Researchers in Canada and the United States report that screening students for infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as universities re-open this fall could reduce the burden of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the broader community.
The team conducted a model-based analysis to estimate the impact that the return of a relatively large student population would have on the rate of COVID-19 infections in a mid-sized city, where the number of cases was relatively few, prior to students returning.
Lauren Cipriano (University of Western Ontario) and colleagues from the London Health Sciences Centre and the University of Minnesota School of Public Health say the findings suggest that the return of such a student population would significantly increase the number of COVID-19 cases in the community.
The study also suggests that routine testing of students would prevent the number of infections in this population and provide significant public health benefits by reducing the number of infections, admissions to critical care, and COVID-19-related deaths in the community.
“Our analysis is relevant to a number of mid-sized cities in North America with relatively large university and college population,” writes the team.
The researchers say the estimated increase in COVID-19 infections following the reintroduction of students is due to the higher number of contacts this group has compared with the general population, their high-density living environments, and relatively high rates of asymptomatic infection.
A pre-print version of the paper is available on the server medRxiv*, while the article undergoes peer review.
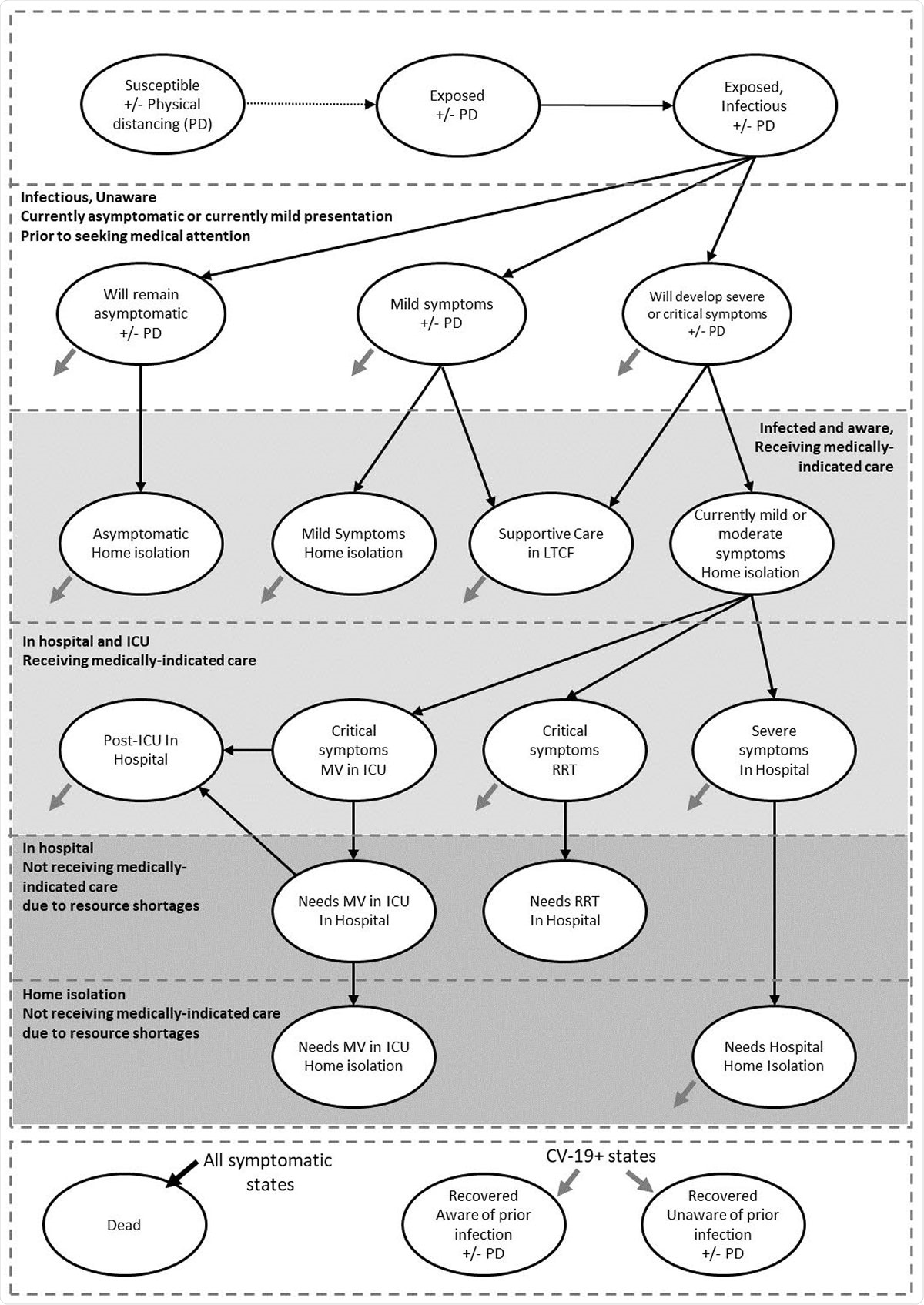
Model schematics of (A) COVID-19 health states and (B) close contact interactions between population subgroups. The number of contacts between groups indicated on the schematic represent the average number of contacts per day in a pre-COVID-19 era.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Potential for spillover from campuses to the broader community
The unprecedented infectivity and spread of SARS-CoV-2 presents substantial public health challenges to local, national, and international communities trying to bring the COVID-19 pandemic under control.
In many communities, one initial measure that was introduced was the closure of university campuses. Over the summer, many universities announced plans to partially or fully re-open campuses and welcome students back with mitigation strategies in place, such as mask-wearing, restricted gatherings, and COVID-19 testing.
“University students live, work, and socialize both on and off-campus, resulting in significant potential for on-campus COVID-19 outbreaks to spill over into the community and vice versa,” said Cipriano and team. “It is therefore important to quantify the expected impact of the arrival of a relatively large number of university students on the broader community.”
What did the researchers do?
Cipriano and team developed a dynamic transmission model of COVID-19 to assess the impact of an outbreak on the community in a representative mid-sized city with a relatively large college campus and with relatively few cases of COVID-19 before students returned.
The team calibrated the model to the observed outcomes in a mid-sized Canadian city between March 1 and August 15, 2020 (before the arrival of a student population), and evaluated the impact of introducing 20,000 students (on September 1) on COVID-19 health outcomes.
The researchers considered multiple scenarios with different infection prevention behaviors, as well as the mitigating effects of different COVID-19 screening strategies among students.
The return of students substantially increased infections in the community
In a city that initially had a relatively low rate of COVID-19 cases, the return of the student population significantly increased the overall number of infections in the community, potentially doubling the number of infections in the city over the fall.
In a scenario where students immediately reduced their contact behavior by 24% compared with pre-COVID-19 levels, the total number of infections in the community increased by 87%, from 3,900 to 7,299.
Notably, more than two-thirds (71%) of the incremental infections occurred in the general population, which increased COVID-19 mortality in the community and accelerated the need to re-engage social and economic restrictions by 3 weeks.
In a scenario where the researchers considered initial, short-term increases in the number of student-to-student contacts, a higher level of contact for just one or two weeks increased the total number of infections in the community by 150% or more.
Routine screening of students benefits the community
In such scenarios, routine screening of asymptomatic students every 5 days reduced the number of infections attributable to the introduction of the students by 42%. It delayed the need for re-engagement of social and economic restrictions by 1 week.
Alternatively, one-time universal screening of students prevented fewer infections than screening every 5 days but was highly effective in terms of infections prevented per screening test performed.
The researchers say that high-density living environments, enthusiasm for the new school year, and relatively high rates of asymptomatic presentation may decrease self-protective behaviors among university students and contribute to increased numbers of COVID-19 among the city community.
“Screening targeted at this population provides significant public health benefits to the community through averted infections, critical care admissions, and COVID-19 deaths,” concludes the team.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources