Healthy and hydrated human skin has the capacity to stretch and then return to normal when released. This process is controlled by two abundant proteins, collagen and elastin, which are found in the muscles, skin, and bones. While collagen gives structure to the skin, elastin allows it to stretch.
Skin that is stretched beyond the normal level is known as hyperelastic skin. This occurs when there is a rapid increase in collagen or the production of elastin becomes low, hence causing the skin to lose its capacity for elasticity.
Stretchiest Skin In The World - Guinness World Records
Major causes of hyperelasticity
Hyperelasticity is often found in people with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS). EDS is a collective group of genetic disorders that alter the connective tissues that play a vital role in structuring and supporting the organs, bones, skin, and blood vessels in the human body.
EDS emerges due to a defect in certain genes that affect the protein collagen and, in turn, makes the connective tissue much weaker. This overall process of EDS, due to mutation in the genes, causes excessive stretchiness of skin.
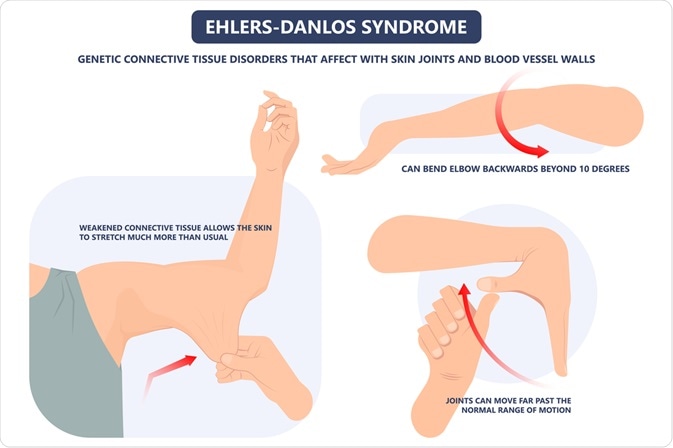
Image Credit: rumruay / Shutterstock.com
The different types of EDS are hypermobility, arthrochalasia, kyphoscoliosis, dermatosparaxis, vascular, and classic. Of these, the most severe is vascular EDS, which affects the walls of the blood vessels and the intestines.
EDS follows an autosomal inheritance pattern; therefore, it affects people in different ways. However, all the above-mentioned types of the syndrome carry hyperelasticity along with it.
Connective tissue and hyperelasticity
Connective tissues are a group of tissues that are essential for the formation and support of the human body. Supporting and transporting other tissues and substances are its secondary duties. A defect in the connective tissue might lead to hyperelasticity of the skin.
A few other disorders that affect the connective tissues and result in stretchy skin include Marfan syndrome, subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma, osteogenesis imperfecta, and pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE)
Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the connective tissues. The fibrillin-1 protein is the most important factor that causes the syndrome. The mutation in this gene increases the production of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and creates a defect in the connective tissue, which also leads to hyperelastic skin.
Subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Lymphoma is a type of skin cancer that arises in the white blood cells of the immune system. It often occurs as skin rashes that can spread all over the body.
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma develops very slowly inside the body. If found in the early stages, there are chances of treatment for recovery from this type of lymphoma.
There are two types of lymphomas known as Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma affects only the skin, causing skin lymphoma. This paves the way for other skin-related disorders, of which hyperelasticity is one.
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a set of genetic disorders characterized by easily breakable bones caused by a disorder in collagen. This type of breakage of bones occurs without any apparent reason. Sometimes, multiple fractures take place simultaneously. There are some rare cases where fractures occur in a baby even before birth. As this is a collagen-related disorder, it is accompanied by stretchy skin,
PXE
PXE is a progressive disorder that is distinguished by the accumulation of calcium and other minerals in the elastic fiber. Elastic fibers make up connective tissues that provide stiffness and flexibility to the entire body. When the accumulated minerals in the fiber damage the connective tissue, it leads to stretchy skin.
PXE affected people develop yellow bumps called papules. These papules are found in the joint bends like the underarms, neck, and elbow.
Age and elasticity
Damage to elastin, which is the elastic tissue present within the body, usually happens due to age. As people grow older, the production of elastin decreases and begins to break down, thereby losing its elastic property. This makes the skin stretch and hangs loosely.
Premature aging of the skin can also cause hyperelasticity. Some of the different factors that can facilitate quick aging include:
- Exposure to sun: Daily exposure to too much sun can damage collagen and inhibit the body from producing new collagen. It increases wrinkles and the skin becomes stretchy. Also, ultraviolet (UV) exposure can break down elastin fibers, making the skin saggy.
- Smoking: Increased production of enzymes called matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) happens due to smoking, which can degrade collagen in the skin. An increase in MMPs can also inhibit collagen synthesis, making skin hyperelastic.
- Dehydration: When the skin lacks adequate water, it starts to become thin and begins to sag. Less intake of water, adverse climatic conditions, overconsumption of dehydrating drinks like alcohol, as well as certain diseases canb cause dehydration.
- Loss of fat: Loss of the fat can result in the loosening of the skin.
References
- Medline Plus, Hyperelastic skin, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003280.htm
- Ehlers-Danlos Arthrochalasia type (VIIA-B) – expanding the phenotype: from prenatal life through adulthood, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4026000/
- Ehlers Danlos Syndrome Network, https://www.ehlers-danlos.com/
- The Marfan Foundation, What is Marfan Syndrome? https://www.marfan.org/about/marfan
- Lymphoma Association, Skin (cutaneous) T-cell lymphoma, https://lymphoma-action.org.uk/
- NIH Genetics Home References, Osteogenesis Imperfecta, https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/osteogenesis-imperfecta
- NIH, Connective Tissue, https://www.niams.nih.gov/
- Study.com, Connective Tissue: Types, Functions & Disorders, http://study.com/academy/lesson/connective-tissue-types-functions-disorders.html
- Livestrong, Aging Skin and Elasticity, http://www.livestrong.com/article/169486-aging-skin-and-elasticity/
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jan 13, 2023