Lidocaine is a widely used local anesthetic and anti-arrhythmic drug with an immediate onset of action. Lidocaine is used topically to alleviate the burning, itching, and pain caused by skin inflammations. It is also used as an anesthetic in dentistry and minor surgeries. Oral gels containing lidocaine are applied to relieve tooth pain.
Lidocaine
Figure 1 shows a 90 MHz proton spectrum for lidocaine dissolved in CDCl3. The resonances are all well resolved and the only 1H-1H proton coupling is that linked to the ethyl group.
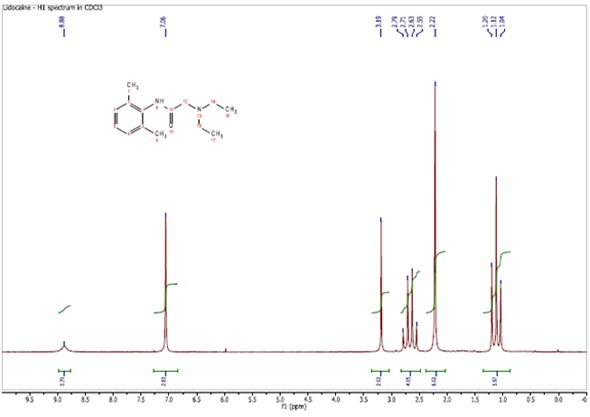
Figure 1. Proton spectrum of Lidocaine in CDCl3
C13 Spectra of Lidocaine
It took around two minutes to acquire each of the two 13C spectra shown in Figure 2. The top spectrum shows lidocaine dissolved in CDCl3 and the bottom spectrum shows lidocaine dissolved in H2O. All of the peaks are well resolved and even the solvent triplet at 77 ppm is clear in the top spectrum.
The peaks in the top spectrum are easily assigned in the following manner (from left to right):
C10:170.1 ppm, C2,3:135 ppm, C1:134.1 ppm, C4,5 :128.1 ppm, C6:126.9 ppm, C12:57.5 ppm, C 14,15:50.7 ppm, C 7,8:18.5 ppm, C 16,17:12.6 ppm.
Although the majority of the peaks in the two spectra are alike, the main difference lies in the peaks associated with the benzene ring.
In the bottom spectrum, the effects of hydrogen bonding are clear. Although the evidence is not completely clear, the following assignments can be made based on the hydrogen bond theory:
C2,3:136.3 ppm, C1:132.9 ppm, C 4,5,6:128.9 ppm.
The hydrogen bonding of H2O to the NH (9) and the carbonyl would be expected to cause a certain amount of deshielding.
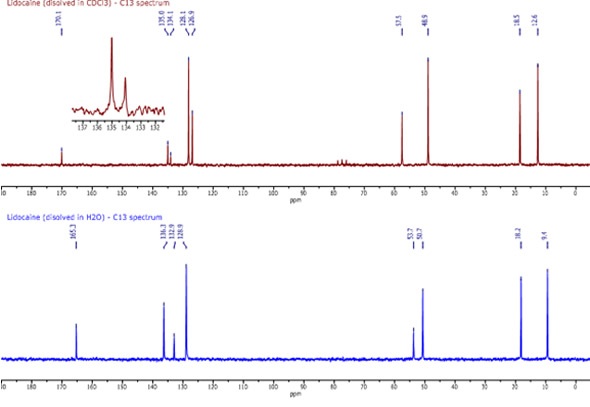
Figure 2. C13 spectra of lidocaine in CDCl3 (top) and H2O (bottom)
Distortionless Enhancement via Polarization Transfer (DEPT)
The preferred polarization transfer sequence for spectral editing is the 13C DEPT experiment. The EFT spectrometer uses three DEPT experiments to differentiate between methyne, methylene, methyl and quaternary groups in a number of compounds.
The 13C DEPT experiment used in the spectrometers generates the DEPT45, DEPT90 and DEPT135 spectra, which are collected in a single data set and automatically processed using the NUTS software program. Single experiments such as the attached proton test (APT) and the DEPT135 are also available.
The peak assignments made in the C13 spectra above are confirmed in the below example (figure 3).
In all three experiments, any carbon missing a directly attached proton does not generate a signal. Here, the carbonyl and the substituted sites on the benzene ring are quenched. The two resonances near 130 ppm were confirmed as CH. Similarly, the two peaks pointing down in the DEPT135 spectrum and situated near 50-60 ppm were confirmed as CH2 and both peaks on the far right were CH3.
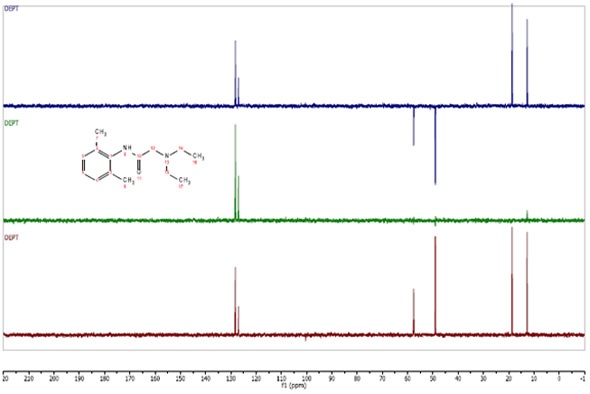
Figure 3. C13 DEPT spectra of Lidocaine in CDCl3
Heteronuclear Correlation
Although the Heteronuclear Correlation (HETCOR) experiment is similar to the Correlation Spectroscopy (COSY) experiment, it does focus on the coupling between two different kinds of nuclei. The HECTOR technique is generally used to correlate proton resonances with those of directly bonded carbon-13 or other nuclei. The axes of the contour plot reflect the proton and the X-nucleus chemical shift ranges. The signals are generated at coordinates that correspond to the shifts of bonded nuclei pairs.
Signals of X-nucleus rather than those of protons are detected in this experiment. Long range coupling data (couplings between proton and X-nucleus via 2-3 bonds), can be obtained by altering the delays in HETCOR.
In figure 4, the spectra of lidocaine dissolved in CDCl3 are shown in maroon and the spectra of lidocaine dissolved in H2O are shown in green. These spectra are superimposed to demonstrate the difference between them, which became clear in the two C13 spectra.
The outcomes of the HETCOR strengthens the assignments made in the C13 spectrum of lidocaine in H2O. The peaks at 136.3 ppm and 132.9 ppm show that the two resonances are not associated with any directly attached protons.
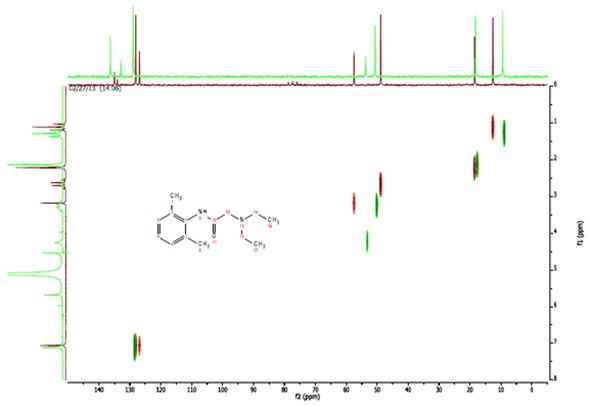
Figure 4. C13-H1 Heteronuclear Correlation (HETCOR) of Lidocaine in CDCl3 (maroon) and H2O (green)
About Anasazi Instruments
 Anasazi Instruments has been providing high quality, rugged, easy-to-use 60 and 90 MHz NMR spectrometers and upgrades to the educational and industrial markets. These instruments have been successfully implemented at hundreds or institutions ranging from large companies and top-tier universities to community colleges throughout North and South America. In research environments, the Eft is a cost-effective workhorse for synthetic and analytical laboratories.
Anasazi Instruments has been providing high quality, rugged, easy-to-use 60 and 90 MHz NMR spectrometers and upgrades to the educational and industrial markets. These instruments have been successfully implemented at hundreds or institutions ranging from large companies and top-tier universities to community colleges throughout North and South America. In research environments, the Eft is a cost-effective workhorse for synthetic and analytical laboratories.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.