The rapid outbreak of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, which has devasted lives and livelihoods worldwide.
Healthcare workers (HCWs) in Japan are vaccinated against contagious diseases, such as measles, rubella, chickenpox, mumps, and hepatitis B, but some are deemed as low responders or those that do not produce sufficient antibodies after vaccination. Japanese HCWs have also been vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2.
A new study, published on the medRxiv* preprint server, investigated the changes in SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels among HCWs after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. The study also assessed whether low responders produced sufficient SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike and neutralizing antibodies.
 Study: Can individuals with low antibody responses to vaccines against other viruses acquire adequate SARS-CoV-2 antibody after vaccination with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine? Image Credit: NIAID
Study: Can individuals with low antibody responses to vaccines against other viruses acquire adequate SARS-CoV-2 antibody after vaccination with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine? Image Credit: NIAID

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Background
SARS-CoV-2 comprises four major viral structural proteins, namely, the nucleocapsid, spike, envelope, and membrane proteins. The spike protein guides viral entry into host cells by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors. Therefore, this is the best target for mRNA vaccines, such as the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine (Pfizer–BioNTech). BNT162b2 is highly effective at preventing severe COVID-19, reducing the incidence of asymptomatic infection, and preventing the spread of the disease.
HCWs are at a high risk of infection with contagious viruses and, therefore, in order to prevent nosocomial infections, they are vaccinated against these viruses. Low responders are those individuals who do not develop adequate antibody titers against contagious viruses post-vaccination. Unfortunately, there is not much evidence to document the antibody production of low responders to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. The current study aims to fill this gap in research by analyzing whether low responders acquire sufficient antibody activity after vaccination with the BNT162b2 vaccine.
A New Study
Scientists carried out a prospective cohort study of 50 HCWs at Kyorin University Hospital in Tokyo, Japan. HCWs received two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine, 3 weeks apart. The HCWs whose antibody levels were below the normal values for preventing infection against measles, rubella, chickenpox, mumps, or hepatitis B viruses, were considered low responders.
SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike antibodies were measured 11 times between the first BNT162b2 vaccination and five months after the second dose. The neutralizing antibody activity was measured twice in low responders, 1 week to 1 month and 5 months after administering the second dose of the vaccine.
Main Findings
Four individuals were found to be low responders, while others were normal responders. The low responders also developed protective levels of neutralizing antibodies post-vaccination with the BNT162b2 vaccine. This result is in line with previous studies that have documented that the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine provides sufficient humoral immunity within the first month after receiving the second dose.
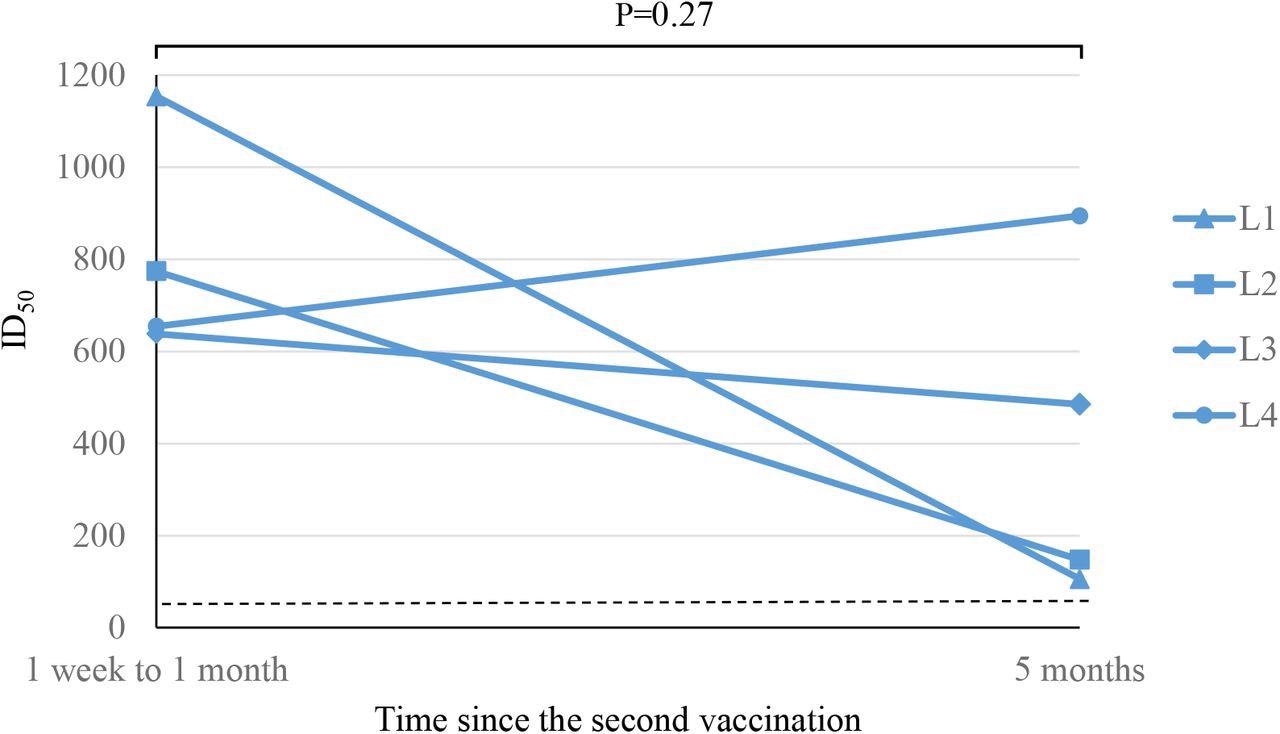
SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity responses after the second dose of BNT162b2 vaccine in participants with low-level responses to previous antiviral vaccines
Scientists observed that the antibody titer was significantly lower among normal responders at 5 months after the second dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine, compared to 1 week after the second dose. However, the decrease in antibody titers in the low responders was not statistically significant.
It is known that antibody levels produced after measles-mumps-rubella vaccination tend to decline almost 15 years after the first dose. The SARS-CoV-2 antibody level is known to peak and then decrease within months after the second dose. Therefore, scientists stated that the third dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine is required – both for low and normal responders.
Concerning SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike antibody production, smoking has been seen to result in low SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers after vaccination. Antibody levels are also significantly lower values in patients with hematological malignancies. The low responders in the current study were healthy and did not have risk factors such as an organ transplant or immunosuppression. It should be further investigated why these individuals failed to produce sufficient antibodies against other diseases but produced adequate antibodies after vaccination with the BNT162b2 vaccine.
Concluding Remarks
A notable limitation of this study is the small sample size and the fact all HCWs were vaccinated at a single hospital. Therefore, multicenter studies with a larger sample size are extremely important. Further, future research should clarify the mechanism by which humoral immunity is acquired after mRNA vaccination in individuals with low antibody responses to other viral vaccines.
In summary, researchers observed that both low and normal responders developed adequate levels of antibodies after two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine. However, lower SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike antibody levels in the fifth month imply that the third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine should be administered to all individuals.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Ogura, W. et al. (2022) Can individuals with low antibody responses to vaccines against other viruses acquire adequate SARS-CoV-2 antibody after vaccination with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine?, medRxiv, 2021.12.26.21268358; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.26.21268358, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.26.21268358v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Ogura, Wataru, Kouki Ohtsuka, Sachiko Matsuura, Takahiro Okuyama, Satsuki Matsushima, Satoko Yamasaki, Hiroyuki Miyagi, Kumiko Sekiguchi, Hiroaki Ohnishi, and Takashi Watanabe. 2022. “Can Individuals with Suboptimal Antibody Responses to Conventional Antiviral Vaccines Acquire Adequate Antibodies from SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccination?” Viruses 14 (5): 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050956. https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/14/5/956.