Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the novel coronavirus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which has become a devastating worldwide pandemic. Patients on maintenance hemodialysis are one of the groups most severely affected by the pandemic as they have to visit clinics or facilities about three times a week for life-sustaining dialysis treatment. This puts them at five times more risk of infection compared to the general population.
Outbreaks have been reported in dialysis units despite adherence to all COVID-19-related public health protocols. Also, dialysis patients are a higher risk group for severe COVID-19. An estimated 63% of chronic dialysis patients with COVID-19 require hospitalization and a 29% fatality rate among chronic dialysis patients with COVID-19 in Ontario, Canada.
Hemodialysis patients are also known to respond poorly to vaccinations. Vaccine immunogenicity remains an open question among patients with kidney disease, since randomized controlled trials involving this population are rare.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Evaluating the antibody response in chronic hemodialysis patients following one vs. two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine
Researchers from Ontario, Canada, recently conducted a prospective observational study to determine the SARS-CoV-2 antibody response in chronic hemodialysis patients following one vs. two doses of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine. The results were compared to health care worker controls and convalescent serum. This study is published on the preprint server, medRxiv*.
The study was performed at a single center in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The participants included 142 in-center hemodialysis patients and 35 controls who were health care workers. The main outcomes measured in the study were SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies to the spike protein, nucleocapsid protein (anti-NP), and receptor binding domain (anti-RBD).
The humoral response in 66 hemodialysis patients who were sampled 28 days after receiving the first dose of the vaccine was compared to 76 patients who received both doses of vaccine sampled 14 days after receiving the second dose and 35 health care workers who received both vaccine doses.
Results show poor immune response in hemodialysis patients receiving a single dose of BNT162b2 vaccine
The results showed that 6% of those receiving one dose of the vaccine had an anti-RBD response above the median level of convalescent serum vs. 41% of those who received two doses of the vaccine. While detectable anti-NP antibodies suggesting natural SARS-CoV-2 infection was detected in 15 out of 142 (11%) patients at baseline, only three patients had prior COVID-19 confirmed by RT-PCR.
In patients receiving a single dose of BNT162b2, seroconversion occurred in 53 out of 66 (80%) patients for anti-spike and 35 out of 66 (55%) patients for anti-RBD 28 days after vaccination. However, only 15 out of 66 (23%) patients and 4 out of 66 (6%) patients, respectively, had a robust response by reaching the median level of anti-spike and anti-RBD in convalescent serum collected from COVID-19 survivors.
In those receiving two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine, seroconversion occurred in 69 out of 72 (96%) patients for anti-spike and 63 out of 72 (88%) patients for anti-RBD by two weeks after the second dose of the vaccine. Also, 52 out of 72 (72%) patients and 43 out of 76 (41%) patients, respectively, reached the median convalescent serum level of anti-spike and anti-RBD. All healthcare worker controls exceeded the median level of anti-spike and anti-RBD found in convalescent serum 2-4 weeks post the second vaccination dose.
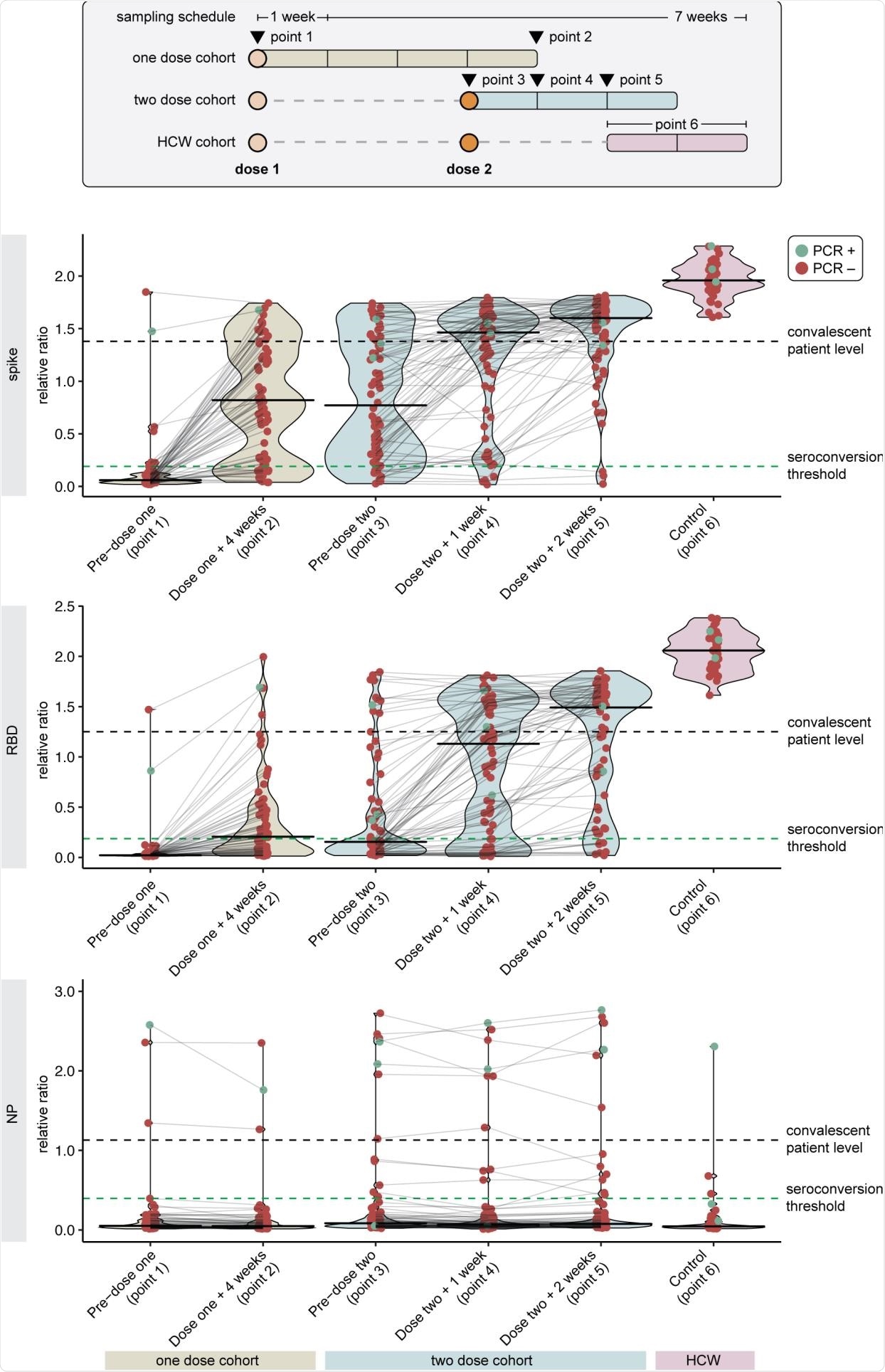
SARS-CoV-2 IgG Spike, RBD, and NP Antibody Response Following One Versus Two Dose BNT162b2 Vaccine in Hemodialysis Patients. Antibody levels are reported as relative ratios to synthetic standards. The samples are grouped into two cohorts who received one (n=66) or two doses (n=76) of vaccine. Dots represent individual serum samples collected at the indicated times, and the samples from the same patients are connected by lines. Green dots indicate individuals with prior RT-PCR confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. Seroconversion threshold represents a positive test and are 0.19, 0.186, and 0.396 for anti-spike, anti-RDB, anti-NP antibodies, respectively. The median level of antigen in convalescent serum taken 21-115 days post-symptom onset is considered a robust antibody response and is 1.38, 1.25, and 1.13 for anti-spike, anti-RBD, and anti-NP antibodies, respectively. Healthy control workers (n=35) received two doses of vaccines with serologic measurement 2-4 weeks following dose 2. Abbreviations: HCW, health care worker; NP, nucleocapsid protein; RBD, receptor binding domain.
Findings highlight the importance of adhering to recommended vaccination schedules in dialysis patients
In summary, the findings of this study confirm poor immunogenicity in hemodialysis patients who receive a single dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine 28 days after receiving the vaccine. This highlights the importance of adhering to recommended vaccination schedules in the hemodialysis population. According to the authors, since hemodialysis patients show poor humoral response to a single dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine, there should be no delay in giving them the second dose of the vaccine.
“Interestingly, we found that symptoms following the second vaccine dose were associated with anti-RBD seroconversion and may help identify patients who develop some protection.”

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
The Humoral Response to the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Hemodialysis, Patients Kevin Yau, Kento T. Abe, David Naimark, Matthew J. Oliver, Jeffrey Perl, Jerome A. Leis, Shelly Bolotin, Vanessa Tran, Sarah Mullin, Ellen Shadowitz, Julie Garnham-Takaoka, Keelia Quinn de Launay, Alyson Takaoka, Sharon E. Straus, Allison J. McGeer, Christopher T. Chan, Karen Colwill, Anne-Claude Gingras, Michelle A. Hladunewich, medRxiv, 2021.05.24.21257425; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.24.21257425, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.05.24.21257425v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Yau, Kevin, Kento T. Abe, David Naimark, Matthew J. Oliver, Jeffrey Perl, Jerome A. Leis, Shelly Bolotin, et al. 2021. “Evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response to the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis.” JAMA Network Open 4 (9): e2123622. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.23622. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783679.