on the entire list of structures composing the system, but the regions considered include the limbic cortex, hippocampal formation, amygdala, septal area and hypothalamus.
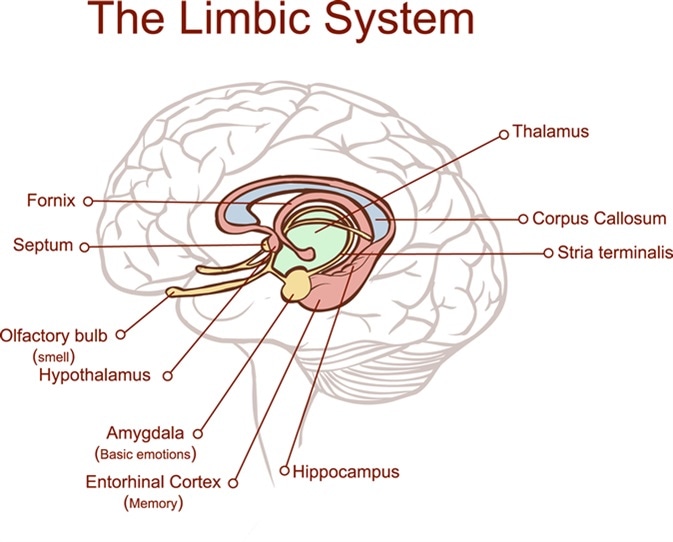
Cross-section through the brain showing the limbic system and all related structures. Image Credit: Corbac40/Shutterstock
Neural networks of the limbic system function in harmony with other brain structures to control a variety of physiological and psychological functions including emotion, behavior, motivation, memory formation, olfaction, sleep (dreaming), appetite, sexual drive, and so on.
A dysfunctional limbic system is associated with many clinical manifestations, such as epilepsy, limbic encephalitis, dementia, anxiety disorder, schizophrenia, and autism.
Limbic system and fear
The limbic system, especially the amygdala, plays a vital role in controlling various emotional behaviors, such as fear, rage, anxiety, etc. The anterior limbic network and related regions, including the orbitofrontal cortex and amygdala, are the main players for regulating such emotions.
The interplay between the dorsal hippocampus, basolateral amygdala, and medial prefrontal cortex is essential in contextual fear conditioning, which requires an integrated representation of a fear-inducing situation and the emotional experience associated with it. In a fearful situation, activation of the dorsal hippocampus does not depend on previous fear conditioning.
This suggests that the hippocampus only encodes spatial information of a fearful situation but is not associated with emotional experiences related to it. In contrast, activation of the basolateral amygdala occurs only if the subject is conditioned with a particular fear.
It indicates that the amygdala specifically encodes the emotional properties of a fear-inducing situation. It is interesting to note that failure of the anterior cingulate and hippocampus to appropriately modulate the activity of the amygdala may result in anxiety disorders.
 Image Credit: decade3d - anatomy online/Shutterstock.com
Image Credit: decade3d - anatomy online/Shutterstock.com
Limbic system and stressful behavior
The fight or flight response, also known as acute stress response, is a survival mechanism that allows individuals to react promptly to a life-threatening situation. The limbic system plays a pivotal role in controlling such behavior.
Neural signals arising from any stressful situation activate the amygdala, which subsequently processes the information and activates the hypothalamus. Afterward, the hypothalamus sends sympathetic discharges to the adrenal gland and facilitates the release of adrenalin into the blood. This in turn activates various autonomic responses to trigger the fight or flight response.
After the initial adrenalin surge, the hypothalamus activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis to suppress the sympathetic discharge. In case of persistent stressful conditions, the hypothalamus secretes corticotropin-releasing hormone and activates the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone.
This hormone activates the adrenal gland and facilitates the secretion of cortisol to keep the body on high alert. After complete dismissal of the stressful situation, the hypothalamus activates the parasympathetic nervous system and inhibits the stress response.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Limbic System
Limbic system and sexual behavior
Male sexual behavior is predominantly controlled by the medial preoptic area of the hypothalamus. Gonadal hormones facilitate the release of dopamine in the preoptic area by increasing the activity of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), which altogether induces various sexual behaviors. The NOS-induced increase in nitric oxide further elevates the release of dopamine.
Glutamatergic projections from the amygdala to the medial preoptic area also participate in releasing dopamine to facilitate mating and increasing sexual responsiveness in the future. Increased release of dopamine in the amygdala triggers sexual behavior by increasing progesterone signaling in females.
An increase in amygdala volume together with reduced connectivity between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex is observed in compulsive sexual behavior.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: May 24, 2021