The coronavirus disease (COVID-19), which has rippled across the globe and affected about 180 countries and territories. The number of infections skyrocketed, prompting many countries and territories to impose lockdowns in an attempt to curb the spread of the virus.
A new study has shown that the restrictions imposed by the United Kingdom are slowing down the spread of the virus, showing promise in the country’s aim to flatten the curve and ease the burden on the healthcare system.
The researchers of the study, published in the Centre for Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Diseases, reveals that the lockdown and social distancing measures imposed by the British government may already be working. The findings of the study hints that the country’s infection rate is declining.
Social distancing measures
The UK Government has announced social distancing measures on Mar. 15, as health secretary Matt Hancock, warns that those who are over 70 years old should self-isolate within weeks, as they are at a high risk of developing severe disease due to COVID-19. The next day, Prime Minister Boris Johnson advised everyone against non-essential travel and contact with others. People were advised not to go to movie theaters, clubs, and pubs, while employers were encouraged to provide work from home schemes.
But on Mar. 20, Johnson ordered the closure of public places, including restaurants, bars, gyms, pubs, and cafes. By Mar. 23, the prime minister announced a nationwide lockdown, a strict measure that aims to restrict movement to stem the spread of the deadly virus. The public was advised to stay at home.
A large number of people follow these measures that the UK government has imposed to stop the spread of COVID-19. It could be driving the reproduction number of the disease o below one. The study by researchers from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine aims to determine if the lockdown efforts are working.
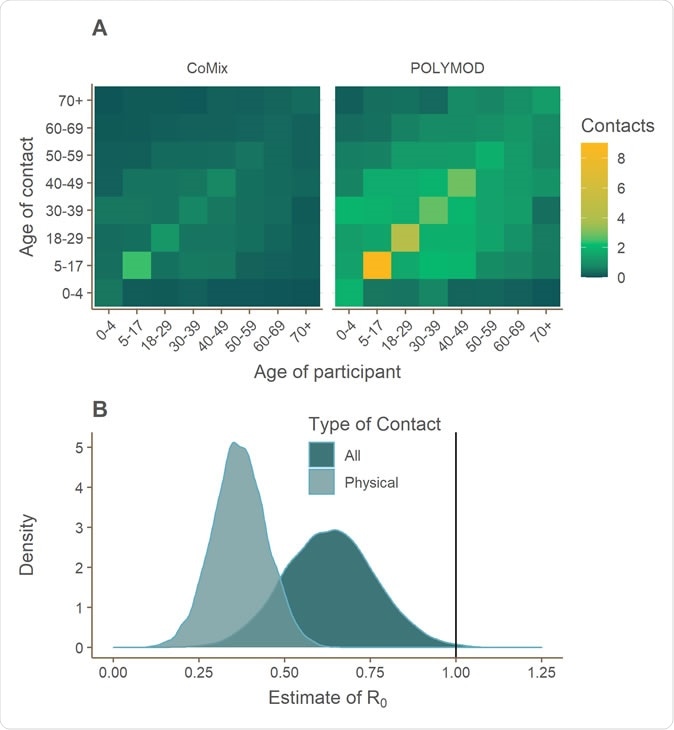
Social contact matrices showing the average total number of daily reported contacts made by participants in different age groups with individuals in other age groups, with results shown for all contacts reported in the CoMix and POLYMOD data. Participants’ contacts in CoMix for age groups 0-4 and 5-17 are imputed using the POLYMOD data. (B) The estimated value of R0 at the time of the survey, assuming values of R0 ~ Norm(2.6, sd = 0.54) prior to physical distancing reducing all contacts.
Reproduction number
One of the critical aspects of an infectious disease’s transmission is the reproductive number. It is defined as the average number of people who will catch a disease from an infected individual. A reproductive number below one hint that the epidemic will start to decline.
The team used an online survey to gather data from 1,300 people, who were asked to list their contacts the previous day. The researchers used the change in contact pattern to compute changes in the reproduction number before the lockdown and after the lockdown. The team unveiled that the mean number of contacts per person measured was more than 70 percent lower now than before the lockdown was imposed.
With the declined contacts, the reproduction number would now be between 0.37 and 0.89.
“If we see similar changes across the UK population, we would expect to see the epidemic to start to decline. However, our estimates are not to be read as ‘job done.’ Rather, they should be used as motivation for us all to keep following UK government instructions,” Professor John Edmunds from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine said.
“It’s imperative we don’t take our foot off the pedal. We must continue to stop transmission of the virus to reduce the burden on the NHS now, and over the coming months,” he added.
The team added that tracking behavioral change can provide a fast and efficient assessment of the impact of social distancing measures that regular epidemiological surveillance.
Global status
The coronavirus disease is infectious and can affect those who are older, with comorbidities, and those who are immunocompromised. The COVID-19 pandemic has killed more than 50,000 people, while the number of confirmed cases increased to over one million.
Italy reports the highest number of deaths, with nearly 14,000 people succumbing to COVID-19. Meanwhile, the United States has the highest number of infections, with more than 245,000 people testing positive for the virus.
Source:
Journal reference:
- Jarvis, C., van Zandvoort, K., Gimma, A., Prem, K., Kelpac, P., Rubin, J., and Edmunds, J. (2020). Impact of physical distance measures on transmission in the UK. Centre for Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Diseases. https://cmmid.github.io/topics/covid19/current-patterns-transmission/comix-impact-of-physical-distance-measures-on-transmission-in-the-UK.html