Animals that develop epilepsy after an infection can be identified as early as three months prior to their first seizure by measuring interactions between the brain and the heart, according to new research using a mouse model of post-cerebral epilepsy. Published in JNeurosci, this finding could inform efforts to diagnose and treat acquired epilepsy.
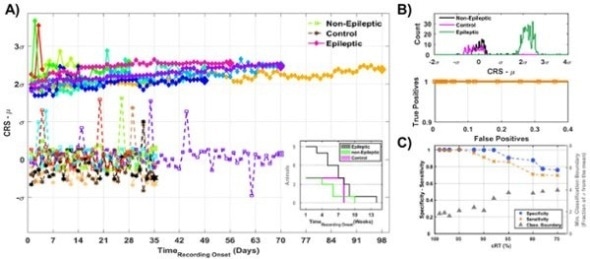
Cerebral malaria afflicts more than three million people worldwide, affects young children, and leads to epilepsy in an estimated 15 percent of survivors. Reducing the risk of developing epilepsy and associated fatal complications, such as sudden unexplained death in epilepsy, requires a reliable way to detect and monitor epileptogenesis.
By recording neural and cardiac activity in a mouse model of cerebral malaria, Fatemeh Bahari, Bruce Gluckman and colleagues discovered a signal transmitted between the brain and the heart that occurred only in the 75 percent of mice that acquired epilepsy. Translating this biomarker to humans has the potential to improve therapeutic approaches in patients at risk of developing epilepsy, such as those recovering from traumatic brain injury or stroke.