Polymeric microspheres play a pivotal role in advancing high-potency therapeutics, offering controlled release capabilities.
Significant progress in biotechnology and combinatorial chemistry has spurred numerous breakthroughs in drug discovery, emphasizing increased potency. However, harnessing the higher efficacy, safety, and selectivity of these potent therapeutics demands meticulous attention to the delivery system.
Utilizing drug-loaded microspheres composed of biodegradable polymers is paramount for sustained-release systems, enhancing the safety and efficacy of novel therapeutics.
Extensive research supports the novelty of pharmaceutical microspheres. Comprehensive release studies on biocompatible, depot-injectable microspheres have showcased their bioavailability and sustained release capacity over extended durations.
Furthermore, their significant commercial potential is evident, with the global drug delivery market projected to reach a valuation of $1,733 billion by 2026.
Given the extraordinary potential of microspheres as drug delivery systems (DDS) and their far-reaching applicability, it is no surprise that various formulation methods have arisen over time. This article will delve deeper into how microsphere formulation works.

Image Credit: Powder Systems
Which methods are used to prepare microspheres?
Polymeric microsphere formulation includes a selection of methods, such as evaporation, spray drying, and coacervation. Each of these synthesis routes allows for relatively good control of individual particle size and bulk particle size distribution (PSD), as well as other central physicochemical properties, which are crucial performance parameters.
This article will outline several methods of microsphere formulation, providing a general overview of some of the most commonly employed techniques. It is important to note that this is not an exhaustive list but rather a brief insight into some of the available methods.
Solvent evaporation is arguably the most common method of microsphere formulation, and this is due to its relative simplicity. A solution of biodegradable polymeric materials is dissolved in an immiscible, organic solvent and agitated.
Emulsification is an example of this method where the polymerization of a combination of monomers is induced in an aqueous surfactant containing an initiator. High-speed rotation is needed to ensure the emulsion reaches a single phase. Emulsifiers are then added for stabilization. It is notable to point out that this technique produces very small particles with a high yield.
Phase separation, or coacervation, is another commonly used method. This technique involves the liquid-liquid phase separation of a homogenous solution, often a polymeric solute dissolved in a volatile solvent.
A coacervating agent is then introduced to initiate separation; subsequently, the polymer aggregates are solidified. Key properties governing microsphere formation, such as size distribution and particle size, are contingent upon molecular interactions among various components.
Another method of microsphere formulation is spray drying, which entails atomizing a solvent containing the dissolved polymer under high pressure. This process generates an extremely fine spray that is quickly dried to produce spherical particles.
While this method is generally straightforward to scale up, it presents challenges in achieving the precise levels of polydispersity necessary for pharmaceutical-grade microspheres, thus requiring additional time for post-processing steps such as sieving and washing.
Typically, some degree of processing is needed after the initial microsphere formulation. One persistent challenge in conventional manufacturing is how to optimize yield and batch reproducibility while minimizing product transfers.
Microsphere preparation: What happens next?
Following preparation, microsphere production moves to downstream processing to be harvested. This multi-step process is complex and often includes de-watering, product washing, drying, and, in some situations, further blending and freeze-drying.
Product transfer via manual handling is involved in several of these stages. This is a time-consuming step slowed by limits to scalability, high investment costs, and relatively low yields.
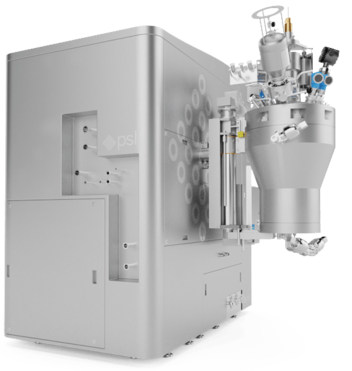
Image Credit: Powder Systems
Powder Systems Limited has developed a novel method of downstream processing that refines the multi-stage process to a single instrument. The Microsphere Refiner (MSR) is an innovative, automated solution with predictive scale-up to the kilogram level offering a high product yield. This enables users to optimize batch reproducibility and streamline production.
About Powder Systems 
Powder Systems Limited (PSL) provides a full range of solid liquid separation solutions for filtration, drying, and processing from research and development activities up to larger commercial production scale.
Quality and innovation are central to everything they do. They are proud of their award-winning track record and have been working with industry partners for over 35 years.
PSL supports clients by developing solutions to overcome challenging manufacturing processes and provide first-class aftercare services.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.