Electrical activity in the motor cortex of rats transforms from redundant to complex over the span of four days shortly after birth. Sleep twitches guide this metamorphosis, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
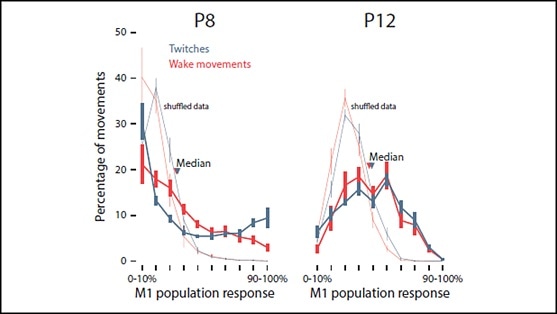
Image Credit: Society of Neuroscience
Despite its name, the motor cortex doesn’t control movement right off the bat. Early in development, this part of the brain is solely a sensory structure. Feedback from self-generated movements — sleep twitches in particular — may build representations of the body that will later orchestrate movement.
To characterize this transition, Glanz et al. recorded electrical activity from the motor cortex of rat pups eight and 12 days after birth while monitoring their behavior. On both days, sleep twitches drove more electrical activity than wake movements. Twitches on postnatal day eight (P8) activated many neurons at the same time — there was high redundance. This redundance disappeared by P12: each twitch activated a smaller group of neurons, a sign of maturing circuits. Larger twitches induced larger responses on P8, a trend not seen on P12. Yet the motor cortex became more sensitive to small twitches by P12. These changes mark a key developmental transition in the motor cortex facilitated by sleep twitches.
Source:
Journal reference:
Glanz, R.M., et al. (2021) Sensory coding of limb kinematics in motor cortex across a key developmental transition. Journal of Neuroscience. doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0921-21.2021.