Vertebroplasty is a surgical procedure used to treat a compression fracture of the spinal vertebrae by restoring the strength and height of the collapsed bone. It is usually performed for patients with severe pain that disables them from normal functions if the pain has lasted for more than 2 months.
Indications for vertebroplasty
Vertebroplasty is indicated for treating the symptoms and complications of compression fractures of the spine. These may be due to osteoporosis, which is the most common cause; cancerous deposits in the spine; or spinal injuries, among other causes.
To assess patients' suitability for the procedure, they undergo a clinical evaluation and a physical examination, followed by imaging tests such as spine X-rays and various scanning techniques such as MRI, CT, or isotope bone scans. These may help to localize the fracture site, as well as distinguish old fractures from new ones.
Vertebroplasty aims to provide mechanical stability to the damaged vertebra by injecting bone cement into it through a needle. Bone cement is chemically called polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), and it comes as a powder to which tantalum and barium sulfate is added to make it radio-opaque.
In most cases, vertebroplasty is carried out percutaneously and is a minimally invasive procedure. It is performed as an outpatient procedure under local anesthesia and image guidance.
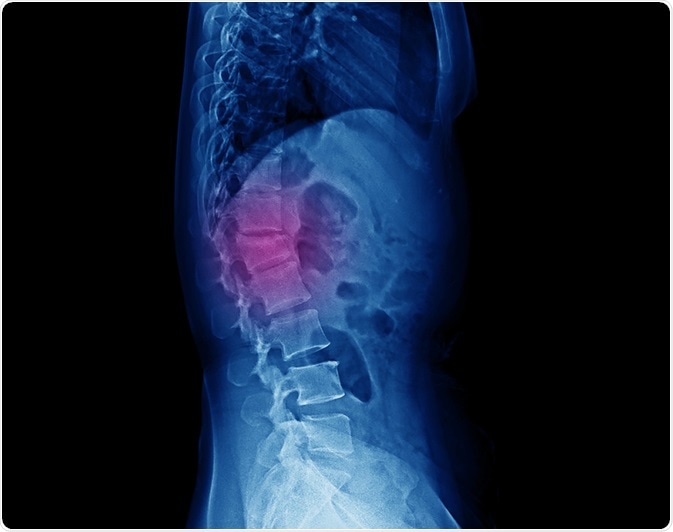
Lateral projection lumbar spine x-ray showing compression fracture at L1 vertebra with mild degree height loss. Image Credit: Yok_onepiece / Shutterstock
Benefits
The benefits of vertebroplasty include relief from pain and functional improvement, with better ability to carry out daily living activities and increased mobility.
Complications
Vertebroplasty may cause the usual complications that follow surgery, such as:
- Infection at the surgical site
- Bleeding and hematoma formation
- Allergic reactions to the anesthetics or other drugs used
- Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias
- Breathing abnormalities
- Specific complications include leakage of the bone cement into neighboring areas, irritating the surrounding nerves and soft tissues. If it leaks into the venous system, pulmonary embolism may be the result.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 4, 2021