Johns Hopkins Medicine and University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) researchers will lead a multicenter, multinational study of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM), the “poliolike” condition affecting children that causes loss of muscle control. The National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases awarded an approximate $10 million contract to UAB that will fund at least 38 research sites across the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom and Peru.
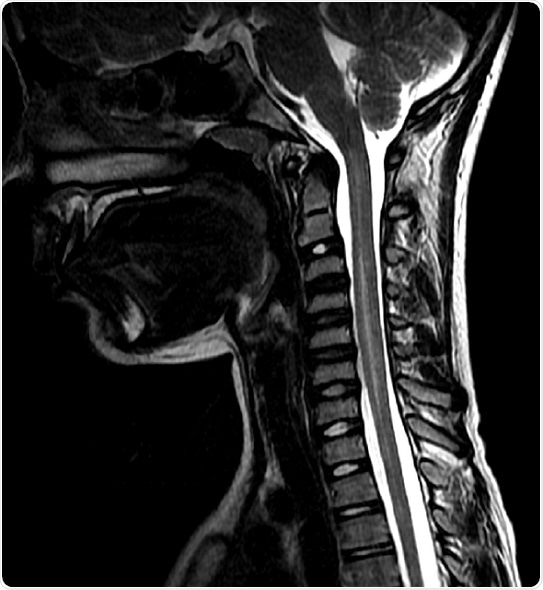
An MRI of a patient with AFM. The lightening on the spinal cord is due to inflammation. Credit: Johns Hopkins Medicine
AFM is a rare condition that causes inflammation and damage to the spinal cord in children, resulting in a sudden paralysis of arms and/or legs and loss of muscle strength and reflexes. Other symptoms can include facial drooping, difficulty swallowing, slurred speech and trouble breathing.
The major problem with AFM as a public health threat is not only the emergence of hundreds of cases around the U.S. and the world, but the fact that AFM produces devastating and long-standing neurological problems for children affected. Thus, there is an urgent need for a concerted collaborative effort around the country to tackle the problem with our best research tools and come up with better options for diagnosis and treatment, to help children and families affected.”
Carlos Pardo-Villamizar, M.D., director of Johns Hopkins Hospital Transverse Myelitis Center and co-principal investigator of the study
The condition can be severely debilitating, and although many children recover fully, it may take many months of physical therapy to regain strength and movement.
AFM’s cause is unknown, though it is thought that a virus brings on the condition. Outbreaks tend to cluster in the late summer and through the fall. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there were 233 confirmed cases in 2018 — the largest outbreak yet.
The investigators will document the clinical course of the disease, including the number and location of cases and variation in symptoms and severity, and they will assess the outcomes from the illness. The researchers will isolate serious and life-threatening viruses that are believed to be connected to AFM cases. The goal is to collect data that can inform how to design clinical trials on treatment of the condition, strategies for management, and establishment of a repository of specimens and data from AFM patients that will be used for future research.
Since at least 2014, children have been at risk of developing a poliolike syndrome likely due to enteroviruses, and this study will provide the basis for understanding the cause of those children’s paralyses. Knowledge gained from this study hopefully will provide the foundation for future treatment studies of antiviral drugs. We hope to better understand why acute flaccid myelitis occurs, which children are most at risk, and to develop the biorepository and associated clinical database to understand what we can do about it in the future.”
David Kimberlin, M.D., co-director of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at UAB and co-principal investigator of the study
This new, five-year study will take advantage of the expertise of clinicians and researchers in the AFM Working Group — a network of neurologists and researchers established in 2018 in response to the AFM outbreak — and the Collaborative Antiviral Study Group, an NIH-funded network of academic medical centers established in the 1970s to study rare viral diseases. Study enrollment is expected to begin in August.
Johns Hopkins and UAB will continue to work closely with the National Institutes of Health, the CDC, investigators at the study sites, and parents and families of AFM patients to ensure that the medical community is making the most informed decisions to direct the national responses to this public health situation.