Obesity leads to cognitive impairment by activating microglial cells, which consume otherwise functional synapses in the hippocampus, according to a study of male mice published in JNeurosci. The research suggests that microglia may be a potential therapeutic target for one of the lesser known effects of this global health epidemic on the brain.
Nearly two billion adults worldwide are overweight, more than 600 million of whom are obese. In addition to increasing risk of conditions such as diabetes and heart disease, obesity is also a known risk factor for cognitive disorders including Alzheimer’s disease. The cellular mechanisms that contribute to cognitive decline in obesity, however, are not well understood.
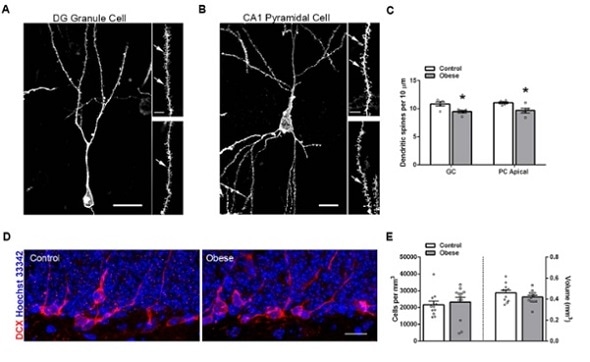
Elise Cope and colleagues replicated previous research by demonstrating diet-induced obesity in mice impairs performance on cognitive tasks dependent on the hippocampus and results in loss of dendritic spines — the neuronal protrusions that receive signals from other cells — and activates microglia.
Using genetic and pharmacological approaches to block microglial activity, the researchers established microglia are causally linked to obesity-induced dendritic spine loss and cognitive decline. The results suggest obesity may drive microglia into a synapse-eating frenzy that contributes to the cognitive deficits observed in this condition.