The United States has reported the highest number of coronavirus disease cases (COVID-19), with more than 6.88 million infections since the start of the pandemic. Now, eight months into the pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports a decreasing percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for the virus.
Despite declining positive respiratory specimens, the death rate tied to COVID-19 remains above the epidemic threshold.
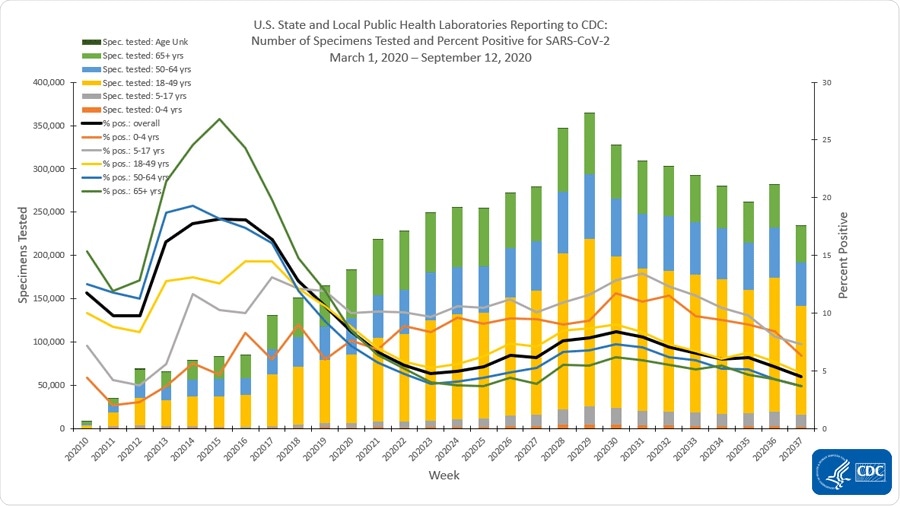
Declining COVID-19 positive specimens
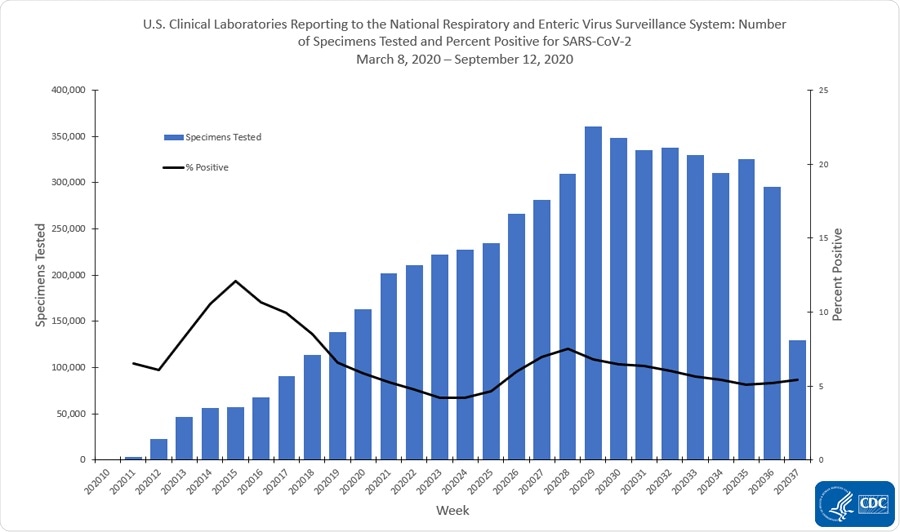
Overall, the report says that the percentage of respiratory specimens that test positive for the virus has decreased from 5.2 percent during the 36th week to 4.8 percent on week 37 of the pandemic in the country.
Based on the report, public health laboratories report a decline from 5.4 percent to 4.5 percent. Clinical laboratories report a decline from 5.2 percent to 5.4 percent, and commercial laboratories said there is a decrease from 5.2 percent to 4.8 percent during the said weeks.
Tracking COVID-19 emergency department visits
Amid the coronavirus pandemic, the United States has established two surveillance networks to track outpatient or emergency department (ED) visits for illness with symptoms linked to COVID-19.
The data gathered by the CDC shows that the percentage of visits due to influenza-like illness remained stable in the 37th week, compared with the previous week. Meanwhile, the percentage of visits for COVID-like illness declined for the ninth consecutive week, from 2 percent to 1.8 percent on week 37.
“Recent changes in healthcare-seeking behavior, including increasing use of telemedicine, recommendations to limit E.D. visits to severe illnesses, and increased social distancing, are likely affecting both networks, making it difficult to conclude at this time. Tracking these systems moving forward will give additional insight into illness related to COVID-19,” the CDC reports.
COVID hospitalizations and death
While most COVID-19 cases are mild to moderate, some people may need hospitalization due to severe symptoms. Nationally, the COVID-19 hospitalization rate was 170.4 per 100,000 people. In people who are more than 65 years old, the hospitalization rate was 460.7 per 100,000, followed by people who are between 50 and 64 years old, with a rate of 255.1 per 100,000.
However, between the 31st week and the 37th week, weekly hospitalization rates decreased for all age groups. Yet, in the same period, weekly rates remained stable for children and adolescents.
People from minorities, specifically non-Hispanic American India, Alaska Native persons, non-Hispanic Black people, and Hispanic or Latino persons, had hospitalization rates about 4.6 times that of non-Hispanic White people.
The percentage of deaths tied to pneumonia, flu, or COVID-19 for the 37th week was 6.2 percent, which is lower than that of week 36, 9.3 percent. However, the death rate is still above the epidemic threshold.
People with underlying health conditions are more likely to be hospitalized due to COVID-19. Of the 11,428 hospitalized adults, 90.3 percent had at least one reported underlying health condition, including hypertension, metabolic disease, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
Of the 371 hospitalized children, 49.1 percent had at least one underlying medical illness, including obesity, neurologic disease, and asthma.
COVID-19 global toll
Globally the SARS-CoV-2 virus has infected more than 31 million people and killing at least 967,000 people. The U.S. reports the highest death toll, with over 200,000 people succumbing to the infection.
Following the United States are India and Brazil, with more than 5.56million and 4.58 million cases, respectively.