Mar 1 2018
A new study conducted by researchers from the University of Bath provides insights into a key protein associated with brain diseases including ALS (motor neurone disease) and dementia. The study observed the ways by which it enters central nervous system cells. The study findings are published in the journal PLOS ONE.
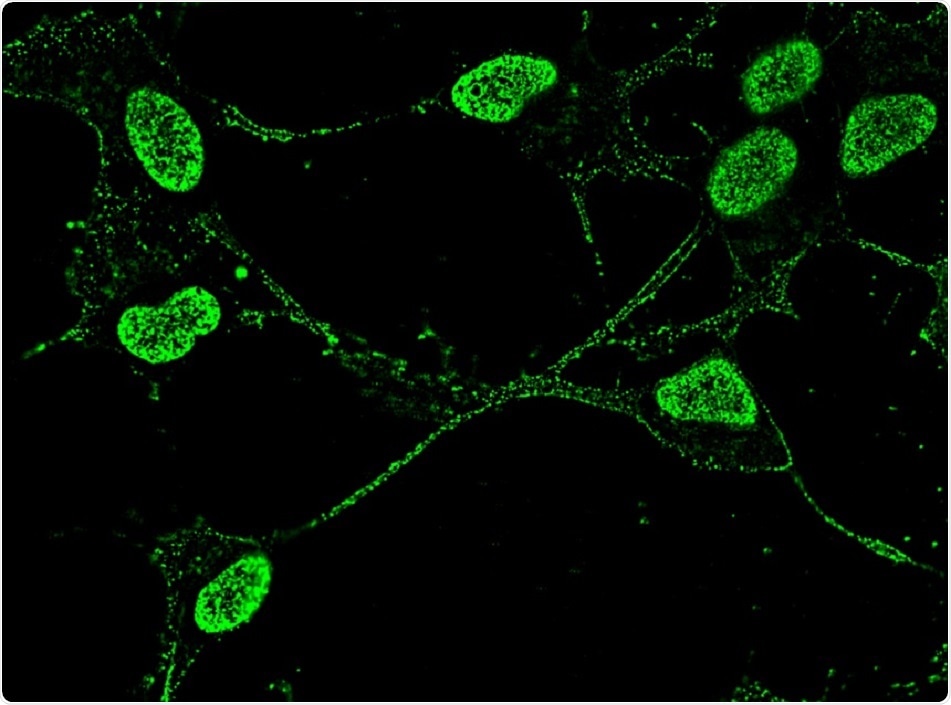
Neuronal cell line showing Angiogenin (green) in the nucleus and in the neurite outgrowths. Credit: Univeristy of Bath
Researchers from the Department of Biology & Biochemistry examined the workings of angiogenin–a protein which crosses into cells and is transported to the cell nucleus.
The protein plays a significant role in developing and safeguarding healthy brains, in growing blood vessels, and in the regeneration of blood stem cells.
However, mutated angiogenin is associated with the brain disease Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neurone disease or Lou Gehrig's disease, and a form of dementia called Fronto-temporal dementia (FTD).
In order to track the protein’s pathway into several types of central nervous system cells, researchers carried out a series of in vitro experiments under various biochemical conditions. The key findings showed that angiogenin uptake into these cells followed more than one biochemical pathway, which is considered to be more complex than previously suspected by the researchers.
Ultimately understanding the precise function of this protein is really important, and understanding how cells take it up is a critical part of that. We discovered that angiogenin is taken up into cells by more than one mechanism which is quite a surprise."
Dr Vasanta Subramanian,University of Bath
Dr Subramanian concluded that arriving at a comprehensive understanding of this proteins application in neurological disease treatment will be challenging, but its participation in multipe crucial biological processes mean it is worth the effort.