Chickenpox is a common viral infection that most people suffer from during childhood. Children younger than 10 years are the most susceptible to chickenpox but it can also occur in adulthood. However, when an adult contracts the disease, symptoms may be more severe, with a higher risk of complication. Chickenpox is listed in the top twenty most painful conditions by the UK's National Health Service.
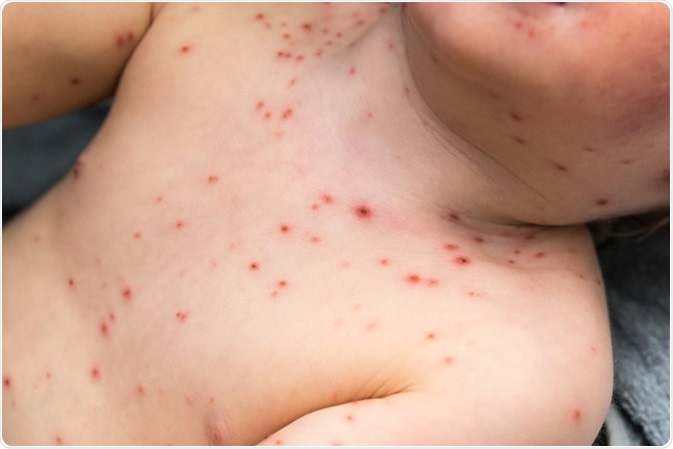
Young Child with Chickenpox - Image Credit: John-Kelly / Shutterstock
Cause and transmission
Chickenpox is caused by varicella-zoster, a highly contagious virus that can be transmitted through the air on sneezing and coughing. Winter and Spring months are the most common periods for the disease to spread but it can affect people at any time of the year.
Varicella zoster virus or varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is one of eight herpesviruses known to infect humans and vertebrates. 3D illustration - Illustration Credit: Tatiana Shepeleva / Shutterstock
Once a person has been ill with chickenpox, they develop immunity against the virus and are unlikely to be reinfected with the disease again in their lifetime. In rare cases, chickenpox can be caught a second time but this is most likely to occur among those with decreased immunity such as individuals with HIV or patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Symptoms
The disease is typically characterized by a rash of red and itchy spots that eventually form blisters. Most patients also develop mild to high grade fever. Usually, the rash initially develops over the torso but may spread to the face, scalp, mouth, nostrils, eyes and almost all the mucosal surfaces within the mouth and throat. The blisters dry out within 5 to 7 days and form scabs or crusts, which may eventually be shed.
Complications
Complications such as secondary bacterial infections are rare but are most common among pregnant women, infants, and elderly individuals. Such infections may be treated using antibiotics. Adults who contract chickenpox are more likely to require anti-viral medications such as acyclovir due to the more severe nature of the disease course during this phase of life.
Diagnosis and treatment
Chickenpox is usually diagnosed on evaluation of clinical symptoms, when the presence of chickenpox blisters is confirmed.
To prevent a child from spreading chickenpox, they are kept away from other children, pregnant women and the elderly, all of whom are more susceptible to the infection and its complications. The illness may last until all the blisters have dried up and turned into crusts, which usually happens after one to two weeks.
Medications such as paracetamol may be used to relieve fever and calamine lotion can ease itching. Aspirin should be avoided in children younger than 12 years due to the possible risk of Reye's syndrome, which can cause severe organ damage, particularly to the liver and brain.
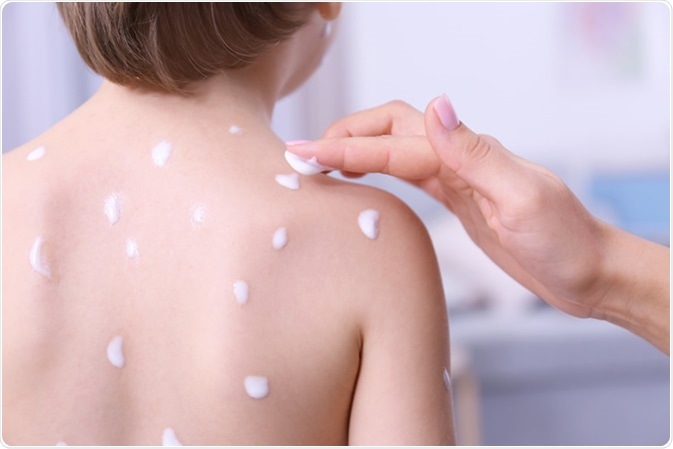
Woman applying cream onto skin of child ill with chickenpox, closeup - Image Credit: Africa Studio / Shutterstock
Prevention
People can be vaccinated against chickenpox to protect against the virus. However, this is not practiced as part of routine childhood vaccination but is used more to protect high risk individuals who are vulnerable to the infection and its complications.
Chickenpox - #VaccinesByTheNumbers
Sources
- http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Chickenpox/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- https://www.lwsd.org/
- http://www.ncirs.edu.au/immunisation/fact-sheets/varicella-fact-sheet.pdf
- https://www.health.wa.gov.au/
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jul 7, 2023