E-cigarette use has increased dramatically over the last decade. With its popularity, the use of e-cigarette spans from adolescents to adults. Now, cardiologists warn against the use of e-cigarettes and how these devices cause damage to vital organs, including the heart, brain, lungs, and blood vessels.

Image Credit: DedMityay / Shutterstock
The researchers from the University Medical Center Mainz in Germany have established that e-cigarettes are dangerous and at the same time, addictive. Hence, they recommend that countries should consider banning these devices, since the use has become rampant, particularly in younger generations. In some countries such as Singapore, Brazil, Mexico, India, and Thailand have already acted in banning these devices.
In the United States alone, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that more than 3.6 million children use e-cigarettes, which increased by 78 percent, from just 11.7 percent to 20.8 percent, among U.S. high school students between 2017 to 2018.
Subsequently, the United Kingdom also reports an increase in e-cigarette use. About 1.6 percent of those who are between 11- and 18-years old use e-cigarettes more than once a week, compared to just 0.5 percent in 2015.
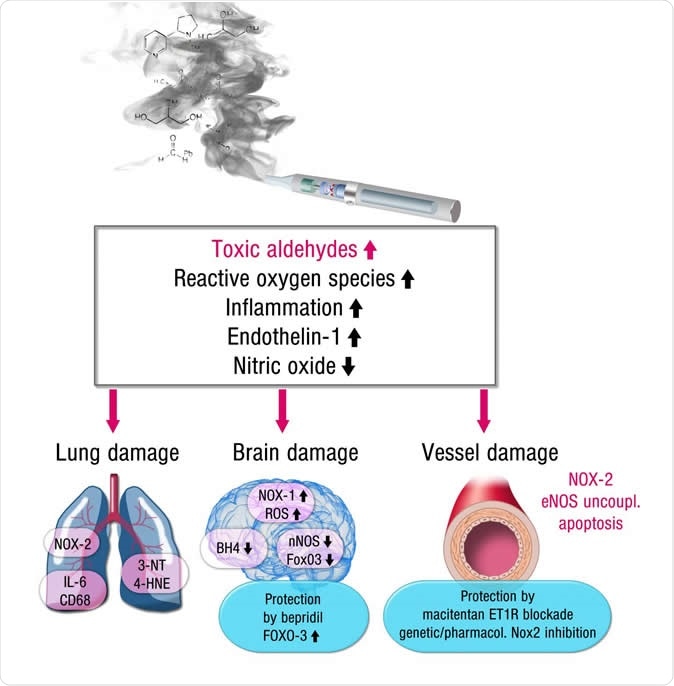
This is an image showing the mechanisms for how e-cigarettes damage the brain, blood vessels and lungs. Credit: European Heart Journal
Actions governments can take
Originally, vapes or e-cigarettes were designed to aid smokers to quit, but providing an alternative source of nicotine, minus the harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke. However, vaping has become a popular trend among youngsters, leading to nicotine addiction, and those who never smoked a cigarette before.
The researchers urge governments to reevaluate their tobacco policies and prevent young individuals to have access to tobacco products and even e-cigarette devices. They can do this by increasing taxes, curbing the market of tobacco products, and raising awareness of the dangers of these products to adolescents and their families. Also, research is important to establish the dangers of e-cigarettes to health.
E-cigarette’s effect on vital organs
To arrive at their findings that were published in the European Heart Journal, the team studied the different effects of e-cigarette vapor on the blood flow to the brachial artery in the upper arm in 20 healthy people who are smoking. The team studied the flow before they vaped e-cigarette and 15 minutes after vaping. They also considered and measured the stiffness of the artery.
Aside from this, they also studied 151 mice models in the laboratory, which were exposed to e-cigarette vapor for about one, three, or five days, six times a day for about 20 minutes.
Alarming results of the study
After the experiments, the researchers found that one vaping session can increase heart rates and stiffened the inner lining of the arteries. The arteries’ endothelium stops working properly among smokers. The endothelium plays an important role in the vasoconstriction and vasodilation o the blood vessels, promote healthy blood clotting processes, regulates inflammation, and protects the tissues from toxic substances. When the endothelium doesn’t work properly, it can lead to cardiovascular disease.
Moreover, in the mice study, the results show that a particular enzyme, called NOX-2, induced damage to blood vessels, especially those found in the brain and lungs. NOX-2 is an enzyme that is involved in the defenses of the body against pathogens, and at the same time, in oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals in the body.
NOX-2 mediated the effects of e-cigarettes in the cardiovascular system and the brain. They also found acrolein, a toxic chemical that is produced after vaporizing the liquids in e-cigarettes, activated the damaging effects of NOX-2.
They also found that in mice that do not produce the said enzyme, they were protected from the adverse and damaging effects of e-cigarette use.
“The results of the present studies identified several molecular mechanisms whereby e-cigarettes can cause damage to the blood vessels, lungs, heart and brain. This is a consequence of toxic chemicals that are produced by the vaping process and may also be present at lower concentrations in the liquid itself,” Professor Thomas Münzel of the Department of Cardiology of the University Medical Centre Mainz said.
The researchers concluded that e-cigarettes are not healthy alternatives to tobacco. Despite companies claiming these devices are safe, the researchers said they have damaging effects on the body. Further, the researchers noted that the long-term effects of e-cigarettes have not been investigated, hence, they warn those who are using e-cigarettes to stop vaping.
Journal reference:
Marin Kuntic, Matthias Oelze, Sebastian Steven, Swenja Kröller-Schön, Paul Stamm, Sanela Kalinovic, Katie Frenis, Ksenija Vujacic-Mirski, Maria Teresa Bayo Jimenez, Miroslava Kvandova, Konstantina Filippou, Ahmad Al Zuabi, Vivienne Brückl, Omar Hahad, Steffen Daub, Franco Varveri, Tommaso Gori, Regina Huesmann, Thorsten Hoffmann, Frank P Schmidt, John F Keaney, Andreas Daiber, Thomas Münzel, Short-term e-cigarette vapour exposure causes vascular oxidative stress and dysfunction: evidence for a close connection to brain damage and a key role of the phagocytic NADPH oxidase (NOX-2), European Heart Journal, , ehz772, https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz772/5621442