Taurine is a substance derived from cysteine that can be obtained naturally in foods. Taurine can also be produced naturally in the body through biosynthesis or by industrial processes involving a sequence of chemical reactions.
The synthesis of taurine is important, as this substance plays many functional roles within the body, which may be enhanced with supplementation. The biological significance of taurine has subsequently increased the demand for the development of an industrial process to synthesize taurine and subsequently increase the intake of this amino acid for the general public.
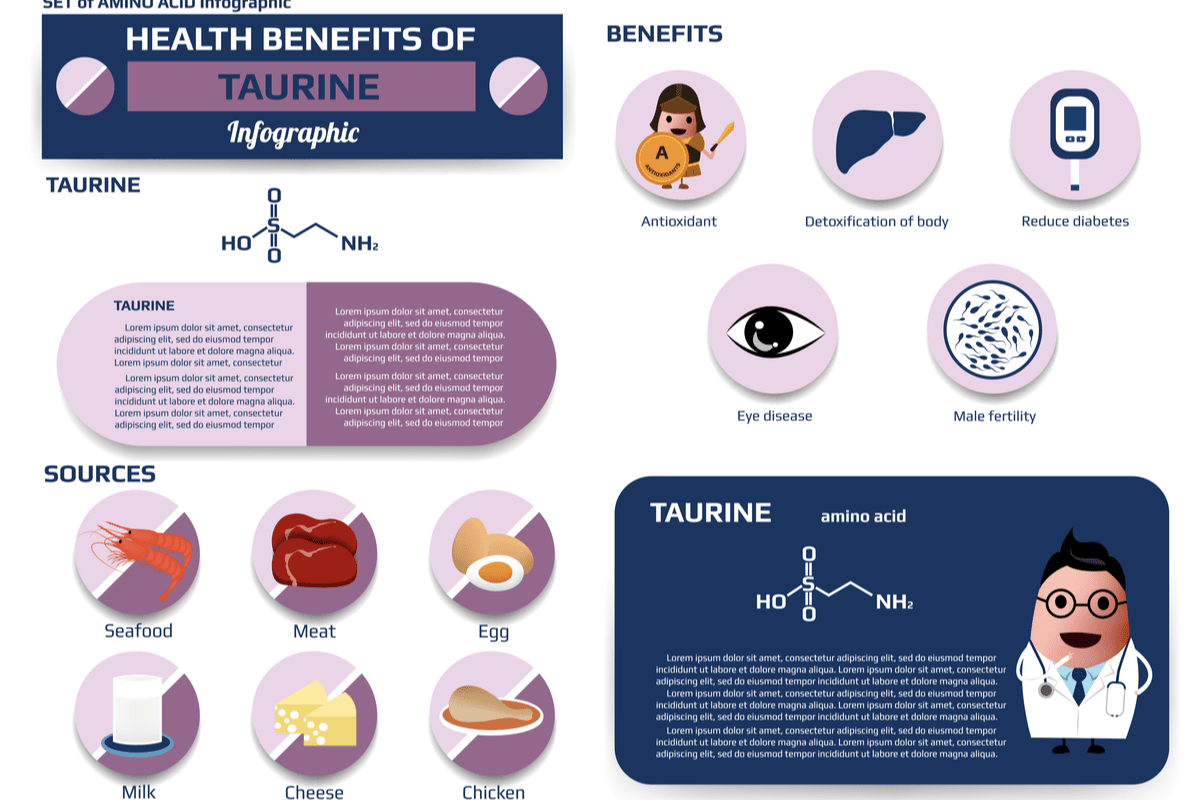
Image Credit: nipada_hong / Shutterstock.com
Naturally occurring taurine and biosynthesis
Taurine is an amino acid that is present in many foods. The average daily intake for taurine is approximately 40 milligrams (mg); however, this value can vary depending on the individual diet. Fish and meat products, for example, have high taurine content; therefore, individuals on a vegetarian or vegan diet tend to have a lower daily intake of taurine.
In addition to its presence in food products, taurine is also naturally found in certain parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal tract, muscular tissue and in bile. These forms of taurine are typically synthesized in the pancreas through the cysteine sulfonic acid pathway, which is otherwise known as the biosynthesis of taurine. The biosynthesis of taurine involves the oxidation of the thiol group of the cysteine, which is followed by a decarboxylation reaction and a final spontaneous reaction to form taurine. Taurine is also produced in the testicles of adult males.
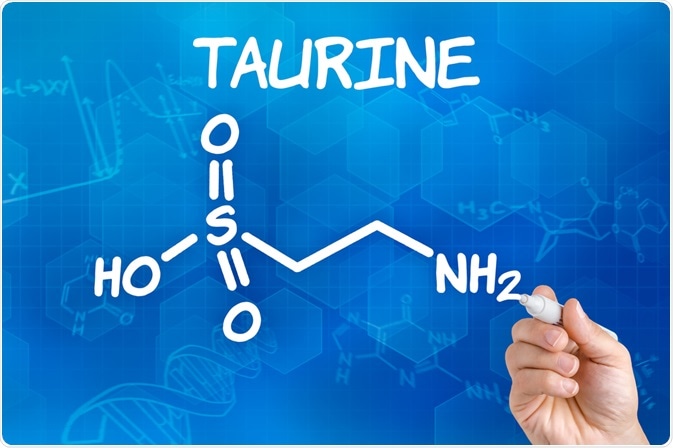
Image Credit: Zerbor / Shutterstock.com
Need for synthesis and production
As a result of the physiological function of taurine in the body, it may be beneficial to increase the daily intake of this amino acid. In fact, up to 2,000 mg per day of taurine has been declared to be safe for most individuals to consume on a daily basis.
Increasing the intake of taurine is believed to improve the maintenance and function of the skeletal muscles. Taurine also plays a role in the regulation of fatty deposits in the liver, which may assist in the prevention of cirrhosis.
Chemical synthesis
There are two main approaches that are commonly used to obtain taurine through industrial chemical reactions.
The first involves a reaction between ethylene oxide and sodium bisulfite to form isethionic acid, which is then used to obtain the synthetic form of taurine. The second type of chemical reaction is between aziridine and sulfurous acid, which results in the production of taurine through a single reactive process.
Commercial production
The consumer demand for products containing taurine continues to increase, thus leading to a greater demand in the industrial production of this substance.
Although taurine is naturally present in numerous food sources, it is economically beneficial to synthesize the amino acid derivative with chemical reactions, rather than extract it from natural sources. For this reason, the vast majority of taurine used in supplements and other food products is chemically synthesized.
Nutritional Supplements : Taurine Benefits
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Sep 26, 2022