The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) first emerged in France at the end of January 2020. Since then, SARS-CoV-2 has infected over 8.76 million French citizens and caused over 122,000 deaths.
Co-infection of respiratory viruses
Researchers have previously observed that the frequency of co-infection with different respiratory viruses was dependent on the season and sampling time of the study. Previous studies involving viral co-infections have also reported essential differences in patient outcomes with reference to the time period and the region of the world where the study took place. Geography has been particularly important, as the occurrence of viral co-infections required a co-incidence of the viral epidemic periods.
Likewise, significant differences have been observed according to the epidemic mode of the respiratory viruses involved in co-infections. This includes whether or not the viruses showed a bell-shaped incidence curve or circulated throughout the year with varying intensities.
About the study
In a recent Viruses study, researchers focused on co-infections with SARS-CoV-2 and human rhinovirus (HRV), as HRV was the most frequently associated co-infection with SARS-CoV-2 that was detected in as many as 41% of patients at Marseille University. To this end, the researchers compared clinical severity in patients coinfected with a SARS-CoV-2 and HRV against those infected only with one of either virus.
A higher number of SARS-CoV-2 co-infections with HRV has been consistently observed in multiple previous studies conducted in various settings and geographical areas. However, the clinical outcome of these cases with SARS-CoV-2 and HRV co-infection remains unknown.
The current study was conducted between March 1, 2020, and February 28, 2021. Herein, the researchers used the reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay to detect SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory viruses from nasopharyngeal samples as part of the routine work at Marseille University hospitals. In addition, bacterial and fungal infections were also detected using standard laboratory tests.
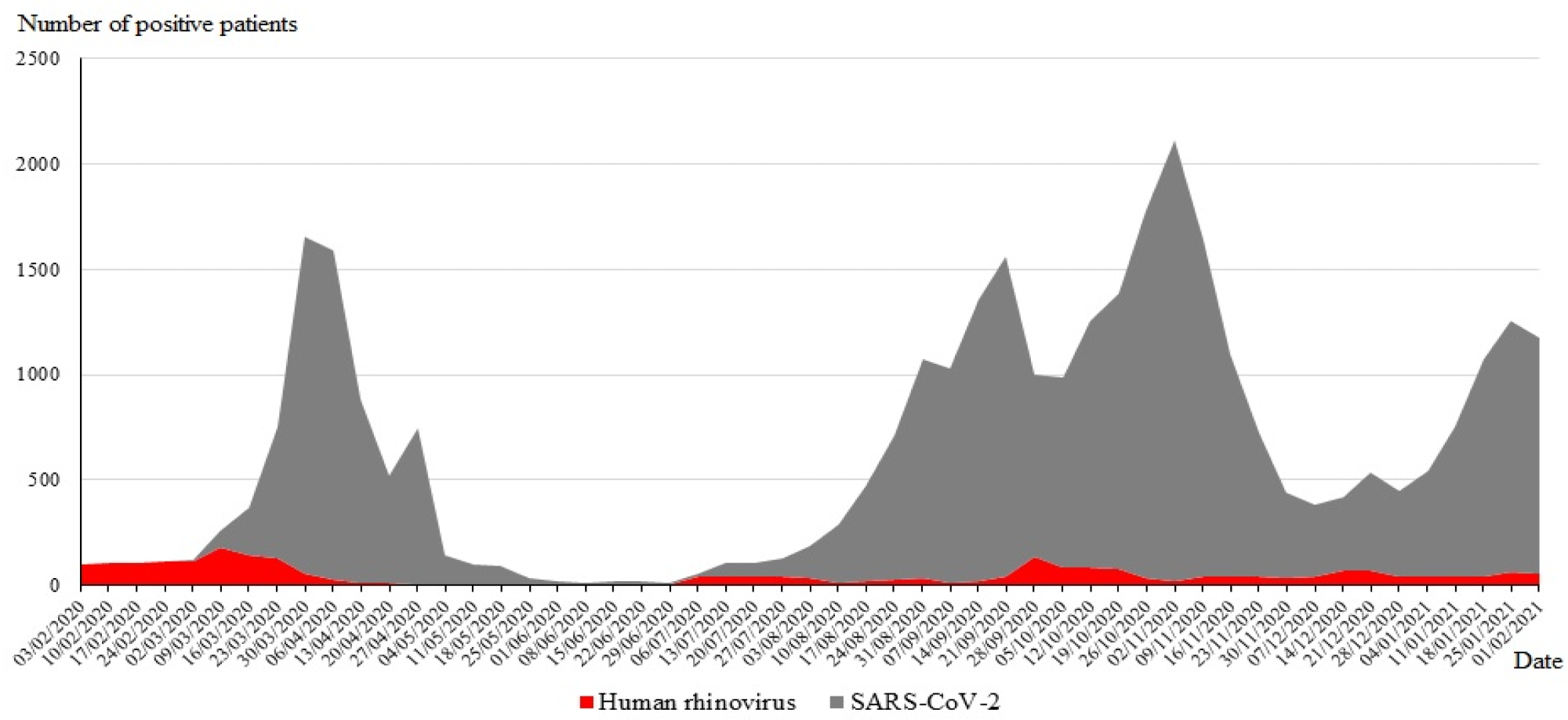 Temporal distribution of the SARS-CoV-2 and HRV diagnoses from 1 March 2020 to 28 February 2021.
Temporal distribution of the SARS-CoV-2 and HRV diagnoses from 1 March 2020 to 28 February 2021.
Study findings
All relevant clinical data were retrospectively collected from medical files. Taken together, a total of 15,157 patients were included in the study, of which 40% (6,034) tested positive for at least one respiratory virus. Furthermore, 93 patients (4.3%) infected with SARS-CoV-2 were coinfected with another respiratory virus, with 67% of these patients (62) testing positive for HRV.
Patients coinfected with SARS-CoV-2 and HRV were significantly more likely to report a cough than those with only a SARS-CoV-2 infection. These patients were also significantly more likely to report breathing discomfort as compared to patients with rhinovirus mono-infection.
Patients with both SARS-CoV-2 and HRV infections were also more likely to experience severe infection, get transferred to an intensive care unit, and die as compared to patients with only rhinovirus infection. However, these differences were not statistically significant.
Implications
The current study highlights that patients with SARS-CoV-2 and HRV co-infections were more likely to have severe consequences as compared to those with either one of the infections. HRV infection was also one of the most common respiratory infections affecting people in the study period. Larger studies are needed to investigate the co-incidence and interactions of SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory viruses, as well as their impact on public health.
Journal reference:
- Le Glass, E., Hoang, V. T., Boschi, C., et al. (2021). Incidence and Outcome of Coinfections with SARS-CoV-2 and Rhinovirus. Viruses. doi:10.3390/v13122528.