Ear cancer most often develops in the outer skin of the ear, though there are a few cases of cancer found in the inner ear.
BLACKDAY | Shutterstock
Melanomas and carcinomas are the tw types of cancer that affect the ear. Squamous cell carcinomas that arise in the outer region of the ear are more common, but basal cell carcinomas and malignant melanomas in the inner or middle ear can also occur.
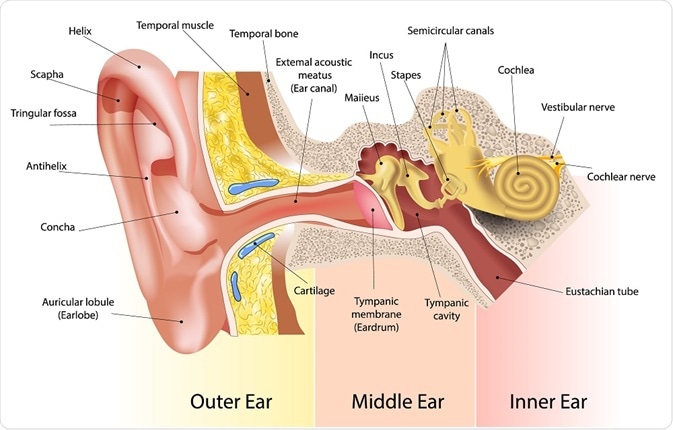
The ear comprises of outer, middle and inner comparments. The middle ear is a tiny cavity with three little bones which allow vibrations to pass from the eardrum up to the inner ear. The inner ear comprises of fluid and the cochlea which contains stereocilia - tiny hairs that vibrate, creating sound.
The minute nerves present in the cochlea convert vibrations into impulses, which then travel up to the brain. The cavities in the inner ear are filled with fluid that helps in maintaining balance.
SVETLANA VERBINSKAYA | Shutterstock
What are the symptoms of outer ear cancer?
Around 5% of skin cancers develop on the ear, and these are typically found on the outer skin. An inflamed spot or sore that persists for more than 4 weeks is the primary symptom for outer ear cancer.
Sores that bleed or become ulcers could be some early signs of cancer. Moles that show changes such as growth, itchiness, and bleeding must be examined. Tumors in the ear may be benign or malignant as in squamous cell cancer. The growth of these tumors is often slow, thus patients are commonly diagnosed early and respond well to treatment.
What are the symptoms of middle and inner ear cancer?
Inner ear cancers are very uncommon; according to researchers, less than one million people in the UK develop cancer in the middle ear. This is important, as the symptoms change depending on the location of the tumor in the ear.
Bloody discharge from the inner ear is the most common symptom for middle ear cancer, but other symptoms include:
- Inability to move the face on the affected side of ear
- Earache (pain) inside the ear
- Hearing loss
- Swelling in lymph nodes of the neck
- Headache
- Dizziness and light headedness
Compared to adults, children are more prone to ear infections. It is, therefore, necessary to have a specialist examine the nasopharynx in people who develop an ear infection for the first time.
What are the types of ear cancer and their symptoms?
Basal cell cancer:
- This type of cancer mostly develops over the face and then spreads to the ear. Ulcers appear as bead-edged and raised and do not heal for a very long time. The ulcer, which may appear to be hard with a crust, bleeds when touched.
- In other cases, ear cancer looks nodular and hard. Basal cell cancer which is aggressive can distort the whole outer ear. Cancers in the basal cell are different from others in that they do not metastasize, but are found to be locally spread and lead to damage to tissues.
Squamous cell cancers:
The structure of the cancer that appears in the squamous cell has the appearance of a cauliflower or as an ulcer. These ulcers are attached at the bottom to tissues. The cancer cells spread to the nearby lymph nodes, through blood, and may even extend to the temporal bone.
Malignant melanomas:
- These normally originate from an existing mole that changes from brown to black color and rapidly grows in size with an uneven border. It may also occur as a blistered ulcer.
- This cancer may expand to nearby tissues in the form of skip and satellite lesions surrounding the primary cancer. They also spread through the lymphatic system and the blood.
Adenoidcystic carcinomas:
- This cancer develops in the external ear canal. It is a rare cancer characterized by slow growth. Adenoid cystic carcinomas appear inappropriately located in the ear and originate from the sweat glands, tissues of salivary glands, and also from the gland secreting earwax.
- Hearing loss, weakness in facial muscles, tinnitus, and acute pain are some of the symptoms. The tissues grow abnormally, and ulcer and swelling may occur. Sometimes, blood or thick yellowish pus may ooze from the affected ear. This cancer may metastasize locally to the salivary glands, bone, lymph nodes, or soft tissues, or even to the distant liver and lung.
Ceruminous adenocarcinoma:
This is type of ear cancer that develops in the glands that secrete ear-wax. Symptoms include an earache and hearing problems like otalgia. The facial nerves are influenced in this type of cancer, leading to paralysis of the facial nerves.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Dec 4, 2018