In Munich, Germany, scientists at Ludwig Maximilian University studied temporal adaptive immunity to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to better understand protection against re-infection. They found functional properties of persisting memory B specific to SARS-CoV-2 may help in protect against the virus.
When a pathogen infects, it elicits an active immune response. The adaptive immunity protects the individual against re-infection. It is associated with the development of antibodies, memory B cells, and several T cell subsets.
Analysis of immune responses to viruses, including coronaviruses, has shown that the lifespan of adaptive immunity varies. Even antibody levels decrease with time. It is reported that the serum antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 persist for more than 6 months after primary infection.
However, in case of mild infection, it is also found that these patients rapidly lose their specific antibodies. While the initial antibody responses are from short-lived plasmablasts (a short-lived differentiation stage between a post germinal center B-cell and a mature plasma cell), the subsequent development of high-affinity and persistent antibodies come from affinity maturation and expansion of B cells in the germinal centers.
Thus, it is vital to study the memory B cell pool, in addition to antibody titers, to estimate the humoral immunity as an indicator of immune protection. In their recent medRxiv* preprint research paper, Prof. Edgar Meinl et al. analyzed the persistence of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) and Immunoglobulin G (IgG) memory B cells specific for SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients.
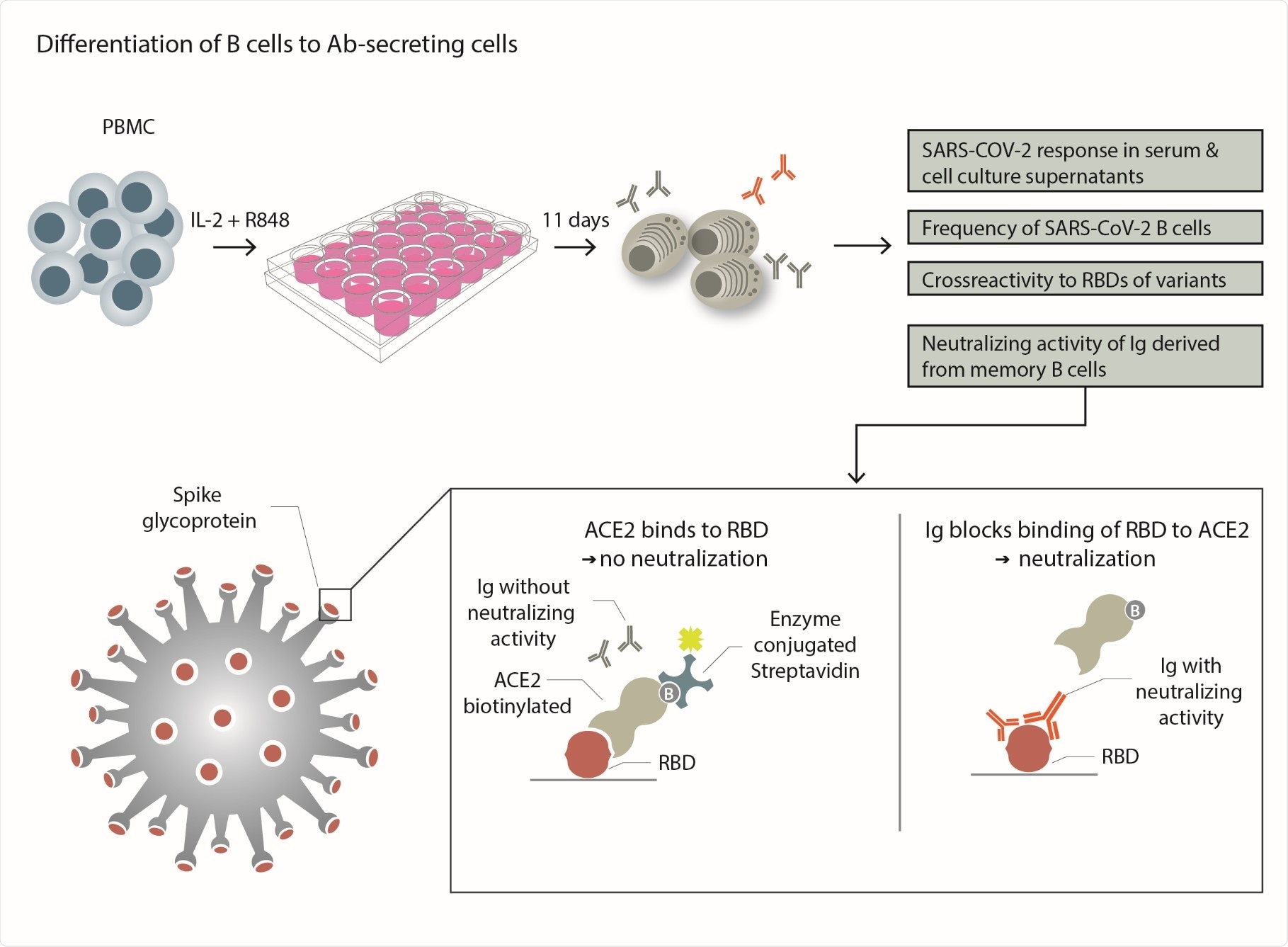
Experimental scheme - PBMCs from each donor were separated into individual wells and stimulated with the TLR7/8 agonist R848 and IL-2 to differentiate to them into Ab-secreting plasmablasts. This was used to compare the serum response to SARS-CoV-2 with that of specific Abs produced in vitro. The frequency of SARS-CoV-2-specific B cells that differentiated into Ab secreting cells was determined. The cross-reactivity to RBDs of emerging variants was tested. The ability of in vitroproduced Abs to block the binding of RBD to its receptor ACE-2 was determined as outlined.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
The researchers specifically looked for SARS-COV-2 infected and recovered individuals who had lost circulating IgG specific to SARS-CoV-2. The researchers investigated if these individuals still harbored specific memory B cells in their blood.
"Memory-B-cell differentiation into antibody-producing cells is a more sensitive method for detecting the previous infection than measuring serum antibodies."
Significantly, one of the study's implications is that the assay employed to differentiate the B cells into antibody-producing cells in vitro is a more sensitive method for detecting previous infections than measuring the serum levels of SARS-CoV-2 IgG.
Specifically, the assay identifies if a seronegative individual was infected with SARS-CoV-2. "This is of relevance in epidemiology and for optimizing urgently needed immunosuppressive treatments," the researchers said.
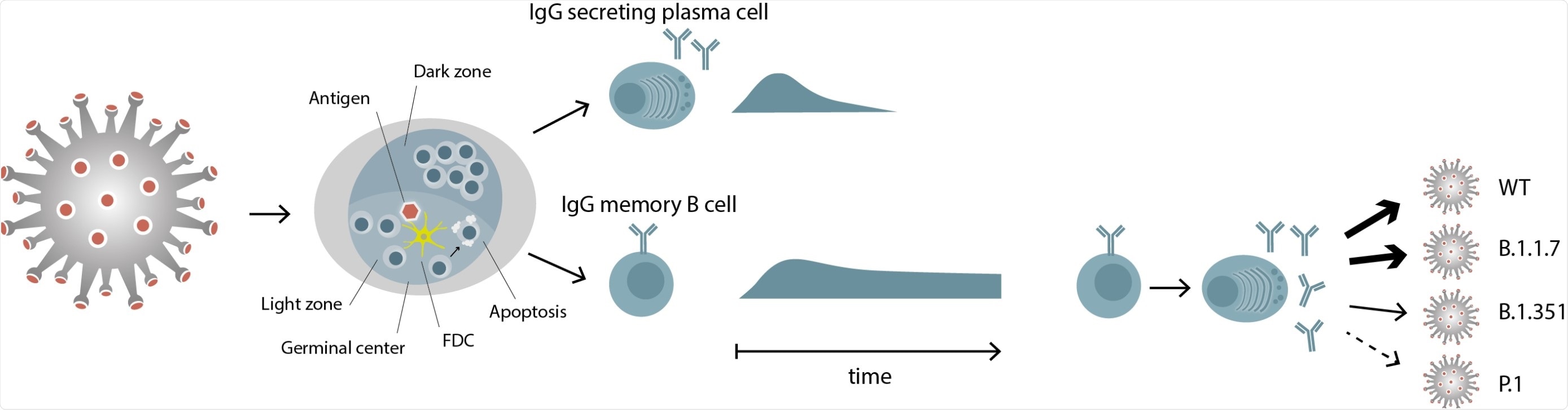
Differential persistence of IgG plasma cells and memory B cells specific for SARS-CoV- 2 SARS-CoV-2 antigen is transported to the lymph nodes, where it induces a germinal center reaction with the activation and differentiation of specific B cells. Two types of immune cells exit the germinal center, IgG secreting plasma cells and IgG memory B cells. IgG memory B cells persist, even when the corresponding plasma cells have disappeared. These memory B cells can differentiate to IgG secreting plasma cells and the IgGs they produce show a differential recognition of RBDs of viral variants.
This study detected circulating IgG memory B cells specific for SARS-CoV-2 in all 16 patients, about 1–8 months after infection. These patients underwent a mild or asymptomatic COVID-19 disease course.
Of these, they also found that 11 participants had specific IgA B cells. The researchers reported that the COVID-19 patients had significantly more SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA B cells than the healthy donors.
Notably, four patients who had lost specific serum IgG after 5–8 months had SARS-CoV-2-specific-B-cell levels which were comparable to those of seropositive donors.
"This study helps us to understand and start to develop models for predicting long-term protection against SARS-CoV-2."
To study the B cells, they converted the blood-derived B cells into antibody-secreting cells in vitro, and they analyzed the secreted antibodies for neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2. They found that the Immunoglobulins produced after in vitro differentiation blocked the receptor-binding domain (RBD) binding to the cellular receptor ACE-2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme), indicating high neutralizing activity.
Towards a potential therapeutic strategy, the researchers recommend, "These persisting B cells can be harnessed to identify a previous infection."
They also tested for cross-reactivity to the recently emerged SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1. The researchers observed that the memory-B-cell-derived IgGs recognized the RBD of variant B.1.1.7 (similarly to the wild-type). At the same time, reactivity to B.1.351 and P.1. decreased by 30% and 50%, respectively. The reduced activity in the latter cases calls for attention and a need for follow-up vaccinations.
Although the recovered individual lost the specific circulating immunoglobulins, the presence of these B cells with neutralizing activity suggests that protection against possible re-exposure with the variant is possible.
"Taken together, the picture is emerging from this study and previous work that when circulating IgG and IgA, mucosal IgA, and circulating IgA memory B cells are gone, circulating IgG memory B cells persist."
This is an important study to understand the long-term protection against SARS-CoV-2. It focuses on the features of SARS-CoV-2-specific memory B cells: 1) circulating SARS-CoV-2 IgG memory B cells persist even after 6 months after infection, despite the loss of systemic IgG; 2) these cells produce neutralizing antibodies; 3) these immunoglobulins show differential cross-reactivity to emerging variants of concern.
This study raises the need to analyze if the patients become reinfected because they have lost a certain type of anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunity or because they are confronted with a new variant, against which they do not yet have a protective immunity, the researchers write.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Persistence of functional memory B cells recognizing SARS-CoV-2 variants despite loss of specific IgG, Stephan Winklmeier, Katharina Eisenhut, Damla Taskin, Heike Rübsamen, Celine Schneider, Peter Eichhorn, Oliver T. Keppler, Matthias Klein, Simone Mader, Tania Kümpfel, Edgar Meinl, medRxiv 2021.05.15.21257210; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.15.21257210, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.05.15.21257210v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Winklmeier, Stephan, Katharina Eisenhut, Damla Taskin, Heike Rübsamen, Ramona Gerhards, Celine Schneider, Paul R. Wratil, et al. 2022. “Persistence of Functional Memory B Cells Recognizing SARS-CoV-2 Variants despite Loss of Specific IgG.” IScience 25 (1): 103659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103659. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01629-1.