Because of global warming, it is estimated that there will be a major surge in mosquito-transmitted diseases which would kill half a billion more people over the next three decades.
A new study reveals that the areas at risk that are newly exposed to this threat include Canada and parts of northern Europe with more people in these regions getting infected with Zika, dengue, yellow fever and Chikungunya among other diseases. These diseases till date affected only the tropical regions of the world say the researchers. The results of the study were published in an article in the latest issue of the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
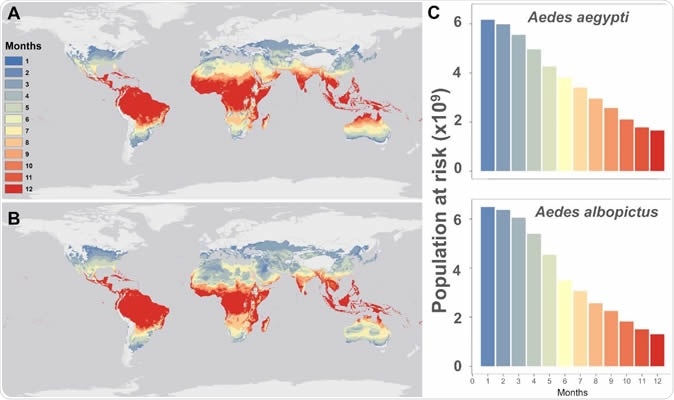
Mapping current temperature suitability for transmission. Maps of current monthly suitability based on mean temperatures using a temperature suitability threshold determined by the posterior probability that scaled R0 > 0 is 97.5% for (a) Aedes aegypti and (b) Ae. albopictus, and (c) the number of people at risk (in billions) as a function of their months of exposure for Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus.
Co-author of the study Sadie Ryan, from the University of Florida, explained that this study shows the effects of these diseases so that policy makers and health care professionals can take notice of the changing epidemiology of these vector borne illnesses. She said, “As you move into a hotter world, the places that get really hot are going to have all kinds of other vulnerabilities with them. Having studies like this that say, hey, this is potentially where these things can show up is going to be one tool in a big tool box.”
The study shows that at present there are over six billion people living in regions where the two species of mosquitoes can survive for a month or more annually. These two species of mosquitoes - Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus were targeted because of their ability to spread disease. The study shows that as milder and warmer climate travels up towards the poles, there are more and more areas where these mosquitoes can breed and survive. Aedes aegypti for example spreads yellow fever and survives in a warm climate. Aedes albopictus, on the other hand survives in cooler climates. The team of researchers looked at possible situations where rise in temperatures could affect the survival of both kinds of mosquitoes.
Ryan said that in 2016 there was a Zika outbreak in southern Florida affecting pregnant women and their unborn babies. The spread of the infection was not just direct but also via travel and immigration say the researchers. Ryan explained, “You might not think to look across the midwest at this point for potential mosquitoes, but what if people are landing in Chicago? Every year we see little bits of malaria showing up in the [US], we see little bits of dengue popping up.”
The team speculated that by 2030 these infections would be common up to the northern limits of the Midlands and by 2050 the spread maybe throughout England and Wales. A report from the UN has warned that there is a record rise in the sea levels and this would lead to floods, heat waves and storms due to the climate change. UN secretary general Antonio Guterres warned “there is no longer any time for delay” speaking about reducing the greenhouse gas emissions.
This study missed out malaria in its analysis. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mosquito borne malaria kills over 400,000 people annually across the globe.
Biologist Colin J. Carlson, a postdoctoral fellow in Georgetown University's biology department, and co-author of the study, in a statement said, “Plain and simple, climate change is going to kill a lot of people… Mosquito-borne diseases are going to be a big way that happens, especially as they spread from the tropics to temperate countries.” On a more optimistic note he added, “I think we don’t talk about [hope] enough. We’re not staring down a certain apocalypse, because I don’t think there’s a future where people take no steps to combat the effects of climate change.”