Postnova Analytics reports that researchers from the University of Utah (Salt Lake City, USA) have used a novel combination of Asymmetrical Flow Field-Flow Fractionation and Centrifugal Field-Flow Fractionation to measure cancer biomarker enrichment in exosomes.
Asymmetrical Flow Field-Flow Fractionation (AF4) and Centrifugal Field-Flow Fractionation (CF3) are high resolution separation techniques for fractionation of macromolecules and biological nanoparticles based on their hydrodynamic size (AF4) and mass (CF3).
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles containing nucleic acid and proteins that show great promise for use in cancer diagnostics and therapeutic applications. As characterization of exosomes had proven challenging with traditional separation techniques due to their inherent heterogeneity and complexity, the Utah researchers turned to a multiple fractionation approach to solve their application challenge.
The goal of the research was to characterize an MCF-7 tumor exosome sample by size using AF4 coupled to multi angle light scattering (MALS), and by mass using CF3. The density of exosomes in CF3 fractions was obtained using hydrodynamic diameter and buoyant mass measured by Nano Tracking Analysis (NTA) and CF3 respectively. Fractions were collected along both size and mass distributions and analyzed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for enrichment of the micro-RNA21 (miR21) cancer biomarker.
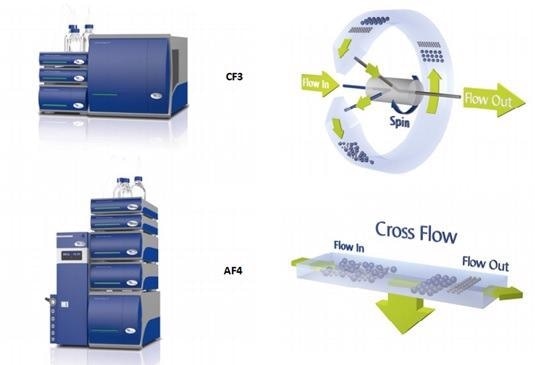
The heterogenous nature of the exosome sample under study was observed to make batch dynamic light scattering or NTA measurements prone to error, and highlights the usefulness of Field Flow Fractionation techniques for separation and characterization of these complex biologic samples. The study showed that the enrichment of miR21 cancer biomarker was highest in the tumor exosomes with the smallest size, smallest mass, and lowest density.
For a copy of the application report describing this research please visit https://bit.ly/3lAu83A. For further information on Asymmetrical Flow Field-Flow Fractionation (AF4) and Centrifugal Field-Flow Fractionation (CF3) used in this research please contact analysed Postnova Analytics on +49-8191-985-6880 / +44-1885-475007 / +1-801-521-2004 or [email protected].