What is cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis refers to the late stage of liver fibrosis. Long term liver damage results in the formation of scar tissue in place of the original cells. This leads to swelling, inflammation and compensated liver function. Late stage fibrosis cannot be reversed, but treatment can slow the progression of the disease and prevent further damage if it is caught early. However, after many years of chronic liver damage, advanced cirrhosis can lead to liver failure and be fatal.
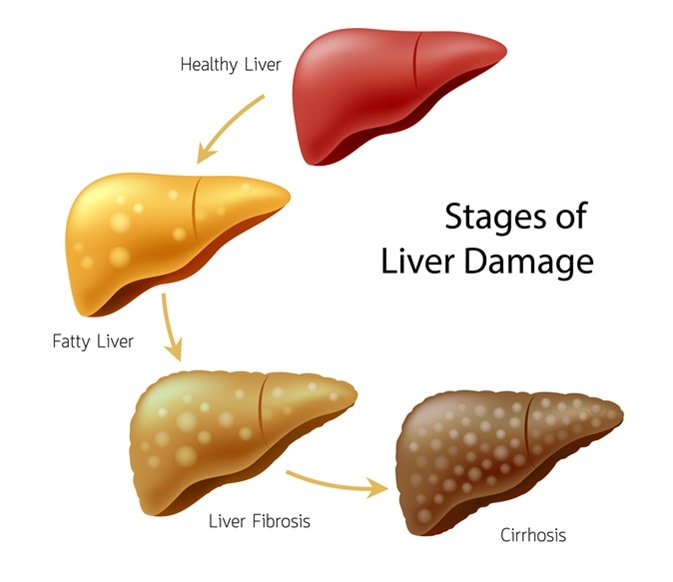
Stages of liver damage. Healthy, fatty, liver fibrosis and Cirrhosis. Image Credit: Shutterstock
What causes cirrhosis?
There are many conditions or diseases which lead to continuing long-term damage of liver tissue, resulting in cirrhosis. In some cases, there is more than one cause, but the most common causes in the United States include:
- Overindulgence in alcohol over many years
- Chronic infection with Hepatitis B or C
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or the more severe condition: non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Less common causes include:
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Diseases of the bile ducts including: primary biliary bholangitis/cirrhosis (PBC), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and biliary atresia (BA)
- Certain hereditary diseases which affect liver function, such as hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease and alpha-1- antitrypsin deficiency
- Budd-Chiari syndrome – a condition which blocks the blood vessels draining the liver
- Prolonged use of certain drugs, such as amiodarone and methotrexate
- Long-term contact with poisons
Silent Killer: Identifying Liver Cirrhosis Before It's Too Late
Alcohol and cirrhosis
Alcohol abuse, referring to both social binge drinking and alcoholism, is one of the leading causes of cirrhosis in the United States. There are three stages in which alcohol-related cirrhosis develops:
- Fatty liver: 90% of people who drink excessively will develop a “fatty liver” as a side-effect of alcohol break down. This is reversible with abstinence.
- Alcoholic hepatitis: 20-30% of those who drink heavily over a prolonged period will develop an inflamed liver. If alcohol consumption is not reduced, it can be life-threatening and lead to liver failure.
- Cirrhosis: In 10% of individual, chronic alcoholic hepatitis can lead to the end stage of irreversible liver damage.
It is undetermined what levels of alcohol over the years lead to this chronic end-stage fibrosis, as it differs between individuals. Not all heavy drinkers develop cirrhosis, whilst some moderate drinkers do. However, it is clear that excessive drinking for 10 or more years increases the risk. Some individuals are also more susceptible than others; for example, women who drink heavily are at a higher risk than men.
Hepatitis and cirrhosis
Chronic hepatitis C results in inflammation of the liver. If left untreated it causes long-term, ongoing damage to the liver and can lead to cirrhosis. 25% of those infected with hepatitis C will develop cirrhosis after many years with the infection. Hepatitis B and D are two other types of hepatitis which can also lead to liver disease. The common route of transmission for these viruses is through contact with contaminated blood or blood products, for example via unprotected sex or sharing dirty needles.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and cirrhosis
Much like alcohol-related liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) presents as a build-up of fatty tissue in the liver. As the disease progresses, it results in severe inflammation and scarring of the liver, leading to cirrhosis. Obesity, diabetes and high triglyceride or cholesterol in the blood are the main risk factors for this condition. However, the disease has very few symptoms and may go unnoticed until cirrhosis develops. The rising levels of obesity in the US mean that NASH may soon overtake alcohol and hepatitis as the prevailing cause of cirrhosis.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Mar 18, 2019