The total confirmed cases of COVID-19 around the world, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), now stands at over 54.82 million infections, with over 1.32 million deaths and 35.21 million recoveries (as of November 16, 2020).
Nonetheless, a precise assessment of the COVID-19 burden has been hindered by the lack of comprehensive data on the disease and the benefits and harms of the measures implemented against it. Moreover, cause-specific death rates can be prone to bias, particularly for a disease with a high asymptomatic burden and testing/reporting differences.
Hence, all-cause mortality trends may give us a much more reliable alternative for appraising the burden of an epidemic in different countries and regions, as well as national strategies that can differ substantially.
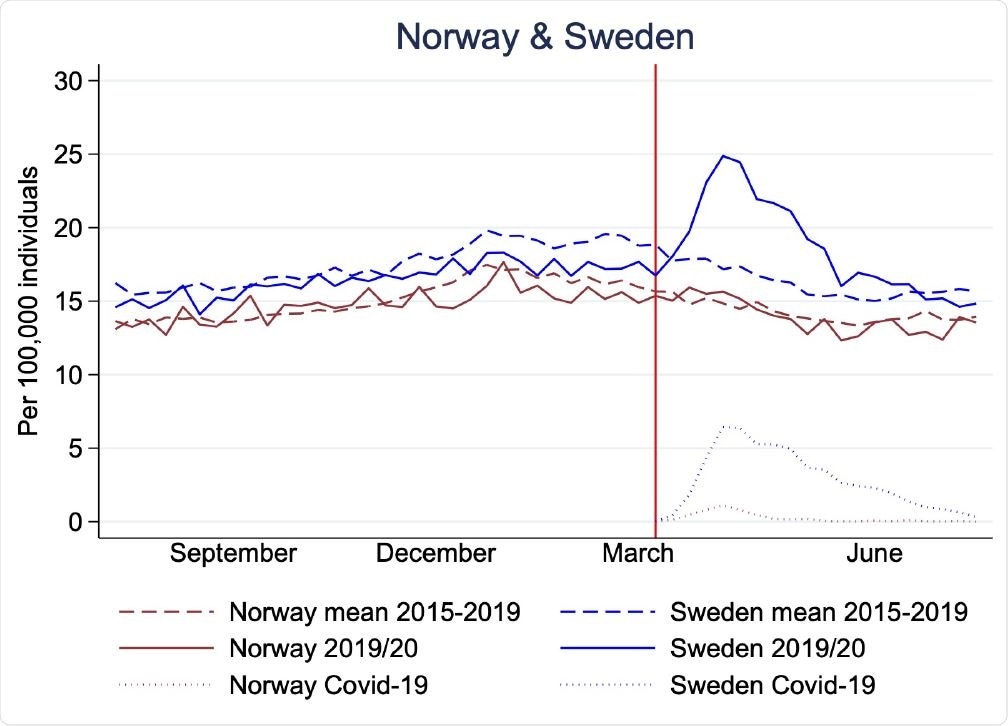
Mortality rates per 100,000 individuals in Norway (brown) and Sweden (blue) for 29th July, 2019 to 26th July, 2020 (solid lines), mean 2015-2019* (dashed lines), and Covid-19 associated mortality rates (dotted). Red vertical line shows the time point for the Covid-19 outbreak in Norway and Sweden (11th and 12th March).
A tale of two neighboring countries
Norway and Sweden are kindred countries in regards to ethnicity, administrative systems, socioeconomics, and public health care systems. Furthermore, both have reliable, stringent, timely, and comprehensive registration of deaths.
In the fight against COVID-19, Norway implemented harsh and extensive measures (such as lock-downs and school closures) and reported lower burden of severe cases and few COVID-19 associated deaths. Conversely, Sweden had a much less intrusive strategy but has been criticized for reporting more COVID-19 associated disease and deaths.
In Sweden, however, mortality was overall lower than expected in the months preceding the epidemic. This sets the stage for a natural experiment and opens the door for specific difference-in-difference analyses.
The opportunity was embraced by researchers from Norway and Sweden, led by Dr. Frederik E Juul from the Clinical Effectiveness Research Group at the Oslo University Hospital and the University of Oslo. They decided to dive deep into data and compare the effect of different national strategies on all-cause and COVID-19 associated mortality.
A cohort study approach
In this study, the researchers calculated weekly mortality rates with 95% confidence intervals per 100,000 individuals and mortality rate ratios to compare the epidemic year (July 29, 2019, to July 26, 2020) with the four preceding years (July 2015 to July 2019).
These scientists have also compared COVID-19 associated deaths and mortality rates for the weeks of the epidemic in Norway and Sweden (between March 16 and July 26, 2020). The data were obtained from the main data registries in these two countries that are close to 100% complete due to mandatory reporting.
All COVID-19 associated mortality (defined as deaths among individuals with a positive COVID-19 test up to thirty days before death) stratified by age has been retrieved from the Institute of Public Health in Norway and the Public Health Agency of Sweden.
All-cause mortality as a key measure?
"Our study shows that although Covid-19 associated mortality rate was almost 15-fold higher in Sweden than in Norway during the epidemic, all-cause mortality was not higher in Sweden compared with three of the four preceding years", say study researchers.
More specifically, mortality rates in Norway were relatively stable during the first three 12-month periods of 2015/16, 2016/17, and 2017/18 (ranging between 14.8 and 15.1 per 100,000 individuals), and slightly lower in the two periods preceding and during the epidemic (2018/19 and 2019/20 with a rate of 14.5 per 100,000 individuals).
On the other hand, all-cause mortality in Sweden was stable during the first three 12-month periods of 2015/16, 2016/17, and 2017/18 (ranging between 17.2 to 17.5 per 100,000 individuals), but lower in the year 2018/19, which immediately preceded the epidemic (16.2 per 100,000 individuals).
In any case, a rise in all-cause mortality was only visible in comparison to the immediately preceding period (2018/19), as mortality was lower when compared to the previous years. Furthermore, excess mortality was limited to individuals older than 70 years.
Conversely, mortality rates were lower than expected for all ages in Norway and those younger than 70 years in Sweden. Finally, the rates of registered infectious diseases other than COVID-19 have decreased.
The role of mortality displacement
"Our study shows that all-cause mortality was largely unchanged during the epidemic as compared to the previous four years in Norway and Sweden, two countries which employed very different strategies against the epidemic," emphasize study authors in this medRxiv paper.
In other words, excess mortality from COVID-19 may be less conspicuous than previously perceived in Sweden, while mortality displacement may be used to explain at least part of the observed findings.
More specifically, mortality displacement implies temporarily increased mortality (i.e., excess mortality) in a certain population as a result of external events, which likely arises because individuals in vulnerable groups die weeks or months earlier than they would otherwise – primarily due to the timing or severity of the unusual external event. The excess mortality is, thus, predated or followed by time periods of lower than expected mortality.
In conclusion, the researchers hope that these findings can open the door for a less polarized and non-judgmental discussion about the benefits and drawbacks of either more lenient or more drastic measures against the COVID-19 pandemic.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Juul, F.E. et al. (2020). Mortality in Norway and Sweden before and after the Covid-19 outbreak: a cohort study. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.11.20229708, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.11.11.20229708v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Juul, Frederik E., Henriette C. Jodal, Ishita Barua, Erle Refsum, Ørjan Olsvik, Lise M. Helsingen, Magnus Løberg, Michael Bretthauer, Mette Kalager, and Louise Emilsson. 2021. “Mortality in Norway and Sweden during the COVID-19 Pandemic.” Scandinavian Journal of Public Health 50 (1): 38–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/14034948211047137. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/14034948211047137.