Lyme disease is an infection that spreads with the bites of an infected tick. For the past four years, a vaccine to protect dogs from this disease has been available. Now, vaccinating humans against this disease has also become a possibility.
Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School have developed a vaccine against Lyme disease that in laboratory mice has been found to be 100 percent effective in preventing the infections. Within the next two or three years, this vaccine may undergo human trials and come into the market.
A regular vaccine works on the principle of teaching the body’s immune system to recognize a virus or a bacterium by exposing them to tiny amounts of the deactivated or dead microbe. Once the body knows the microbe, when it actually comes across the said virus or bacteria, it can fight off the infection leading to protection.
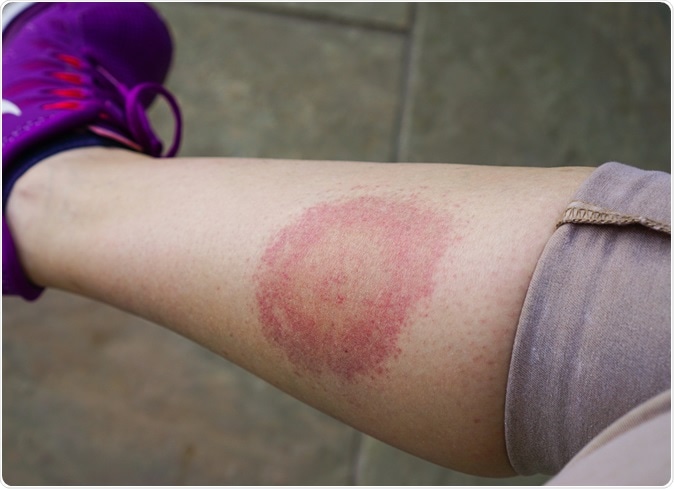
Lyme disease, Borreliosis or Borrelia, typical lyme rash. Image Credit: AnastasiaKopa / Shutterstock
This new vaccine against Lyme disease works a bit differently from this usually concept. The injection termed Lyme PReP has a special antibody that can target the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi that leads to the infection Lyme disease. So when the infected tick bites the mice, the antibodies provided from the vaccine would detect these bacteria in blood and immediately destroy it. It is capable of killing all the invading bacteria. The antibody however has a life of only six to nine months and thus the vaccine may have to be administered before every summer when the risk of transmission is highest.
Dr Mark Klempner who was one of the team that developed this vaccine explained that the mice in the labs were bitten by several infected ticks after being injected with the vaccine. Despite this they did not develop the infection. Several bits are something that most humans who develop the infection would not face, he explained. The vaccine is likely to cost around £150 each and could prevent the hundreds of cases of Lyme disease in UK.
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi that spreads from one person to another by infected tick bites. The symptoms of the disease usually take around 2 to 30 days to develop. There is initially a bull-eye-shaped rash and the infection spreads via blood to joints and nervous system and then to the brain and heart. Some patients may begin the course of their illness with flu like disease and no typical rash.
Treatment is usually with antibiotics. Left untreated Lyme disease can cause serious damage to the joints and the heart. It can cause damage to the joints after several months leading to arthritis with painful swollen joints. About 10 to 20 percent of untreated people will go on to develop chronic (long-lasting) arthritis. Knees are most commonly affected. Lyme disease may also affect the nerves and the nervous system leading to severe headaches, stiff neck, paralysis of the facial nerves and pain and numbness of the limbs etc. One in 10 persons with Lyme disease may also develop heart problems, such as irregular heartbeat, which can start with dizziness or shortness of breath. Such heart problems generally show up several weeks after infection. Other conditions such as liver damage or hepatitis, eye problems, etc. may also be seen.
There are around 2,000 to 3,000 new cases of Lyme disease in England and Wales annually according to some estimates.
Blood tests should be used if doctors suspect Lyme disease. Antibiotics such as doxycycline, cefuroxime axetil, or amoxicillin, taken orally for a few weeks is generally the treatment administered. When Lyme disease occurs in children younger than 9 years, or in pregnant or breast-feeding women, they usually are treated with amoxicillin, cefuroxime axetil, or penicillin.