As researchers continue to search for effective antivirals to counter the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a new study presents the potential utility of a herbal decoction called Respiratory Detox Shot (RDS).
In both pandemics caused by SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, traditional Chinese medicines (TCM) have been extensively employed in China as an immediate course of management. In fact, it is estimated that over 85% of COVID-19 patients in China have received TCM as of now. The current study aimed to explore the efficacy of some of the important TCM therapies so as to enable their rational use.
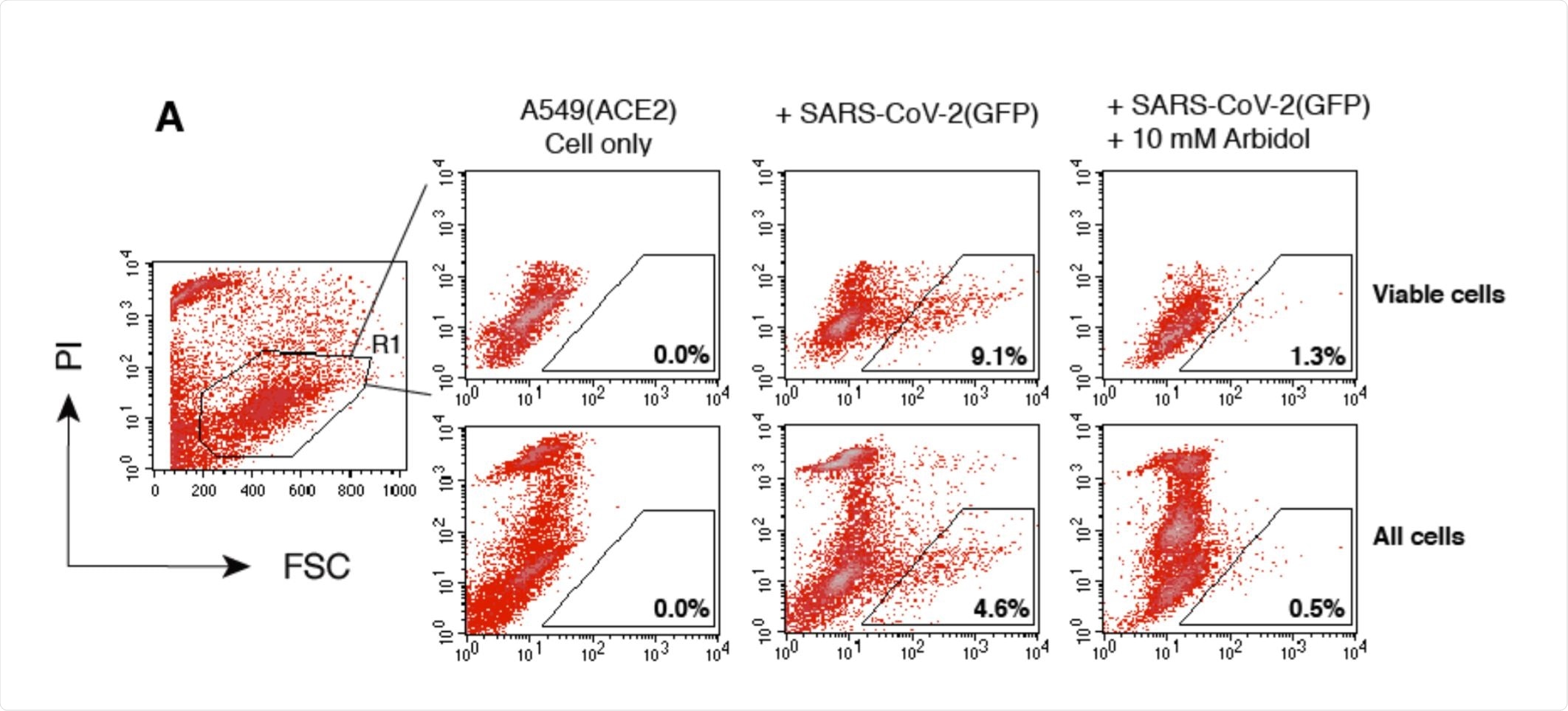
Validation of SARS-CoV-2 S protein pseudotyped reporter viruses for the screening and quantification of antiviral drugs and neutralization antibodies. Image Credit: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.10.420489v2.full.pdf

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Herbal extracts prove ineffective
The researchers screened a number of herbal extracts, about 40, as well as a commercially available oral liquid called RDS.
The extracts from the herbs were tested for viral inhibition against a SARS-CoV-2-expressing pseudovirus-human lung cell system. The lung cells were induced to express the viral receptor, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). The pseudoviruses had either a green fluorescent protein (GFP) or luciferase (Luc) reporter fused to the spike protein, to detect and quantify its expression in the infected cells.
The effects of adding a known antiviral inhibitor, Arbidol, and human antibody-containing serum to the pseudovirus-exposed cells were first tested to validate their use. The researchers observed that the pseudovirus was not inhibited by any of the herbal extracts regardless of the concentration and even in the presence of significant cytotoxicity.
RDS blocks SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro
They also tested the ability of RDS to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection. This is used as a commercial food supplement in the U.S.A. in order to keep the respiratory system in good health. Its ingredients include nine different herbs used to treat lung disease and inflammation, including Panax ginseng and Schizonepeta tenuifolia.
The cells were first treated with RDS at varying dilutions and then exposed to the virus for 4-6 hours. They were then cultured without the RDS and flow cytometry was carried out at 48 and 72 hours to test for viral inhibition. Dead and dying cells were picked out by propidium iodine (PI) staining and GFP-positive cells were counted as viable cells.
The researchers found a dose-dependent inhibition of the pseudovirus in the presence of RDS, which was confirmed using another cell line that naturally expressed the ACE2 receptor, the Vero E6 cell line. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration IC50 was at a dilution of 1:230 RDS dilution and the half-maximal lethal (cytotoxic) dosage at approximately 1:12 RDS dilution.
The same effects were seen with wild-type SARS-CoV-2 as well. RDS prevented infection with this virus and reduced viral cytopathic plaque formation at dilutions above 1:40. At this dilution, viral replication was reduced by 2-3 logs. Thus, the active ingredients in RDS prevent infection by SARS-CoV-2. The mechanism of action is not known but may be by directly inactivating the virus or by disrupting the early steps of infection.
RDS blocks SARS-CoV infection
Again, RDS was tested for its ability to inhibit SARS-CoV-expressing pseudoviruses. Here too, the RDS showed dose-dependent inhibition of the Luc-reporter pseudovirus, which was confirmed and quantified as before. The IC50 was at ~1:70 RDS dilution.
Potential broad antiviral spectrum of RDS
To understand the role of the ACE2 receptor, they also tested another RNA virus, the influenza A virus, which infects host cells via its attachment to the hemagglutinin HA receptor and α-sialic acid. The influenza virus genome segments were assembled by co-transfection into a cell line, along with the GFP reporter. The complete virus was then used to infect MDCK cells pretreated with RDS. Again, dose-dependent inhibition of the influenza virus was observed, with complete inhibition at 1:80. The cytoxicity was also assessed, with the LC50 at ~1:19.
Implications and future directions
These results suggest that the anti-viral activities of RDS are not virus-specific, and may broadly inhibit multiple respiratory viruses such as coronaviruses and Influenza A.”
There are other herbal extracts and other TCM preparations, like licorice root and Shuanhuanglian preparation, which also show activity against SARS-CoV replication and SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease activity, in virus isolates and in vitro respectively.
However, the active ingredients and the mechanism of action appear to be different from RDS. The current study presents in vitro findings and these will require in vivo validation. Animal studies are ongoing to measure RDS efficacy in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection of human cells.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Hetrick, B. et al. (2020). A traditional medicine, Respiratory Detox Shot (RDS), inhibits the infection of SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and the Influenza A virus in vitro. bioRxiv preprint. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.10.420489. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.10.420489v2
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Hetrick, Brian, Dongyang Yu, Adeyemi A. Olanrewaju, Linda D. Chilin, Sijia He, Deemah Dabbagh, Ghaliah Alluhaibi, et al. 2021. “A Traditional Medicine, Respiratory Detox Shot (RDS), Inhibits the Infection of SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and the Influenza a Virus in Vitro.” Cell & Bioscience 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00609-1. https://cellandbioscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13578-021-00609-1.