The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines tend to carry mild side effects such as muscle achiness at the injection site, but there is always a small risk of severe adverse events. For example, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report a case of multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MISC) in a 22-year-old woman in South Korea after vaccination. The woman had no prior severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection.
The condition is rare but deadly and can be found in both adults and children. The study authors note that if SARS-CoV-2 spike protein or antibodies that target the spike protein is associated with MIS-C, there is the potential of this side-effect being more prevalent in children.

Study: Postvaccination Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Adult with No Evidence of Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Image Credit: Tomas Ragina/Shutterstock
The case study was recently published in the CDC’s journal Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Case study details
On April 2021, a 22-year-old healthcare worker presented to a South Korean hospital with a 2-day fever, muscle weakness, sore throat, diarrhea, vomiting, and recent chest pain. The symptoms came 10 days after receiving the first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine and 8 days after getting her wisdom teeth removed.
The woman had no comorbidities and had no history of COVID-19 infection in the past 3 months. After hospital admittance, she was tested and was negative for COVID-19.
After examination, the patient was confirmed to have a high fever of 37.8 °C, tachycardia, mild pharyngeal injection, muscle tenderness, and limb weakness. There was no evidence of a dental infection. Medications used to reduce fever had minimal effect.
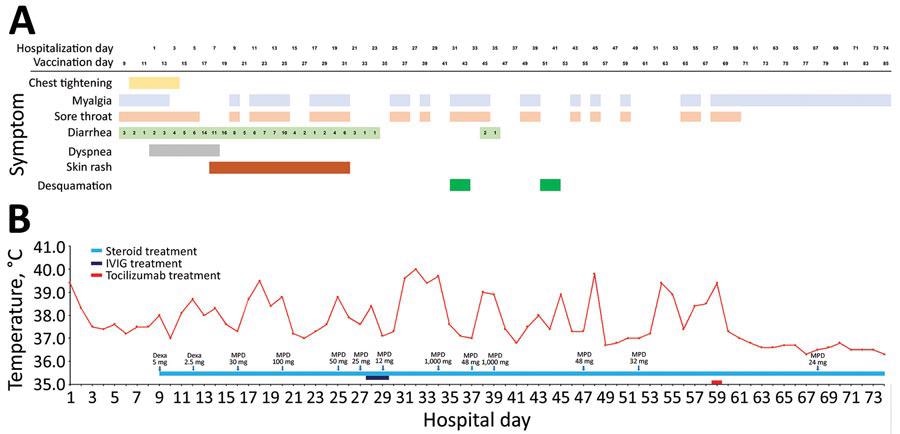 Clinical course of illness in an adult with postvaccination multisystem inflammatory syndrome and no evidence of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, South Korea. A) Signs/symptoms according to the day of hospitalization and the days since vaccination. B) Patient’s maximum body temperature and anti-inflammatory therapy according to the day of hospitalization. Dexa, dexamethasone; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; MPD, methylprednisolone.
Clinical course of illness in an adult with postvaccination multisystem inflammatory syndrome and no evidence of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, South Korea. A) Signs/symptoms according to the day of hospitalization and the days since vaccination. B) Patient’s maximum body temperature and anti-inflammatory therapy according to the day of hospitalization. Dexa, dexamethasone; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; MPD, methylprednisolone.
Lab tests showed increased inflammation, including inflammation of the small and large intestines was observed.
Six hours after arriving at the hospital, the patient’s blood pressure fell to 70/45 mm Hg but returned to normal levels after norepinephrine treatment. Soon after, the patient was diagnosed with myocarditis and pericarditis. Further tests showed elevated cardiac enzymes, ST-segment elevation, and a small pericardial effusion.
PCR tests were negative for a series of viruses including the adenovirus, metapneumovirus, rhinovirus, bocavirus, parainfluenza virus, and flu virus.
On the fourth day of her hospital visit, the patient developed hypotension along with atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response. Fortunately, two cardiac treatments helped normalize blood levels and revert cardiac activity to sinus tachycardia.
After a week, a macular rash emerged and was treated with steroid medication. During this time, the patient showed unstable inflammatory levels, fever, and rash. Additionally, the patient had a 1-cm deep pericardial effusion despite a lack of evidence of inflammation in the heart.
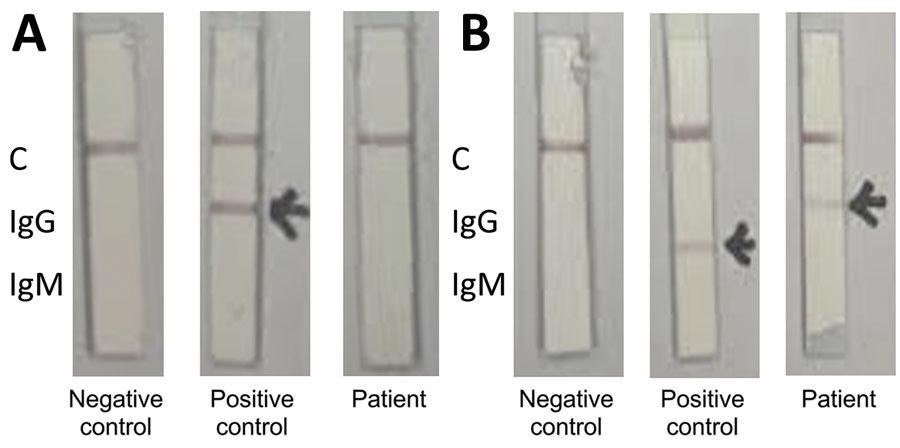 Colloidal gold qualitative immunoassay for antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, South Korea. A) Nucleocapsid protein conjugate; B) spike receptor-binding domain conjugate. The positive control serum contains antinucleocapsid IgG and anti–spike protein receptor-binding IgM. C, control.
Colloidal gold qualitative immunoassay for antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, South Korea. A) Nucleocapsid protein conjugate; B) spike receptor-binding domain conjugate. The positive control serum contains antinucleocapsid IgG and anti–spike protein receptor-binding IgM. C, control.
Treatment plans during hospitalization and diagnosis of MIS-A
The doctors administered multiple rounds of antimicrobial drugs for three weeks. Because tests assessing for bacterial infection were negative, the patient was later given a diagnosis of MIS-A.
"Although we cannot rule out other infections, autoimmune causes, or malignancies, the most reasonable diagnosis for this patient is MIS-A” explained the researchers.
Treatment then consisted of human immunoglobulin therapy on days 28 and 29 because the patient continued to exhibit a high body temperature and elevated inflammation as seen in high C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. However, it proved ineffective. Steroid dosage also increased, but no noticeable benefit to disease control was observed.
By this time, the patient’s physical condition had deteriorated. Muscle weakness increased and the patient was not capable of standing by herself. In addition, her fever spiked to 40°C and inflammation increased.
Steroids were gradually reduced, and doctors extended steroid pulse therapy for one more week.
By day 30, the skin on her fingers began to peel. By day 40, the skin on her toes shed as well.
After a month of hospitalization, further tests confirmed signs of myopathy though there were no changes to her coronary arteries.
At two months, doctors administered 8 mg/kg of tocilizumab. Afterward, the patient showed no signs of a fever, and muscle pain in the extremities decreased.
Seventy-four days after hospitalization, the patient was discharged. However, she continued to show lingering muscle weakness that would require future physical therapy.