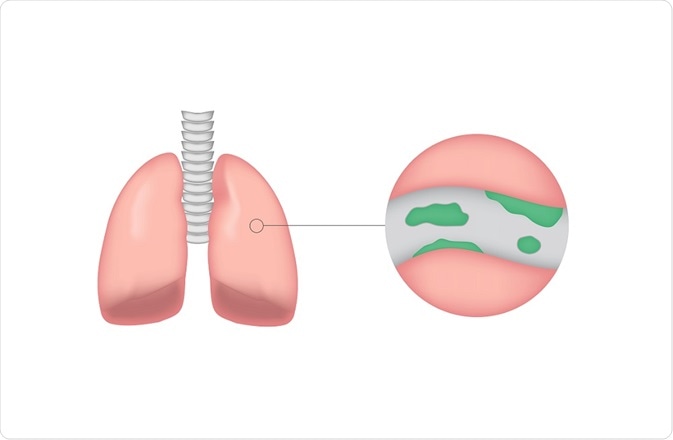
Bronchiectasis is a condition in which the lung’s airways (bronchi) are dilated, causing an accumulation of mucus. This, in turn, makes the patient more vulnerable to infection, which can cause permanent damage. Most affected patients are middle-aged.
 Joshya | Shutterstock
Joshya | Shutterstock
Treating bronchiectasis
It is recommended that people with bronchiectasis avoid close contact with people suffering from colds or the flu, to reduce the risk of contracting an infection. Other health and lifestyle changes that may relieve the symptoms of bronchiectasis are:
- Stopping smoking
- Getting vaccinated against the flu and pneumococcal infection annually
- Exercising regularly
- Staying hydrated
- Ensuring a balanced diet
Breathing exercises under the instruction of a trained physiotherapist, using corrective breathing apparatus, and taking medications that relax the airways and thin the mucus are also recommended. Surgery can be helpful but is only carried out in very rare instances.
Prognosis for bronchiectasis
The incidence rates of bronchiectasis have been reported to be 52 out of 100,000; however, data varies. Most people with the condition have a normal life expectancy, however, severe bronchiectasis can prove fatal if the lungs are unable to work normally. Lung failure can be caused by the condition itself or as a complication of infection.
Bronchiectasis complications
Infective exacerbation
People with bronchiectasis can develop severe lung infections that require immediate medical attention. In this condition the cough becomes worse, with more phlegm which may smell foul or be greener than before. Breathing difficulty may also worsen. Chest pain while breathing is another sign of infection, as is hemoptysis and a feeling of illness.
The symptoms of a severe lung infection include:
- Cyanosis (blue skin and lips)
- Confusion
- A temperature of 100.4F (38C) or above
- Rapid breathing (more than 25 breaths per minute)
- Severe chest pain that makes it hard to cough
Massive hemoptysis
Hemoptysis is the term used to describe coughing up blood. Massive hemoptysis is caused by the bursting of a large blood vessel that supplies the lungs and and is classed as a medical emergency.
The symptoms of massive hemoptysis include:
- Coughing up more than 100 ml of blood in 24 hours
- Difficulty breathing
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Having cold and clammy skin
To stop the bleeding, bronchial artery embolization (BAE) is required. In this procedure, an X-ray of the arteries is taken after first injecting a contrast dye. Dye leakage indicates the source of the bleeding, and tiny particles are then injected to plug the hole and stop the bleeding.
Respiratory failure
Respiratory failure describes a lack of oxygen from the lungs to the blood, and a lack of waste (carbon dioxide) removal.
Symptoms of respiratory failure include shortness of breath, quick breathing, and air hunger (when a person feels as though they can’t take in enough air). Acute respiratory failure requires emergency medical attention whereas chronic respiratory failure has a much slower onset and can be treated at home.
Non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM)
Non-tuberculous mycobacteria are naturally occurring organisms. They are usually found in water and soil. When someone inhales NTM, they may develop a chronic, progressive infection that requires treatment with a long course of antibiotics. Most people who inhale NTM do not contract an infection, but susceptible individuals have a higher risk.
The prevalence of NTM in people with bronchiectasis is not well understood, but studies suggest that it may be an underlying cause of bronchiectasi or a complication of existing bronchiectasis.
Atelectasis
Atelectasis is a condition in which part of the lung collapses or is unable to expand properly. This causes reduced delivery of oxygen to the blood. It may not cause symptoms if the collapse is restricted to a small portion of collapse. However, if collapse occurs in larger areas of the lung, symptoms may include wheezing, fever, coughing, and shallow breathing. If left untreated, atelectasis can lead to a build-up of fluid, pneumonia or respiratory failure.
Heart failure
The symptoms of heart failure include shortness of breath, tiredness, swollen ankles, feet, legs, as well as swelling in the abdomen and the veins in the neck. In heart failure, the heart is unable to pump.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jan 10, 2019