An international team of researchers from Canada, Australia, the Netherlands, and the United States has identified dozens of genes that could contribute to the pathology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and serve as potential therapeutic targets.
The genes are co-expressed with two proteins that severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) uses to gain host cell entry. Many of these genes could potentially be targeted with drugs that are already available.
Molecule of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus main protease, 3D illustration. Image Credit: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Using bioinformatics databases, Ana Hernandez Cordero (University of British Columbia) and colleagues studied the biology of the genes. They identified drug-gene interactions that could be explored to help fast-track the development of COVID-19 therapeutics.
The team says the study shows how computational in silico approaches can help to quickly identify potential drugs that could be repurposed as COVID-19 treatments.
“Given the exponential spread of COVID-19 across the globe and the unprecedented rise in deaths, such rapidity is necessary for our ongoing fight against the pandemic,” write the authors.
A pre-print version of the paper is available on the server bioRxiv*, while the article undergoes peer review.
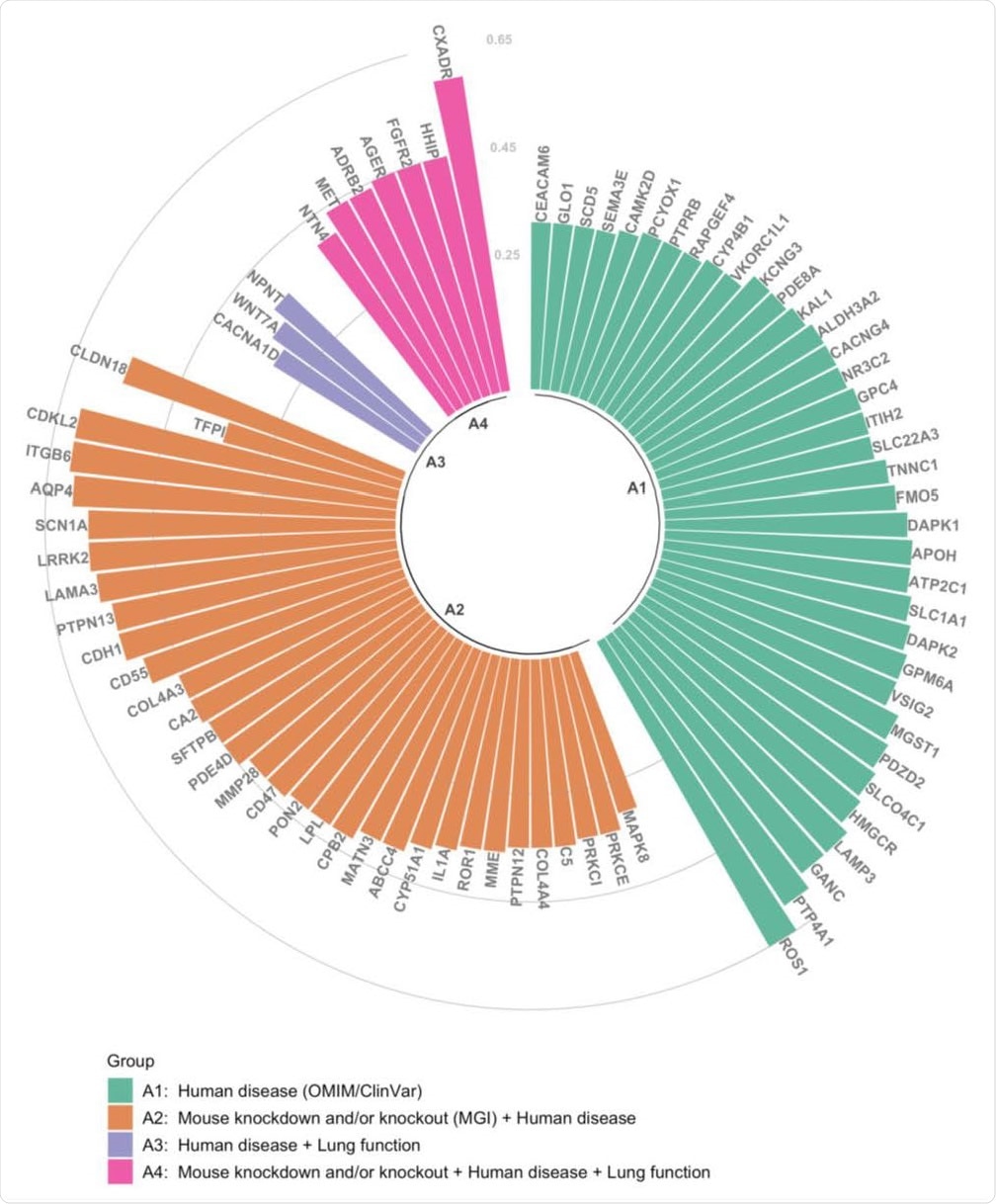
Correlation level and annotation of TMPRSS2-correlated genes. Each bar represents a single gene (all with druggability scores Tier 1-3 12), and the Pearson correlation coefficient (r) between the gene and TMPRSS2 within the module is shown on the y-axis. Colors of bars represent combined biological information: green (group A1) represents genes related to human diseases based Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) and ClinVar databases; orange (group A2) are genes associated with human diseases, which also have phenotypic information on knockdown or knockout mouse models based on Mouse Genome Informatics (MGI) database; purple (group A3) represents genes associated with human diseases and with genetic variants associated to lung function traits 14; pink (group A4) represents genes associated with human disease, with phenotypic information on knockdown or knockout mouse, and genetic variants associated with lung function.
Speeding up the identification of potential drug targets
Since SARS-CoV-2 first infected people in Wuhan, China, late last year, it has quickly spread across the globe infecting millions and killing hundreds of thousands.
Researchers worldwide have been racing to develop effective therapies, particularly for severe disease. However, it may take months or years and billions of dollars of investment to develop treatments and a vaccine, which may ultimately fail to be effective.
“Bioinformatic approaches, however, are able to rapidly identify relevant gene-drug interactions that may contribute to the understanding of the mechanisms of viral infection and reduce the time to finding potential drug targets and existing drugs that could be repurposed for this indication,” write Cordero and colleagues.
For SARs-CoV-2 to gain viral entry, its Spike protein must bind angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and undergo subsequent priming by transmembrane protease, serine 2 (TMPRSS2).
Given that the availability of these proteins is a rate-limiting step in the infection process, a detailed understanding of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 biology could help to identify potential therapeutic targets.
Now, using the 1,038 lung tissue samples, Cordero, and colleagues have performed a gene expression network analysis to identify and investigate the co-expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
What did the authors find?
The ACE2 and TMPRSS2 gene networks that were built contained genes that could contribute to the pathophysiology of COVID-19.
Twelve ACE-2 correlated genes were already known to interact with existing drugs. One example was DPP4, which encodes the glycoprotein dipeptidyl-peptidase 4. This protein plays a key role in glucose and insulin metabolism and is associated with diabetes, which is now a well-known risk factor for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19.
DPP-4 is also the receptor used by Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus to gain host cell entry, and researchers have studied its interaction with dozens of existing compounds.
“Because of the similarities between MERS and SARS-Cov-2, this is an interesting potential target, particularly for patients with diabetes,” said Cordero and colleagues.
Another ACE2-correlated gene that could be an exciting target was IL13RA2, which encodes the alpha-2 subunit of interleukin-13 (IL-13) receptor. The IL-13 is a well-known effector of the airway remodeling process in asthma and is also involved in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
“Both the IL-13 258 and DPP-4 pathways could be intriguing possibilities for novel COVID-19 therapeutics,” writes the team.
What about TMPRSS2?
The researchers found that 53 of the TMPRSS2-correlated genes were already known to interact with existing drugs. One example was CD55, which codes for an inhibitor of complement activation.
The complement system can trigger a hyperinflammatory state in response to viral infection, and CD55 inhibits the formation of complement component 3 (C3).
Researchers have shown that mice deficient in C3 have lower levels of inflammatory cytokines in their lungs and less respiratory dysfunction.
“Thus, it is possible that preventing the formation of C3 via CD55 could be beneficial in COVID-19,” say the authors. Again, compounds that are known to specifically target CD55 already exist, they add.
Fast-tracking the development of COVID-19 therapeutics
Cordero and colleagues say that dozens of genes co-expressing ACE2 and TMPRSS2 have plausible associations with the pathophysiology of COVID-19, and many of them could potentially be targeted with existing drugs, thereby helping to “fast-track the development of COVID-19 therapeutics.”
Furthermore, “computational in silico approaches can lead to the rapid identification of potential drugs, which could be repurposed as treatments against COVID-19,” they conclude.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources