Immunocompromised individuals, particularly those with B-cell deficiencies or who are currently taking immunosuppressive medications, are not capable of developing an adequate immune response to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination. This makes such individuals, who constitute close to 3% of the United States population, more susceptible to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and the development of severe COVID-19.
Previous studies have shown that a single dose of REGENCOV®, which is a combination drug consisting of both casirivimab and imdevimab, is effective in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, outpatients with COVID-19, and in post-exposure prophylaxis. A recent study posted on the medRxiv* preprint server assesses the efficacy of repeat monthly subcutaneous (SC) doses of REGEN-COV in SARS-CoV-2-negative adults who were healthy or had chronic medical conditions.
 Study: Repeat Subcutaneous Administration of REGEN-COV® in Adults is Well-Tolerated and Prevents the Occurrence of COVID-19. Image Credit: PHOTOCREO Michal Bednarek / Shutterstock.com
Study: Repeat Subcutaneous Administration of REGEN-COV® in Adults is Well-Tolerated and Prevents the Occurrence of COVID-19. Image Credit: PHOTOCREO Michal Bednarek / Shutterstock.com

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
About the study
The current study was a Phase 1, double-blind, and placebo-controlled study that was executed at seven sites throughout the U.S. and constituted a baseline/screening period, a treatment period, and a follow-up period of up to seven days, 24 weeks, and 28 weeks, respectively. There were 705 and 235 subjects in the REGEN-COV and placebo groups, respectively. The rationale for enrolling the 940 subjects in the study was to obtain sufficient safety data to support multiple REGEN-COV dose administration.
Eligible subjects were healthy adult volunteers between the ages of 18–90 years who were confirmed to be SARS-CoV-2 negative by central lab reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) of nasopharyngeal swab before or within 72 hours of randomization. For the duration of the study, subjects who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, elected to receive COVID-19 vaccination, or experienced an adverse event (AE) were excluded and moved to the follow-up stage.
All eligible subjects received up to six doses of either SC REGEN-COV 1,200 mg or placebo for four weeks. However, only those subjects who received more than 1 dose of REGEN-COV were classified in the REGEN-COV group.
Evaluating safety, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity of REGEN-COV
The primary endpoints assessed in the current study included the incidence of AEs of special interest (AESIs), as defined as grade ≥3 injection-site reactions (ISRs), or hypersensitivity reactions. AESIs occurred within four days of administration of REGEN-COV or placebo.
The secondary endpoints assessed the proportion of subjects with treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs) and immunogenicity to REGEN-COV, which was measured using anti-drug antibodies (ADAs). Exploratory efficacy endpoints assessed the incidence and severity of symptomatic COVID-19 during the treatment and follow-up periods.
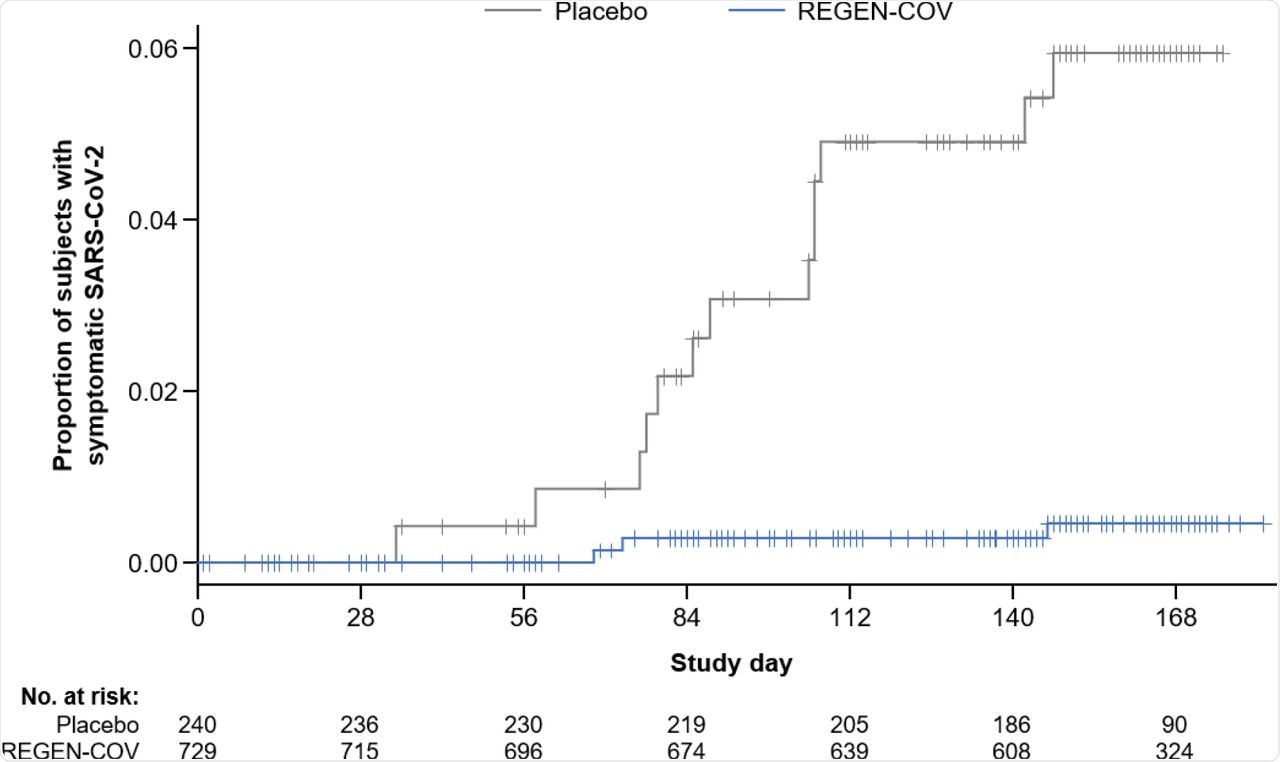 Risk of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection during the treatment period. The proportion of subjects with the reported adverse event of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to the number of subjects at risk for infection in the REGEN-COV group and placebo group is shown here by study day. Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) determination was made by the investigator on the basis of clinical assessment.
Risk of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection during the treatment period. The proportion of subjects with the reported adverse event of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to the number of subjects at risk for infection in the REGEN-COV group and placebo group is shown here by study day. Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) determination was made by the investigator on the basis of clinical assessment.
The effect of monthly doses of REGEN-COV
The current study was the first ever to investigate the effect of monthly doses of REGEN-COV. To this end, the current study findings demonstrate that monthly doses of REGEN-COV are well tolerated and could prevent COVID-19 for over six months.
As per the results of the exploratory efficacy analysis, REGEN-COV treatment resulted in a 92.4% relative risk reduction (RRR) in clinically defined COVID-19 and a 100% RRR in laboratory-confirmed COVID-19, which is strikingly similar to the risk reduction seen in the vaccine trials.
The results demonstrate a significant reduction in the production of SARS-CoV-2 anti-nucleocapsid immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies among REGEN-COV-treated subjects over the six-month course of therapy, as assessed by seroconversion rates. The observed seroconversion rate among placebo recipients was 9.6% and 0% among received REGEN-COV, thus suggesting that REGEN-COV is effective as a chronic treatment for immunocompromised individuals.
REGEN-COV-treated subjects showed a slightly higher frequency of ISRs as compared to placebo-treated patients, which suggests that multiple doses of REGEN-COV were well tolerated. The overall ISR rate with REGEN-COV was 36.5% across all six doses combined; however, the ISR rate between sites varied significantly and two outlier sites were driving forces behind these incidences.
Conclusion
Taken together, the assessments made in this study are consistent with a previous Phase III study and further establish the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of repeated monthly doses of SC-administered REGEN-COV. The current study reports that all ISRs were mild to moderate in severity and that repeated dosing did not increase the incidence and/or severity of ISRs. Furthermore, treatment-emergent immunogenicity remained low, while no grade ≥3 hypersensitivity reactions were reported.
It is important to note that during the study, the concentrations of casirimivab and imedivimab remained within the therapeutic range.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Isa, F., Forleo-Neto, E., Meyer, J., et al. (2021). Repeat Subcutaneous Administration of REGEN-COV® in Adults is Well-Tolerated and Prevents the Occurrence of COVID-19. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.11.10.21265889. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.11.10.21265889v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Isa, Flonza, Eduardo Forleo-Neto, Jonathan M Meyer, Wenjun Zheng, Scott Rasmussen, D Armas, Masaru Oshita, et al. 2022. “Repeat Subcutaneous Administration of Casirivimab and Imdevimab in Adults Is Well-Tolerated and Prevents the Occurrence of COVID-19.” International Journal of Infectious Diseases 122 (July): 585–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.045. https://www.ijidonline.com/article/S1201-9712(22)00380-0/fulltext.