Milia is a skin condition in which multiple tiny white bumps (cysts) can be seen on a newborn. It is extremely common and most babies will develop these keratin-containing cysts.

Milia is seen in nearly half of newborn babies at birth. Its lesions may be seen on the face, scalp, and upper part of the torso, but there is nothing abnormal about them. In fact, these will usually resolve and disappear spontaneously.
Cysts of a similar nature that are found inside the mouth of a newborn are called Epstein’s Pearls. If they are formed on the palate they are called Bohn nodules. These two conditions do not require any treatment either as the cysts will disappear in some time.
Causes of milia
Milia occurs when dead skin cells from the epidermis get trapped within small pockets on the skin’s surface rather than falling off. This causes the tiny, white coloured, pearl-like bumps on the skin of the baby.
The bumps are often confused with baby acne, but they are not the same condition. An experienced paediatrician will be able to make the distinction by merely examining the skin. No diagnostic tests are required to confirm the presence of Milia. Milia may continue to affect the skin of the baby for a few years in some rare cases.
Symptoms of milia
Milia is primarily characterized by white-coloured, pearl-shaped bumps, which can be seen on the newborn baby’s skin. They are most common on the nose, cheeks and chin on the face. The bumps may also be seen on the scalp of the baby, especially when hair is sparse. In some cases the bumps may spread to the upper torso and limbs or even present in the mouth and palate.
Milia will clear up on its own within three months of the baby’s birth. If it does not resolve in that time period, the baby should be taken to the doctor for a consultation and recommendation of some ointment or cream.
Managing milia in babies
There is no established treatment recommended for milia, although a daily skin care routine needs to be followed. Most of the bumps on the baby’s skin will heal spontaneously, though it takes a couple of weeks post-birth to fully resolve.
Basic skin care includes washing the baby’s skin with a gentle cleanser and warm water. The skin should not be rubbed hard while drying, instead should be patted dry with a towel. One should not try to scrape off the bumps or pinch them as this encourages the risk of infection. The skin of the baby should be moisturised with a non-perfumed, oil-free moisturiser to ensure that it doesn’t dry out.
Milia does not hurt the baby. It does not cause itchiness but if the baby scratches the bumps, a redness or swelling may develop around them. This is a sign of a secondary infection which must be shown to the doctor.
Types of milia in older children
Neonatal milia
This is the form of milia which occurs in babies.
Primary milia
Older children and even adults can suffer from milia. Primary milia in older children is seen on the eyelids, the cheeks and the forehead. Some children may develop a line of milia along the side of the nose. Milia may also be seen around the genitalia.
Juvenile milia
The skin condition may be present at birth or appear a few years later in older children. Juvenile milia may be associated with inherited disorders such as Rombo syndrome, Gardner syndrome, basal cell naevus syndrome, pachyonchia congenita, Bazex Dupre Christol syndrome.
Milia en plaque
Milia en plaque is a set of multiple lesions that spread over many centimetres in diameter on the skin. They can be caused in association with skin disorders such as pseudoxanthoma elasticum, discoid lupus erythematosus, and lichen planus.
Multiple eruptive milia
When there is recurrent milia that affects the face, arms and torso, it is termed multiple eruptive milia. The milia may be asymptomatic like neonatal milia, but in some cases it may be itchy. Milia can be triggered as a reaction to certain topical medication like phenols, corticosteroid creams, 5-fluorouracil cream and hydroquinone.
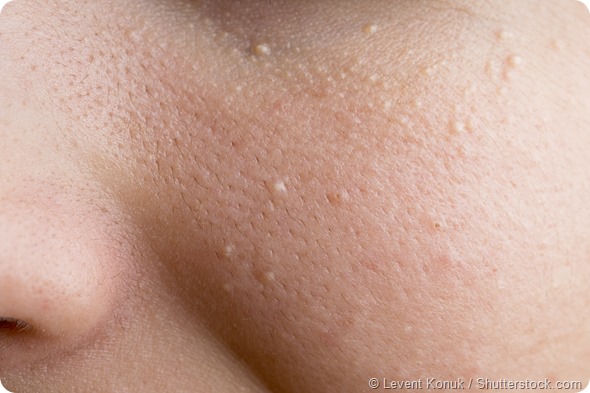
Traumatic milia
Traumatic milia refers to the skin condition which arises at the location of a skin injury. The milia comes from the eccrine sweat ducts and is reminiscent of a calcified nodule. Common injuries of the skin which can result in milia include thermal burns, blistering rashes and dermabrasion.
References
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001367.htm
- http://raisingchildren.net.au/articles/milia.html
- http://www.babycentre.co.uk/a72/spotty-skin
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/
- http://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/milium-milia/
Further Reading
Last Updated: Dec 29, 2022