Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), continues to spread worldwide. Over 96.97 million cases have been confirmed across 191 countries and territories, and over 2 million people have lost their lives.
Many studies have tested the effects of various drugs and agents in the past. To date, there is still no targeted antiviral treatment for COVID-19.
A team of researchers from Academia Sinica and the National University in Taiwan and the La Jolla Institute in the US evaluated the efficacy of 2,855 agents against SARS-CoV-2. They found that agents like mefloquine, nelfinavir, and extracts of plants such as Ganoderma lucidum (RF3) or Lingzi, Perilla frutescens, or Korean perilla, and Mentha haplocalyx or mentha, were found to be effective against SARS-CoV-2 infection in animal models.
The study
To arrive at the study findings, which were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America (PNAS), the researchers utilized a cell-based infection assay to screen more than 3,000 agents used in humans and animals. From there, the team has identified 15 with antiviral activity.
The team used in vitro enzymatic assays alongside computer modeling to test and confirm the activity of the chosen agents against the viral protease and RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2.
The team used these agents by developing a challenge assay with hamsters. They identified five agents that can be used to develop new therapeutics to contain the current pandemic.
Cell-based study
The Vero E6 cell-based study has identified the 15 chemicals from a library of compounds approved for human and animal use. The team categorized the chemicals into five clusters – viral protease inhibitors, inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 function, guanine analog, ion channel modulators, and ionophoric antibiotics.
The chemicals include nelfinavir, boceprevir, thioguanine, cepharanthine, emetine, moxidectin, ivermectin, mefloquine, ivacaftor, azelnidipine, penfluridol, dronedarone, salinomycin, monensin, and maduramicin.
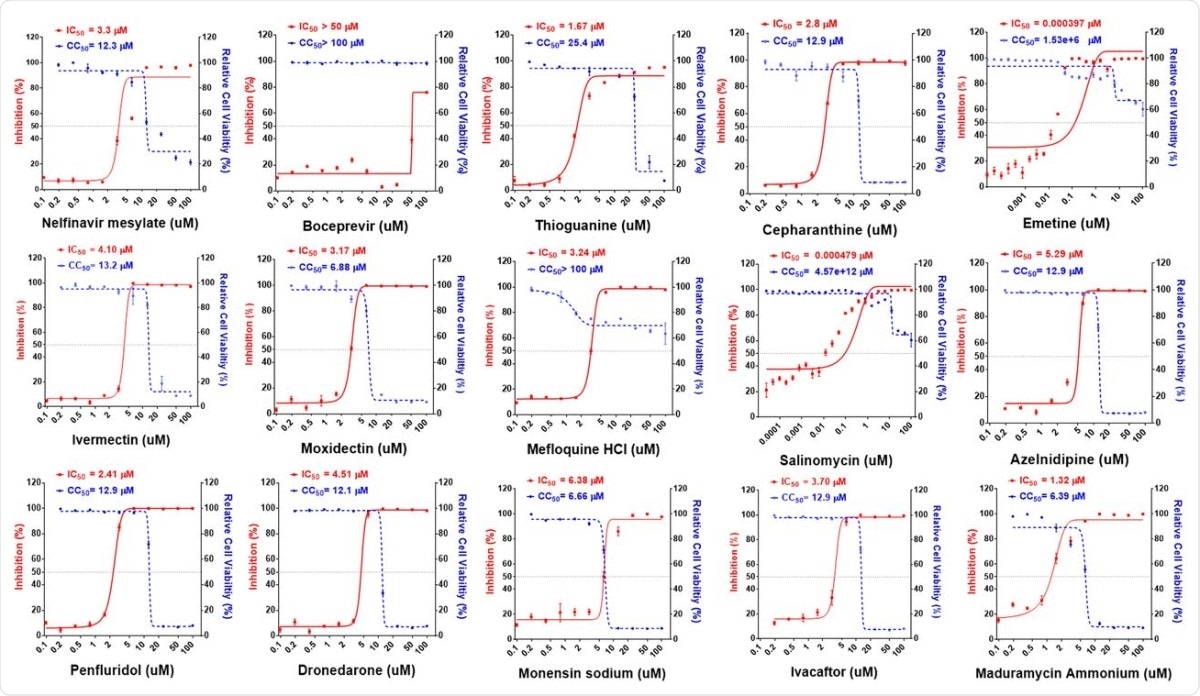
Dose–response relationships of 15 selected antiviral compounds. Vero E6 cells were pretreated with compounds at indicated doses followed by SARS-CoV-2 infection for 48 h. The percentage of viral titer determined by antinucleocapsid antibody after drug treatment (red) and cell viability (blue) were measured and expressed as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments.
Many Chinese herbal medicines and supplements were also tested, including species of Asterceae, Theaceae, Mentheae, and Lamiaceae.
The team found that several drugs like mefloquine, nelfinavir, and extracts of Ganoderma lucidum (RF3), Perilla frutescens, and Mentha haplocalyx were effective against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The team also noted that since the safety and pharmacological characteristics of these drugs were already studied, the preclinical and clinical evaluation of the active compounds is expected to be faster. Hence, it can reduce the time, effort, and cost for further development of these agents.
Conclusion
The herbal compounds found to be effective in combating SARS-CoV-2 could be interesting sources to discover and develop new therapeutics that inhibit viral activity. These compounds may also be used in human trials to determine their safety and efficacy in patients with COVID-19.
While the vaccination campaign is rolling out in some countries, it is still important to determine drugs and agents to combat the pandemic. This way, those who do not have the vaccine yet may be assured of an effective treatment.
Source:
Journal reference: