Introduction
What causes vaginitis?
What are the symptoms of vaginitis?
How is vaginitis diagnosed?
What treatment options are available for vaginitis?
How can you prevent vaginitis?
References
Vaginitis, also known as vulvovaginitis, is a term used to describe inflammation of the vulva and the vagina. It can occur as a result of various conditions, including those that cause an infection due to the presence of yeast, bacteria, or viruses and irritation from chemicals or clothing in the area.
It is normal for the vagina to produce a discharge that can vary in quantity and consistency throughout the month. Vaginitis usually involves a significant change in the discharge from the vagina that may be itchy or have a pungent smell. The condition is relatively common and can affect any woman, from young girls to elderly women.

Image Credit: Doucefleur/Shutterstock.com
What causes vaginitis?
There are various types of vaginitis, according to the cause of the symptoms of inflammation.
- Candida (yeast) infection
- Bacterial infection
- Trichomoniasis infection
- Chlamydia or gonorrhea infection
- Viral infection
- Atrophic vaginitis
- Reaction to chemical substance or clothing
What are the symptoms of vaginitis?
The symptoms of vaginitis depend on the cause of the inflammation and can vary significantly between individual women. In some cases, no notable symptoms are present, whilst other women experience symptoms that substantially impact their quality of life. These symptoms may include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Unpleasant odor from the vaginal area
- Itching or burning around the vagina
- Pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Light bleeding or spotting between periods
How is vaginitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis is usually made upon questioning the presence of symptoms and may be confirmed upon physical examination and swab tests of the vaginal discharge.
It is essential that the correct diagnosis is drawn, as there are several causes of vaginitis, each requiring a specific treatment.
A candida infection is associated with a thick, white discharge that is often described as similar in consistency to cream cheese. It does not usually have a distinctive smell but may be very itchy.
A bacterial infection, including sexually transmitted infections, is associated with abnormal discharge, which can vary from milky white to frothy green with different bacteria. Some women may note itching, pain, or soreness, but this is not uniform with all bacterial infections.
If vaginitis results from a non-infectious cause, such as a chemical irritant, the most significant symptom is usually pain or burning in the area, and there is little change in the vaginal discharge.
What treatment options are available for vaginitis?
The treatment of vaginitis is targeted to the cause of the inflammation for the most effective results.
An infection caused by candida overgrowth is usually managed with an antifungal medication such as clotrimazole, econazole, or miconazole. These are available in a cream or pessary form, which can be applied directly to the vaginal area.
An infection caused by bacteria can be treated with antibiotics such as metronidazole, which can be applied locally to the vaginal area.
If an inflammatory response due to a chemical irritant is responsible, the irritant should first be removed, followed by treatment to soothe the irritation. This may include corticosteroids, a sodium bicarbonate bath, or some oils.
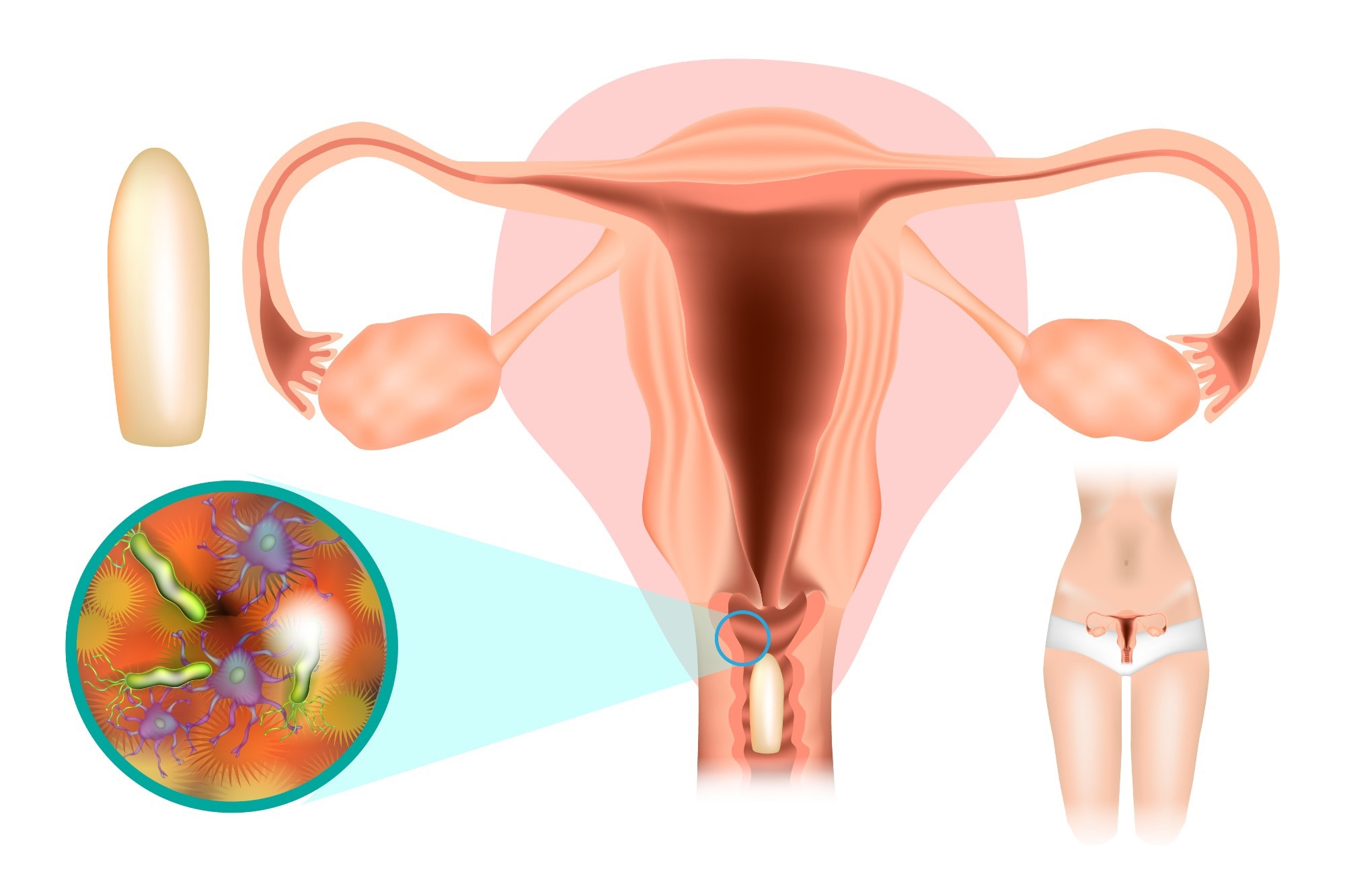
Image Credit: Sakurra/Shutterstock.com
How can you prevent vaginitis?
The prevention of vaginitis is important, particularly for those women who are prone to the condition and experience symptoms regularly.
Some clothing is associated with a higher risk of vaginitis, such as those made of synthetic materials and designed to be of a tight fit. Instead, cotton underwear is a better choice, and loose-fitting clothing can also help to reduce the number of vaginal infections.
Good hygiene is essential, which involves basic cleaning of the genital area with water without washing the normal discharge away. The natural vaginal discharge cleans the area and maintains the optimal pH balance. It is not recommended to flush the area with water, also known as douching, or use chemical-based products that may upset the natural balance.
Using adequate protection when engaging in sexual activities can help to reduce the risk of acquiring a sexually transmitted infection, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomoniasis. In particular, the use of condoms should be advocated to prevent vaginitis.
References:
- nhs.uk. (2017). Vaginitis - NHS. [online] Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vaginitis/.
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Vaginitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & Prevention. [online] Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9131-vaginitis.
- medlineplus.gov. (n.d.). Vaginitis - self-care: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. [online] Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000566.htm [Accessed 26 Jul. 2022].
- https://www.facebook.com/WebMD (2002). Vaginitis (Vaginal Infection). [online] WebMD. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/women/guide/sexual-health-vaginal-infections.
- Mayo Clinic. (2016). Vaginitis - Symptoms and causes. [online] Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vaginitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354707.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Sep 18, 2023