By using a diverse set of transcriptomic SARS-CoV-2 signatures, US researchers put to use their previously developed drug repositioning pipeline to pinpoint potential drug candidates for the treatment of coronavirus disease (COVID-19). The study is currently available on the bioRxiv* preprint server.
While many efforts are currently underway to identify potential therapies targeting various aspects of COVID-19, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), there is still a lack of clinically proven approaches available in our armamentarium.
Drug repositioning is one of the approaches that has been extensively explored during this pandemic. More specifically, high-throughput screening pipelines have been put forth as viable strategies to test drug candidates as they are identified quickly.
A similar approach has been taken by a group of scientists led by Dr. Brian L. Le from the Department of Pediatrics and Bakar Computational Health Sciences Institute at the University of California San Francisco.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Appraising inhibitory effects
In this study, the researchers applied their existing computational drug repositioning pipeline to SARS-CoV-2 differential gene expression signatures derived from publicly available RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data. The transcriptomic data has been generated from distinct types of tissues, which means they could predict therapeutics for each signature and then combine the results.
"We utilized three independent gene expression signatures, each of which consisted of lists of differentially expressed genes between SARS-CoV-2 samples and their respective controls", study authors further explain their methodological approach in this bioRxiv paper.
Moreover, validity was confirmed by showing 16 of their drug hits' inhibitory effects, which could significantly reverse multiple SARS-CoV-2 profiles in live antiviral assays. Two types of cell lines were used: Calu-3 (human lung cell line) and kidney 293T cells overexpressing ACE2 (293T-ACE2 cells).
Finally, using a rank-based pattern-matching strategy based on the non-parametric and distribution-free Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic, the signatures were queried against drug profiles from Connectivity Map (CMap) – a resource that utilizes transcriptional expression data in probing relationships between diseases, cell physiology, and therapeutics.
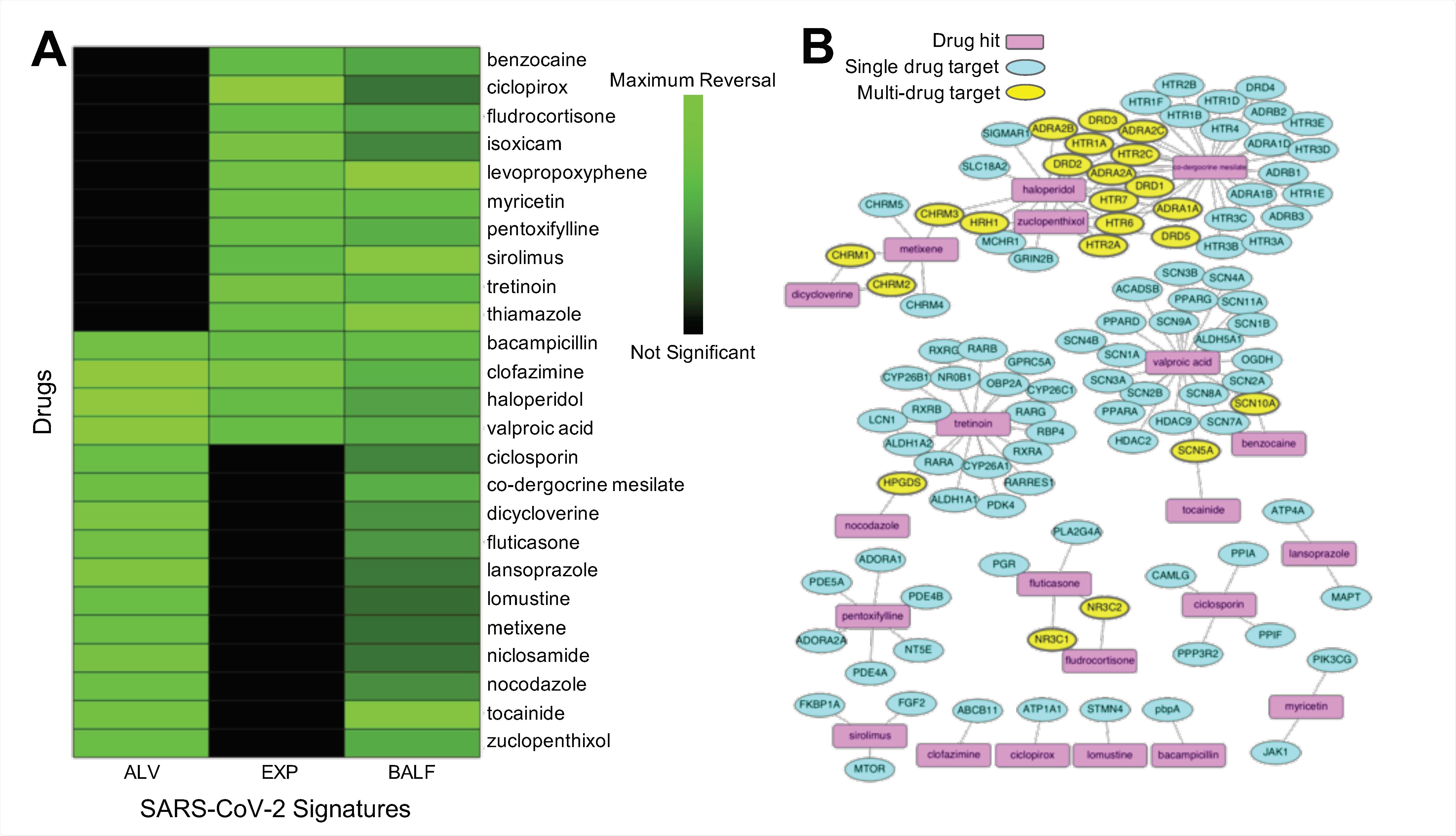
Twenty-five common drug hits were shared by at least two of the signatures (p = 0.0334), with four consensus drug hits (bacampicillin, clofazimine, haloperidol, valproic acid) across all three signatures (p = 0.0599) (A). Characterized common hits by examining interactions with proteins in humans. Known drug targets from DrugBank32 and predicted additional targets using the similarity ensemble approach (SEA)33. Visualized the known interactions from DrugBank in a network (Figure 3B)
Unveiling potential drug candidates
Overall, by utilizing a diverse set of transcriptomic SARS-CoV-2 signatures across two human cell line assays, the researchers identified 25 potential therapeutic candidates from 102 unique drug hits. Further validation experiments revealed SARS-CoV-2 antiviral activity for 11 of 16 drug hits.
After further refining these exciting results, it was shown that three of our four consensus drug hits demonstrated significant antiviral efficacy. More specifically, haloperidol showed reproducible inhibition in Calu-3 cells, while clofazimine and bacampicillin demonstrated inhibiting viral activity in 293T-ACE2 cells.
Several inhibitors showed micromolar to sub-micromolar antiviral efficacy, such as ciclosporin, ciclopirox, and metixene. The findings were also explored in the context of other computational drug repurposing efforts for COVID-19.
"These initial results are encouraging as we continue to work towards a further analysis of these predicted drugs as potential therapeutics for the treatment of COVID-19", say study authors.
The undeniable predictive power
This study confirms the power of these predictive methods and successfully identified different clinically-approved drugs with repurposing potential for the treatment of COVID-19 – many of which can be administered orally.
Hence, the diversity of found signatures and the overlap of highlighted drugs accentuates the utility of the current pipeline for unveiling drugs that have therapeutic effects for a wide array of SARS-CoV-2 infection effects.
Still, several limitations of this type of approach should be recognized. First and foremost, data generated from cell lines might not correctly represent the biological changes and manifold responses in human infection. Moreover, the drug profiles from CMap were generated from cell line data.
Encouraged by these initial results, future research endeavors on the topic should gather samples from a larger pool of patients to obtain a more robust gene expression signature and better inform any treatment predictions.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Le, B.L. et al. (2020). Transcriptomics-based drug repositioning pipeline identifies therapeutic candidates for COVID-19. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.23.352666, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.10.23.352666v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Le, Brian L., Gaia Andreoletti, Tomiko Oskotsky, Albert Vallejo-Gracia, Romel Rosales, Katharine Yu, Idit Kosti, et al. 2021. “Transcriptomics-Based Drug Repositioning Pipeline Identifies Therapeutic Candidates for COVID-19.” Scientific Reports 11 (1): 12310. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91625-1. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-91625-1.