The Cucurbitaceae family comprises about 115 genera and 960 species of different fruits and vegetables, which are rich sources of proteins, vitamins, minerals, dietary fibers, and many bioactive compounds. Based on their morphological, cytological, and floral characteristics, these plants are classified into two primary subfamilies: Cucurbitoidea and Zanoniodeae.
Cucumis L. is a genus of the Cucurbitaceae family. It is commonly consumed fresh or used in various foods and beverages. It is also used in various topical formulations and pharmaceutical vitamin A and C products.
Momordica species of the Cucurbitaceae family are cultivated in tropical regions and often have a bitter taste due to the presence of alkaloid phytochemicals. Bioactive compounds and trace elements found in these plants are useful for treating various health conditions, including asthma, fever, neuropsychological, dermatological, and digestive disorders.
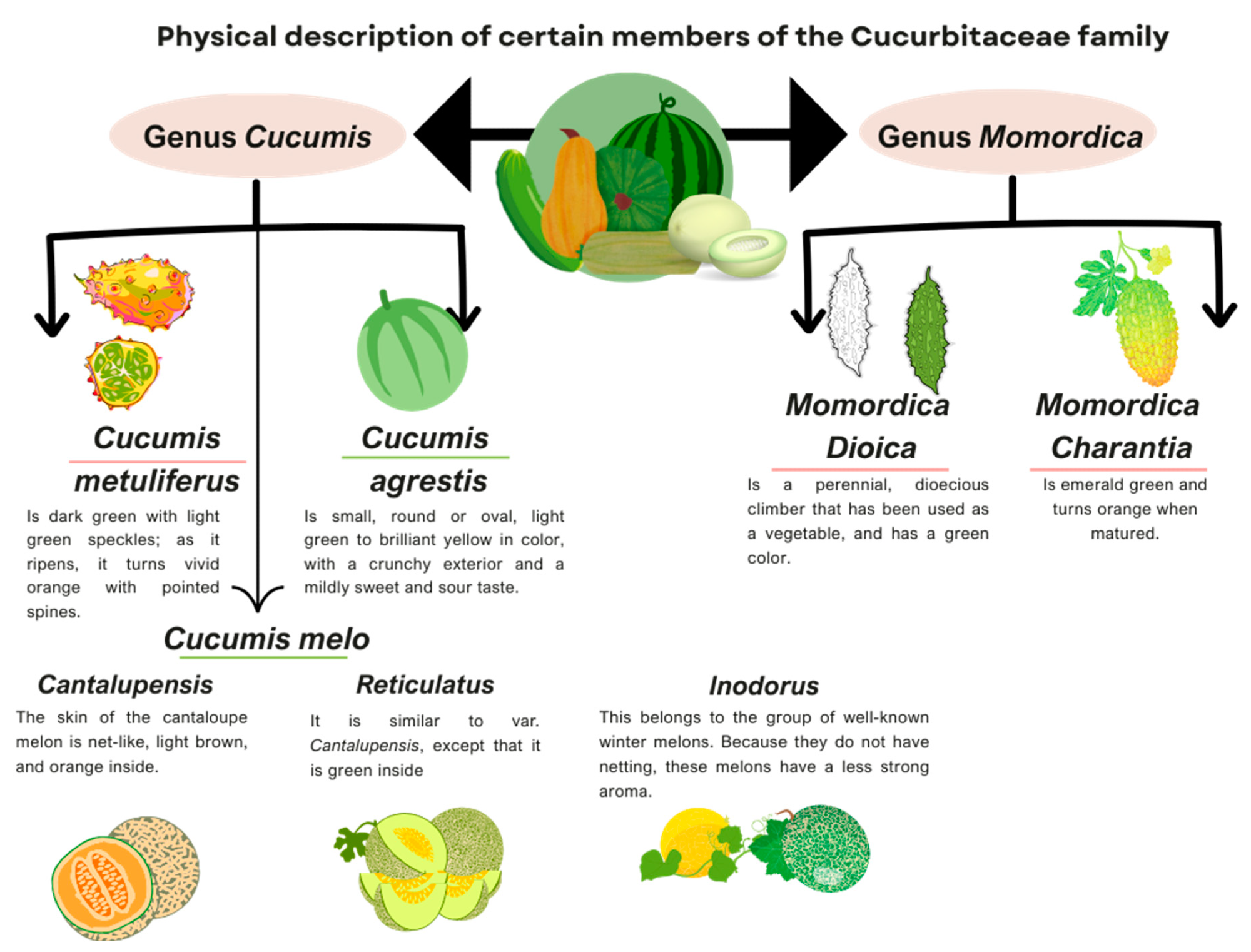 Physical description of the members of the Cucurbitaceous family discussed in this article
Physical description of the members of the Cucurbitaceous family discussed in this article
Health properties of Cucumis metuliferus
Cucumis metuliferus, which is commonly known as Kiwano or horned melon, grows mostly in tropical regions, including Nigeria and South Africa. Polysaccharides present in the Cucumis metuliferus peel have immunomodulatory, ferrous ion-chelating, and prebiotic activities.
The Cucumis metuliferus pulp contains high amounts of potassium salts and low amounts of sodium salts, as well as rutin and lutein, which have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and platelet aggregation-inhibiting activities.
C. metuliferus extract can exert hypoglycemic effects by inhibiting the activities of key enzymes like β-glucosidase or α-amylase involved in glucose metabolism. The hydroethanolic extract of Cucumis metuliferus can exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic effects due to the presence of ursolic acid.
The anti-inflammatory properties of C. metuliferus methanolic extracts primarily depend on the high phenol and flavonoid content of these fruits. These extracts may also reduce nephrotoxicity and increase total white blood cell (WBC) counts in animals.
Health properties of Cucumis agrestis
Cucumis agrestis is generally consumed as a vegetable and contains multiple phytoconstituents, including alkaloids, tannins, flavonoids, carbohydrates, proteins, glycosides, steroids, triterpenoids, and phenolic acids.
The hydroalcoholic extract of Cucumis agrestis is associated with anti-diabetic and anti-hyperlipidemic properties. Comparatively, the methanolic fruit extract has shown strong antioxidant activity, which makes it a potential adjuvant candidate for the treatment of liver cancer.
Health properties of Cucumis melo L.
Cucumis melo is a rich source of vitamin C, vitamin E, polyphenols, carotenoids, and phytochemicals, all of which are associated with potential cardiovascular, diuretic, digestive, and antiparasitic benefits.
Cucumis melo var. cantalupensis, commonly known as rock melon, exhibits high provitamin A activity and may, therefore, prevent chronic inflammation. Rock melon pulp and peel extracts have also shown efficacy in preventing edema formation.
Cucurbitacin B from Cucumis melo var. Cantalupensis has demonstrated anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic activities against lung cancer cells by inhibiting inflammatory processes.
Cucumis melo var. reticulatus or Galia melon is a rich source of phenolic compounds, flavonoids, minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and essential amino acids.
Cucumis melo L. inodorus is a rich source of vital nutrients and minerals, such as magnesium, potassium, iron, vitamins C, A, and B6, calcium, pantothenic acid, omega-3, omega-6, and zinc. Some varieties of this melon have been shown to effectively manage insulin resistance and adipose tissue inflammation, as well as protect the cardiovascular system.
Health properties of Momordica charantia
Momordica charantia, which is a bitter melon, is a rich source of proteins, carbohydrates, dietary fibers, vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds like gallic acid, tannic acid, catechin, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, and benzoic acid.
Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase (BG-4) extracted from Momordica charantia seeds is associated with strong trypsin-inhibiting and anti-inflammatory activities, particularly in the context of impaired glucose metabolism.
Phenolic compounds present in Momordica charantia can exert anti-diabetic effects by inhibiting intestinal carbohydrate absorption, stimulating insulin secretion, and protecting the islets of Langerhans from degradation. In fact, a novel insulin receptor-binding protein isolated from Momordica charantia exhibits gastric resistance and hypoglycemic activities.
Momordica charantia extracts have shown antibacterial activity against K. pneumoniae and B. licheniformis, with water extracts showing stronger activity than ethanolic extracts.
Among variations of Momordica charantia, previous studies have reported the antibacterial activity of var. muricata against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Micrococcus luteus, and Staphylococcus aureus, whereas var. charantia has shown antibacterial activity against S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli.
Momordica charantia extracts have shown anticancer activity against breast, lung, and colon cancer cells. In ovarian cancer, Momordica charantia extracts elicit anti-proliferative, anti-metastatic, and pro-apoptotic effects through its protein kinase-activating activity.
Momordica dioica is a rich source of many bioactive compounds, fats, carbohydrates, and dietary fibers. Previously, Momordica dioica has demonstrated anticancer activities against ovarian and cervical cancers. In fact, the purification and isolation Momordica dioica proteins have supported recent advancements in peptide-based drug delivery.
Journal reference:
- Romo-Tovar, J., Cerda, R. B., Chavez-Gonzalez, M. L., et al. (2024). Importance of Certain Varieties of Cucurbits in Enhancing Health: A Review. Foods. doi:10.3390/foods13081142