Recent studies have found that current severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccines are three- to five-fold less effective against the Delta variant when compared with the Alpha variant. This efficacy is further reduced in organ transplant recipients, who are required to be on immunosuppressants in order to prevent organ rejection.
Study: A fourth dose of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine improves serum neutralization against the delta variant in kidney transplant recipients. Image Credit: guteksk7 / Shutterstock.com

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Kidney transplant patients exhibit insufficient antibody response after three doses of mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
Standard vaccination schemes are hampered by low immunogenicity in immunocompromised individuals who remain prone to develop severe complications when diagnosed with the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Previous reports have suggested that even three doses of SARS-CoV-2 messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based vaccines were unable to stimulate a sufficient immune response in immunocompromised kidney transplant recipients. Consequently, French health authorities allowed offering a fourth vaccine dose to weak responder solid organ transplant recipients from June 2021 onwards.
In the current study, Dr. Ilies Benotmane and colleagues have characterized the neutralizing antibody response against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta strain before and after a fourth dose of the mRNA-1273 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients who had experienced a weak antibody response after three previous doses. The team also assessed the correlation between the neutralizing capacity and levels of immunoglobulin G (IgG) against the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein.
About the study
The current study was conducted on a kidney transplant cohort comprising of 67 patients, with no history of COVID-19 infection, who exhibited weak serological response one month after the third mRNA-1273 vaccine dose and, as a result, were injected with a fourth dose.
All patients were kept on some combination of immunosuppressants, 97% being treated with calcineurin inhibitors, 82% with mycophenolate mofetil, 76% with steroids, and 18% with mTOR inhibitors.
Anti-IgG antibody titers were measured in binding antibody units (BAUs)/mL. With reference to previous data, titers less than 143 BAUs/mL were considered to reflect a weak humoral response against the wild-type virus and its common variants including the Alpha, Beta, and Gamma strains.
Neutralization of the live Delta strain was investigated and neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) was expressed as the concentration capable of inhibiting 50% of the virus inoculum (IC50),. A titer greater than 30 was considered positive.
Both anti-RBD IgG and NAbs were quantified one month after the third and fourth vaccine doses, respectively. Finally, the correlation between IgG and NAbs levels was calculated against the RBD.
Study findings
The team observed that a fourth dose significantly increased the neutralizing response against the currently dominant Delta variant in the cohort of 67 kidney transplant recipients who showed a weak immune response after three doses of the mRNA-1273 vaccine. Specifically, the proportion of patients harboring NAbs against the Delta strain rose significantly from 16% to 66% after the fourth vaccine dose, respectively.
The median titer of anti-RBD IgG increased significantly from an average of 2.6 BAUs/mL to 112.5 BAUs/mL. In parallel, the IC50 titers of NAbs increased significantly from less than 7.5 to 47.1.
Patients with undetectable NAbs after the third dose were less likely to have their neutralizing capacity increased after the fourth dose. Notably, patients receiving combined therapy with tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and steroids displayed lower NAb titers. Interestingly, NAb titers against the Delta variant were positively correlated with anti-RBD titers.
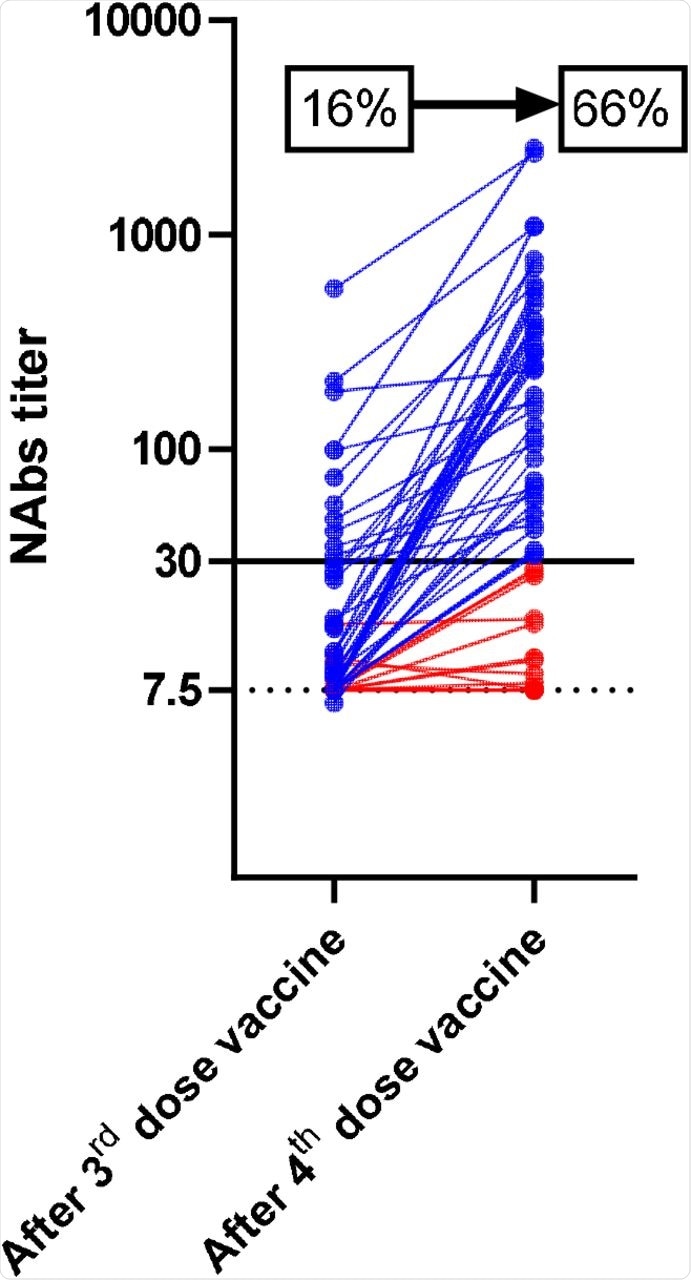
Neutralizing antibody titers against the delta variant after the third and fourth doses of the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine in 67 kidney transplant recipients. Neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) were expressed as the concentration capable of inhibiting 50% of the virus inoculum (EC50%; limit of detection: 7.5, dotted line). A titer >30 was considered as positive (black line). The percentages of patients harboring NAbs against delta variant before and after the fourth dose are shown in the graph. Lines in blue represent patients with NAbs with a titer is above 30 while red lines represent patients with NAbs with a titer is below 30.
The team did not find any major adverse effects after the fourth dose.
However, as the fourth injection was still unable to elicit NAbs against the Delta variant in roughly one-third of the cohort samples, the team advises that such patients maintain strict sanitary protection measures and/or be considered as candidates for prophylactic administration of monoclonal anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
“While immunosuppressive modulation during vaccination could be another alternative to improve vaccine response, this approach should be weighed against the risk of developing acute rejection.”

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Benotmane I., Bruel, T., Planas, D., et al. (2021) A fourth dose of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine improves serum neutralization against the delta variant in kidney transplant recipients. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.11.25.21266704. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.11.25.21266704v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Benotmane, Ilies, Timothée Bruel, Delphine Planas, Samira Fafi-Kremer, Olivier Schwartz, and Sophie Caillard. 2022. “A Fourth Dose of the MRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Improves Serum Neutralization against the Delta Variant in Kidney Transplant Recipients.” Kidney International, February. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2022.02.011. https://www.kidney-international.org/article/S0085-2538(22)00168-5/fulltext.