The current pandemic of COVID-19 is due to the single-stranded RNA virus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is generally acquired by inhalation of respiratory droplets. This coronavirus genome contains an abundance of GU-rich sequences that are associated with a hyperinflammatory and procoagulant immune activation. A new study published on the preprint server bioRxiv* in August 2020 reports the disease-mitigating effects of a serum protein called serum amyloid P (SAP) in mice exposed to a peptide that mimics the clinical signs of severe COVID-19 in humans.
The characteristic lung histology in severe COVID-19 includes a build-up of proteinaceous cell-free exudate in the alveoli with septal thickening, with infiltration of immune cells. Excessive coagulation activity is evident with many patients showing disseminated intravascular coagulation and fibrin clots in the lung tissue.
Macrophages accumulate in the lung tissue, unlike the neutrophilic predominance seen when secondary pneumonia sets in. Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) in COVID-19 patients, especially NK cells, are high in this fluid though peripheral blood lymphocytes are lower in number than in healthy individuals.
ORN06 Induces Lung Inflammation
Single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) with high GU content produces similar changes in the body, causing a surge in inflammatory cytokines. In the current mouse model, when the ssRNA peptide ORN06 was injected into the tail vein, it caused the onset of pulmonary edema and bleeding with inflammation, which led to mortality within 72 hours.
The aspiration of ORN06 by mice caused the same changes, namely, thickening of the septa with inflammation and exudation into the lung alveoli. However, these mice did not die, unlike those which received tail vein injections.
Male mice developed more severe symptoms in all cases following ORN06 aspiration than female mice. Thus, this peptide can mimic the response of males vs. females to COVID-19 disease.
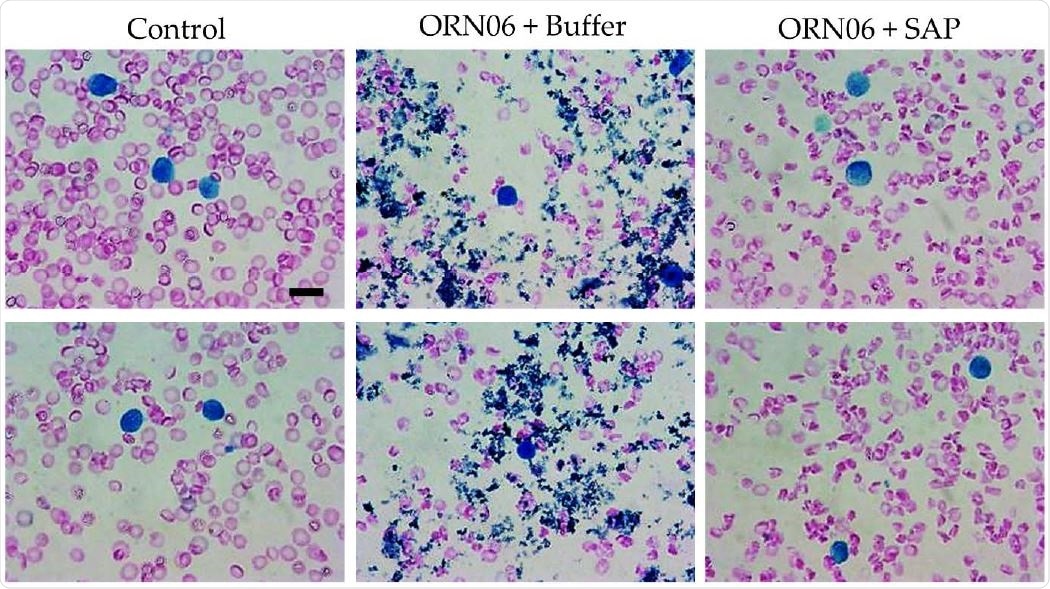
SAP attenuates ORN06-induced clot formation in mouse BAL. Cell spots of BALF at day 3 were stained with Wright-Giemsa stain. The left two images are of BALF cell spots from two different control male mice. The middle two images are of BALF cell spots from two different male mice treated with buffer after ORN06 insult. The right two images are of BALF cell spots from two different male mice treated with SAP after ORN06 insult. Bar is 10 μm.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
ORN06 Increases Cytokine Levels and Clot-Like Deposits
These mice also had high levels of several cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12p70, IL-23. Clot-like fibrin deposits were seen in the lung fluid.
Aspiration of ORN06 Increases Cells in Mouse Lung Fluid
In COVID-19, there is a severity-dependent increase in the number of peripheral CD14+CD16-DR+ “classical” monocytes. These are perhaps increased because of high levels of IL-6 and altered monocyte formation within the bone marrow. Macrophages in the lung fluid are more abundant in patients with severe COVID-19 and seem to be derived from monocytes recruited from the peripheral blood.
Along with this, CD11c+ and CD45+ macrophages were also increased. Still, their origin is unclear, whether from resident lung macrophages, conversion of one type of macrophage to another, or migration of these cells from the interstitial fluid to the lung. The latter is likely, say the researchers.
SAP
Serum amyloid P (SAP; PTX2) is a member of the pentraxin family of proteins that includes C-reactive protein. SAP is made by hepatocytes and secreted into the blood. SAP binds to a variety of molecules, including DNA and apoptotic debris, bacterial polysaccharides, amyloid deposits, and bacterial and viral proteins.
SAP also binds to C-type lectin receptors on these cells. Its presence seems to have a dampening effect on the formation of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic monocytes and macrophages while enhancing that of macrophages that inhibit the immune response. In fact, it also elicits the secretion of IL-10, which is an anti-inflammatory cytokine.
In experimental mice exposed to an inflammatory agent, the administration of SAP leads to lower neutrophil levels in the lung. In other animals and human clinical trials, SAP has been found to dampen the formation of fibrous tissue and inhibits influenza A virus from successful infection.
SAP Prevents Cell Build-Up in Lungs Induced by ORN06
In mice that had aspirated ORN06, the administration of SAP injections inhibited all the lung inflammatory changes and cytokine secretion cascades. This suggests that this protein could play a therapeutic role in severe COVID-19 disease, and other disease conditions accompanied by cytokine oversecretion.
SAP reduced macrophage build-up by reducing the number of recruited macrophages but without impacting the lung resident macrophages or causing a rise in neutrophils. It also prevented the expected rise in lymphocytes in the lung fluid following ORN06 administration.
SAP Reverses ORN06 Effects on Lungs and Cytokines
ILCs are potent producers of many cytokines, which may depend on the number and composition of this cell population. The cytokine storm seen in severe COVID-19 is also mirrored by ORN06 administration. However, SAP injections prevented this change.
The cytokine IL-17A is anti-inflammatory and is expressed at higher levels in female mice than in males. This is, like some other diseases, a mirror of lower susceptibility to the disease agent or to its severity in one or the other sex. While ORN06 reduces IL-17A levels in female mice but not in males, this was reversed by SAP administration.
Implications
The study concludes, “Together, our results and the work described above suggest the intriguing possibility that aspiration of oligonucleotides such as ORN06 could be a simple model for COVID-19 infection. In addition, SAP strongly attenuated the effects of aspiration of ORN06, suggesting that SAP could be a potential therapeutic for severe COVID-19 disease and possibly other diseases where a cytokine storm is a contributing factor for disease severity or progression.”

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources