After a child's milk teeth have fallen out, which occurs between 6 and 12 years of age, the adult teeth begin to erupt. The emergence of these permanent teeth usually overlaps with the shedding of the milk teeth and the child's jaws grow to accommodate the larger and greater number of permanent teeth.
Number and appearance
The milk teeth begin to appear around the age of 4 to 6 months and usually form a complete set of 20 milk teeth by 3 years of age.
These 20 teeth include:
- 4 central incisors or front teeth for cutting and biting (two per jaw)
- 4 lateral incisors (two per jaw)
- 4 canines or cuspids for tearing (two per jaw)
- 4 first molar teeth or back teeth for grinding and chewing (two per jaw)
- 4 second molar teeth (two per jaw)
The adult teeth that replace the milk teeth begin to appear at around 6 to 8 years of age and usually form a complete set by the age of 18 to 20 years.
This adult set contains 32 teeth which include:
- 4 central incisors or front teeth (two per jaw)
- 4 lateral incisors or side front teeth (two per jaw)
- 4 canines (two per jaw)
- 8 premolar teeth (4 per jaw)
- 4 first molar teeth or back teeth (2 per jaw)
- 4 second molar teeth or back teeth (2 per jaw)
- 4 third molar teeth or wisdom teeth (2 per jaw)
In most children, 28 of the permanent teeth have already erupted by the time the child is around 13 years of age. These include four central incisors, four lateral incisors, eight premolars, four canines, and eight molars. The last of the permanent teeth are the third molars or the wisdom teeth that begin to appear between ages 17 and 21 years.
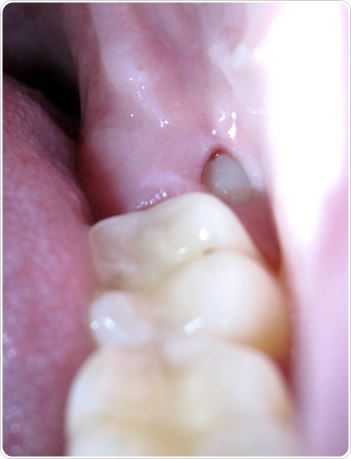
Molar / Wisdom Teeth
Care for permanent teeth
Permanent teeth can last a lifetime and it is very important to maintain them to prevent tooth decay developing and damaging them. Tooth decay can be prevented through brushing and flossing daily and attending regular dental checkups. These maintenance techniques prevent plaque from forming across the teeth and eroding the enamel and causing decay of the material inside.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Mar 15, 2023