Numerous studies have repeatedly demonstrated that a large percentage of those with a prior severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection exhibit lingering symptoms such as fatigue, dyspnoea, and impaired pulmonary function, particularly amongst those with a history of severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
This state has come to be known as long-COVID, and in a paper recently uploaded to the preprint server medRxiv* by Simjanoska et al. (September 7th, 2021) the biochemical parameters of long-COVID patients with prior mild, moderate, or severe COVID-19 that resulted in hospitalization are tracked in detail, finding a characteristically dysregulated immune and inflammatory response in the most seriously ill.

 *Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
*Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
Who is most likely to develop long-COVID?
168 COVID-19 patients that had been hospitalized for at least three days and had robust laboratory data available were recruited for the study. All donated further samples for testing on average two months later.
56.5% of all participants reported long-COVID symptoms at the time of second sampling, and as the participants were categorized based on disease severity at the time of admission and during their stay at hospital the group note that 63.54% of those with long-COVID had previously been diagnosed with severe COVID-19, compared with around 20% each of those classed as mild or moderate, respectively.
60.4% of those that had previously suffered from severe COVID-19 developed long-COVID, while 47.4% and 58.6% of patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 developed long-COVID, respectively, according to clinical assessment of symptoms.
Unlike other studies, this suggests that there is no significant correlation between disease severity and the probability of developing lingering symptoms. However, those with prior severe illness made up a more significant proportion of those with long-COVID in the sample.
Additionally, the participants in this study were each hospitalized for at least three days, and thus results are likely to be skewed towards individuals more likely to experience poorer health.
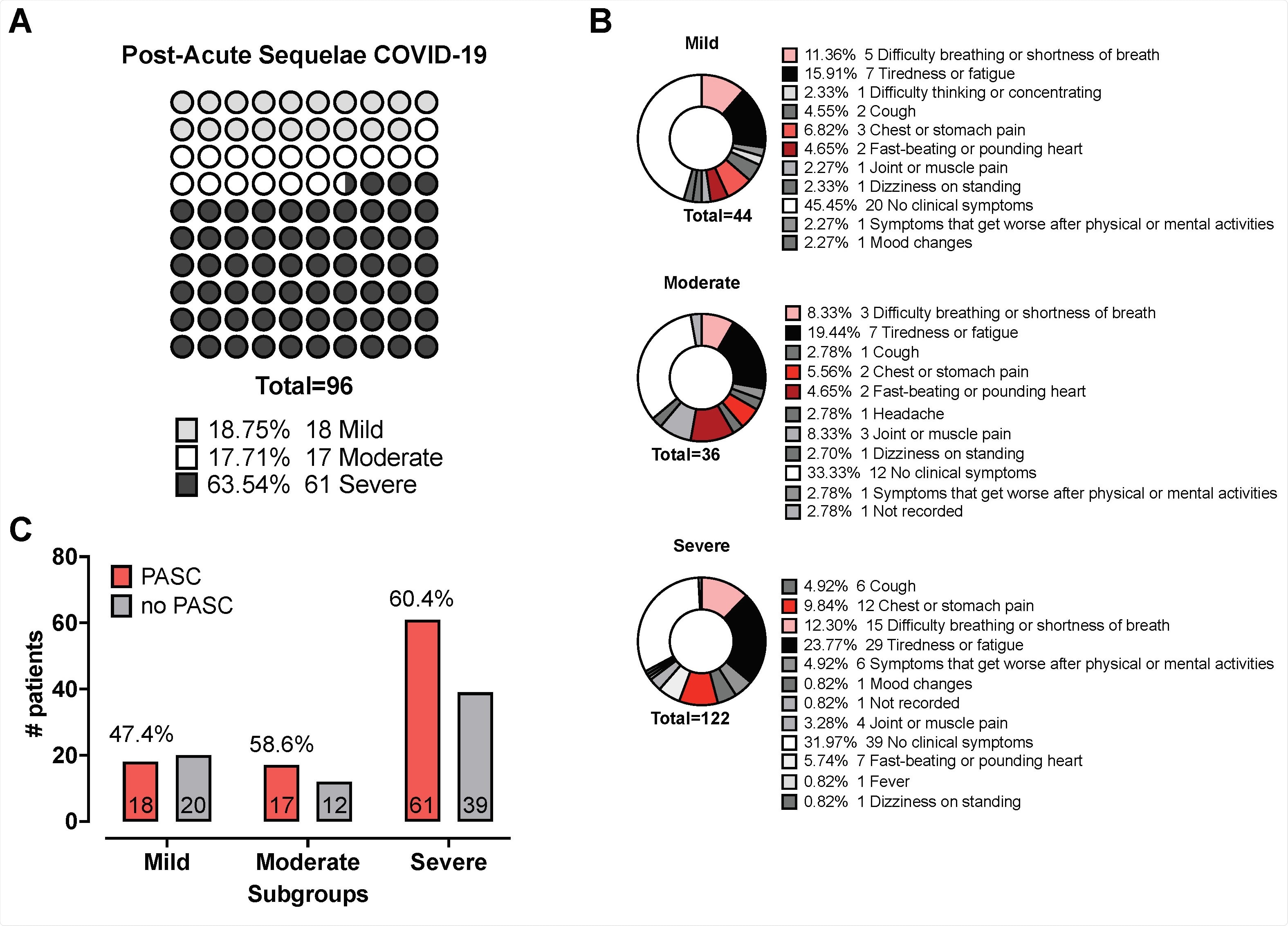
Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) Panel A shows pie charts indicating the distribution of reported PASC among the mild, moderate, and severe subgroups. (%) Numbers correspond to individuals who reported said PASC; colours indicate respective PASC. Panel B depicts a dot plot graph visualising the distribution of % Number of individuals reporting PASC according to clinical disease severity. Panel C shows the contingency table comparing the proportion of mild- to moderate cases vs severe cases with PASC; numbers in bar represent the patient count, % above the grey and red bar are the reported proportion of no PASC and PASC, respectively
How did biochemical markers differ by disease severity?
Biochemical testing of severe COVID-19 patients now with long-COVID demonstrated upregulated ferritin, D-dimer, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), C-reactive protein (CRP), and interleukin(IL)-6 levels at later time points, with the most severe cases also displaying dysregulated white blood cell profiles.
In those with mild to moderate COVID-19 only D-dimer levels were slightly elevated, with all other tested parameters returning to baseline by the second sampling.
More elevated levels of D-dimer and ferritin were observed amongst the severely ill at hospital admission and at later time points, as has been reported in other studies, with ferritin, in particular, exhibiting extremely high levels, in particular, the severely ill.
The authors speculate that this may be due to unbound iron playing a role in inflammation. They also suggest that sustained LDH levels in the severely ill may be an indication of ongoing lung repair. At the same time, elevated inflammatory agents such as CRP and IL-6 may result from greater levels of lung damage and hypoxia experienced during illness.
Other studies have reported ongoing elevated levels of IL-6 with the presence of pulmonary lesions in those recovering from severe COVID-19, which the authors suggest coincides with the reported greater incidence of long-COVID symptoms in this group. Among the most commonly reported symptoms from the severe group with long-COVID was lung or chest pain, which is reported around half as often by those with prior mild or moderate COVID-19, with fatigue being most commonly reported in 16%, 20%, and 24% of mild, moderate, or severe patients, respectively.
Individuals that experienced only mild or moderate COVID-19 and were considered to have long-COVID based on symptoms appear to have been overrepresented in this study, with almost 60% of individuals in any category of severity reportedly experiencing lingering symptoms for as long as three months post-hospitalization.
Although the biochemical profile of those with either mild or severe COVID-19 differed substantially during hospitalization and follow-up, those with a history of severe COVID-19 could be differentiated from the mildly or moderately ill by their significantly dysregulated biochemical profile.

 *Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
*Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.