The right hemisphere of the brain can take over language functions when the left hemisphere is damaged early in development, according to research in four-year-old children published in eNeuro. These findings offer insight into typical language development in children and the flexibility of the brain in response to injury.
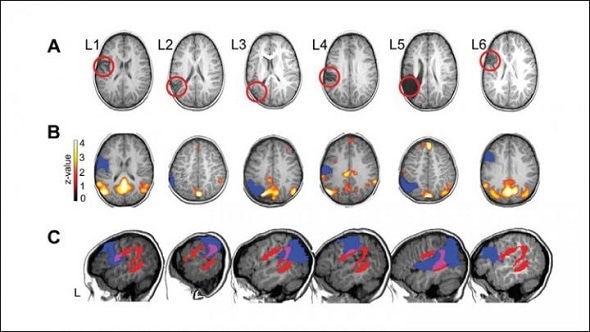
Language functions are typically localized in the left hemisphere of the brain, a distinction that is present at birth but becomes more pronounced during development. Damage to the language regions of the left hemisphere often causes speech aphasia, which does not generally happen in child stroke patients.
In order to study the flexibility of language development, Clément François and colleagues at the University of Barcelona compared the brains and language skills of healthy children with children that had a left-hemisphere stroke as infants. Using magnetic resonance imaging, the research team observed that the arcuate fasciculus, a brain region involved in language, had a greater volume in the right hemisphere and a lower volume in the left hemisphere in the stroke patients. Among the stroke patients, the children with the largest right volume performed best on language tests.
Source:
Journal reference:
François, C. et al. (2019) Right structural and functional reorganization in 4-year-old children with perinatal arterial ischemic stroke predict language production. eNeuro. doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0447-18.2019.