A brain region involved in processing information about ourselves biases our ability to remember, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
People are good at noticing information about themselves, like when your eye jumps to your name in a long list or you manage to hear someone address you in a noisy crowd. This self-bias extends to working memory, the ability to actively think about and manipulate bits of information: people are also better at remembering things about themselves.
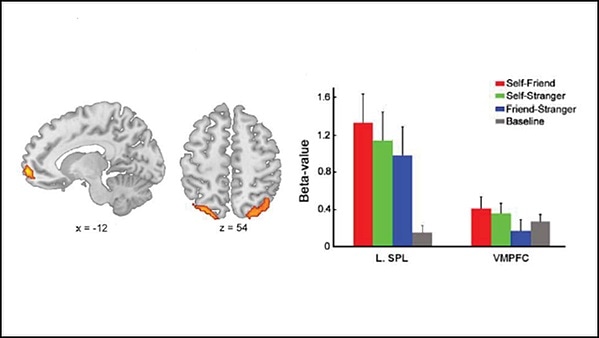
To pinpoint the source of this bias, Yin et al. measured participants’ brain activity in an fMRI scanner while they tried to remember the location of different colored dots representing themselves, a friend, or a stranger. The participants’ fastest response time came when recalling the dot representing themselves, even though it was an arbitrary connection. When people held the self-representing dot in working memory, they had greater activity in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (VMPFC) — an area involved in processing self-relevant information. Greater synchrony between the VMPFC and working memory regions corresponded to faster response times. When the researchers interfered with VMPFC activity with transcranial direct current stimulation, the self-bias disappeared, indicating activity in the region drives the bias.
Source:
Journal reference:
Yin, S., et al. (2021) Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex Drives the Prioritization of Self-Associated Stimuli in Working Memory. Journal of Neuroscience. doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1783-20.2020.