Since the start of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, we are faced with more than 728 thousand deaths and almost 20 million infections around the world (as of August 10, 2020). As an effective treatment is still elusive, many people share the hope that an effective COVID-19 vaccine may be our ticket back to the old normal, or at least something close to it.
Vaccine efforts against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), a causative agent of the current COVID-19 pandemic, are mostly focused on viral spike glycoprotein – the primary target for neutralizing antibodies.
Of note, SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein enables cell entry by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which serves as the viral receptor. Previous studies provided cryo-electron microscopy structures of the spike glycoprotein ectodomain trimer, which served as a blueprint for designing vaccines and inhibitors of viral entry.
Novavax Inc, a late-stage biotechnology company known to develop next-generation vaccine approaches for serious infectious diseases, designed a stable, prefusion protein with nanoparticle technology that includes a proprietary Matrix-M adjuvant for boosting the immune response.
In this new paper, a group of scientists from the Scripps Research Institute and Novavax Inc. in the United States performed a structural analysis of the Novavax SARS-CoV-2 full-length immunogen formulated in polysorbate 80 detergent.
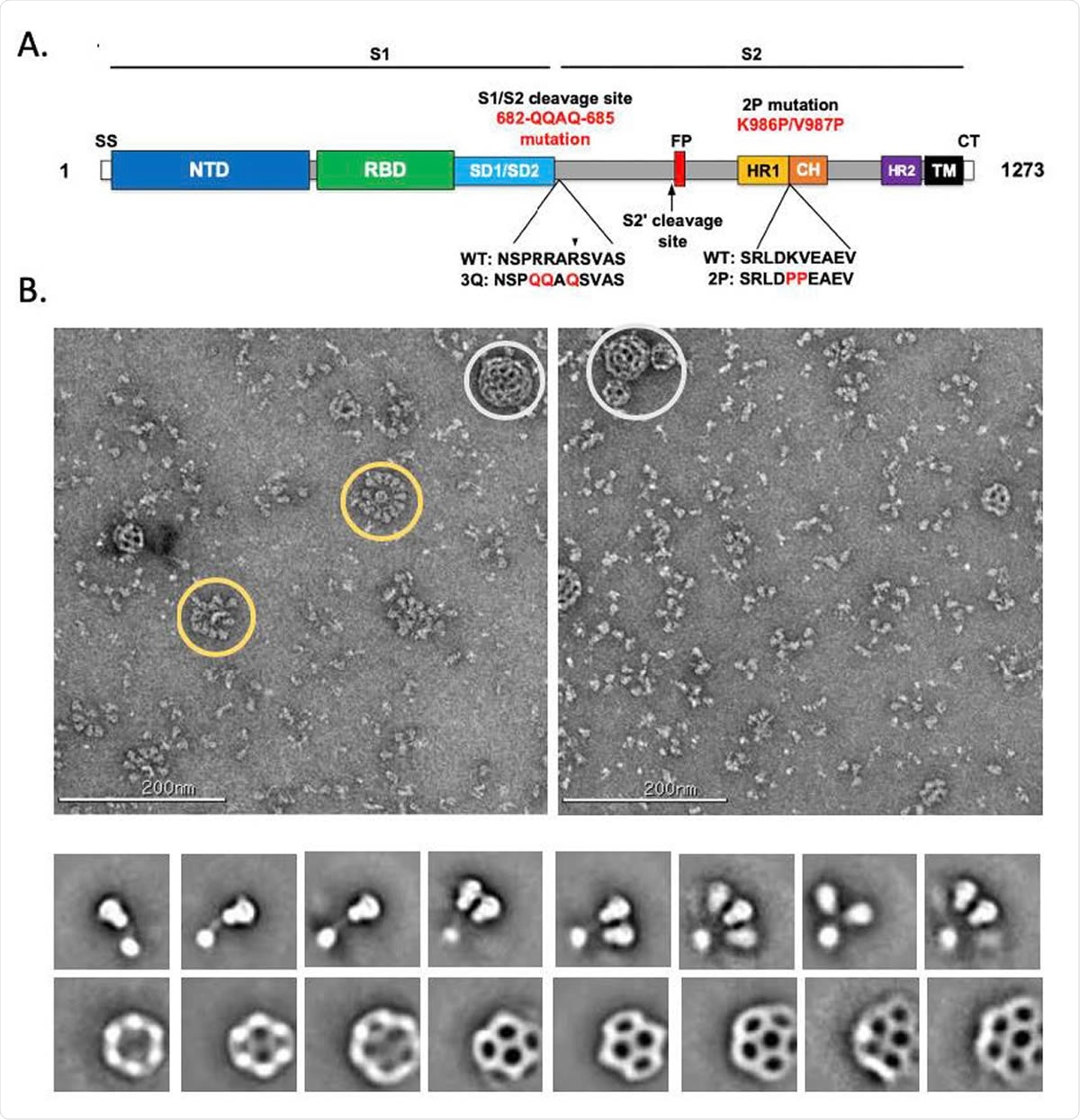
Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 3Q-2P-FL spike glycoprotein. (A) Linear diagram of the sequence/structure elements of the full-length SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein showing the S1 and S2 ectodomain. Structural elements include a cleavable signal sequence (SS, white), N-terminal domain (NTD, blue), receptor binding domain (RBD, green), subdomains 1 and 2 (SD1/SD2, light blue), protease cleavage site 2’ (S2’, arrow), fusion peptide (FP, red), heptad repeat 1 (HR1, yellow), central helix (CH, brown), heptad repeat 2 (HR2, purple), transmembrane domain (TM, black) and cytoplasmic tail (CT, white). The native furin cleavage site was mutated (RRAR→QQAQ) to be protease resistant and stabilized by introducing two proline (2P) substitutions at positions K986P and V987P to produce SARS-CoV-2 3Q-2P-FL spike. (B) Representative negative stain EM images and 2D classes of SARS-CoV-2 3Q-2P-FL, formulated in polysorbate 80 detergent in the presence of Matrix-M adjuvant. In the raw micrograph, spike rosettes are circled in yellow and Matrix-M adjuvant cages are circled in white. 2D classes showing individual spikes, higher order spike nanoparticles and Matrix-M cages of different sizes.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Recapitulating the prefusion spike glycoprotein
In a nutshell, this study provides an in-depth structural appraisal with the use of cryo-electron microscopy and site-specific glycan analysis of the Novavax full-length vaccine candidate (currently being tested in humans) that adequately recapitulates the prefusion spike.
In order to assess whether the multimerization phenomenon seen in the full-length spike construct has a role in viral replication, the researchers performed pseudovirus replication assays utilizing the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type spike and two mutant spike proteins.
Furthermore, site-specific glycosylation of the SARS-CoV-2 prefusion spike protein produced in insect cells was analyzed with the use of recently described mass spectrometry proteomics-based method.
Stable conformation and novel interactions
"Our results show that polysorbate 80 detergent forms detergent micelles around the transmembrane domains of one or more spike proteins, enabling the formation of nanoparticle-like rosettes", emphasize study authors in their bioRxiv paper.
It can be said that the structural analysis of the full-length spike immunogen in this study yielded several significant findings. First and foremost, a stable prefusion conformation of the spike immunogen was demonstrated, with tiny differences in the S1 subunit of the spike glycoprotein when compared to published spike ectodomain structures.
The researchers have also observed two non-spike densities within the spike trimer that corresponded with polysorbate 80 detergent and linoleic acid. Interestingly, new interactions between the spike trimers that allow the formation of higher-order spike complexes were described as well.
Consequently, these larger nanoparticles enable a multivalent display of the spike immunogen with the potential for improved immunogen trafficking and B cell activation, as described previously for nanoparticle-based immunogens.
Capitalizing on the previous success
"Our structural work is consistent with the burgeoning body of structures available of the spike protein, albeit with the important differences described above," accentuate study authors.
Therefore, this advanced protein subunit vaccine candidate that is currently being tested in humans appears rather homogeneous, stable and locked in the antigenically preferred prefusion conformation.
Moreover, firm clustering of the spikes in the nanoparticle formulation may result in much more vigorous immune responses over soluble trimers alone, in accordance with glycoprotein immunogens in other viruses.
"It appears that the remarkable speed at which this vaccine was designed did not compromise the quality of the immunogen, and that building off the previous success in formulating respiratory syncytial virus F glycoprotein and influenza hemagglutinin nanoparticle immunogens could readily be extended to SARS-CoV-2 spike", conclude study authors.
Finally, after obtaining these pivotal biophysical, structural and antigenic insights, further evaluation of the vaccine in humans will give us the much-desired proof-of-principle for this specific concept.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources