The new function of unused brain regions is not restricted by the function of nearby regions, according to new research in adults born with one hand published in JNeurosci.
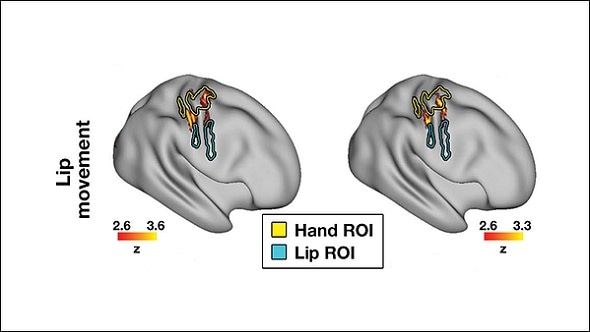
Sensory and motor functions for each body part are mapped onto the brain in a “body map”, which is often reconfigured following the loss of a sense or body part. Previous research on remapping has been inconclusive, but the leading idea is that neighboring regions take over the unused region.
Using functional magnetic resonance imaging, Hahamy and Makin measured the brain activity of adults born without one hand when they moved their arms, feet, lips, and intact hand.
Both the cerebellum and the cortex displayed activation during arm, foot, and lip movement, even though those body parts were mapped differently in either region. Only the arm region neighbors the unused hand region, meaning that cortical location is not the only factor that determines remapping.
In light of this new knowledge, the research team thinks that the remapping process begins upstream in the putamen, an area involved in planning movement. Additionally, the body parts that the participants use to compensate for the missing hand in everyday life might influence the remapping.
Source:
Journal reference:
Hahamy, A., et al. (2019) Remapping in cerebral and cerebellar cortices is not restricted by somatotopy. Journal of Neuroscience. doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2599-18.2019.