Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly contagious disease characterized by respiratory failure and death in severe conditions. It is caused by a novel coronavirus called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which originated in Wuhan, China, in late 2019.
COVID-19 is associated with many inflammatory conditions such as macrophage activation and cytokine storm triggered by increased production of interleukins, C-reactive protein (CRP), and tumor necrosis factors-α (TNF-α). Coagulopathy and renal and liver inflammation have been reported to increase the mortality risk in severe COVID-19 patients. Evidence from other studies suggests that COVID-19 causes more deaths in males than females.
Analyzing gender differences in hyperinflammatory conditions resulting in COVID-19 mortality
Recently researchers from India analyzed gender differences in COVID-19-related hyperinflammatory conditions resulting in mortality in Indian patients. The study is published on the preprint server, medRxiv*.
The study group included 2,997 patients treated at Era's Lucknow Medical College and Hospital (ELMCH), ERA University, in northern India. Blood samples were randomly collected from 150 COVID-19 patients with severe disease requiring oxygen. The study was conducted between August 10 and September 15, 2020.
The team of researchers analyzed HICs and related laboratory markers such as hematological dysfunctions (lymphocytopenia and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio), hyperferritinemia (serum ferritin), cytokinemia (Creactive protein levels), coagulopathy (D-dimer), renal inflammation (blood urea and creatinine), liver inflammation (aspartate aminotransferase), and hyperglycemia (random blood glucose). The cut-off limits of these markers used for analyzing the mortality risk in male and female COVID-19 patients were defined based on a scale validated by Webb et al. (2020).
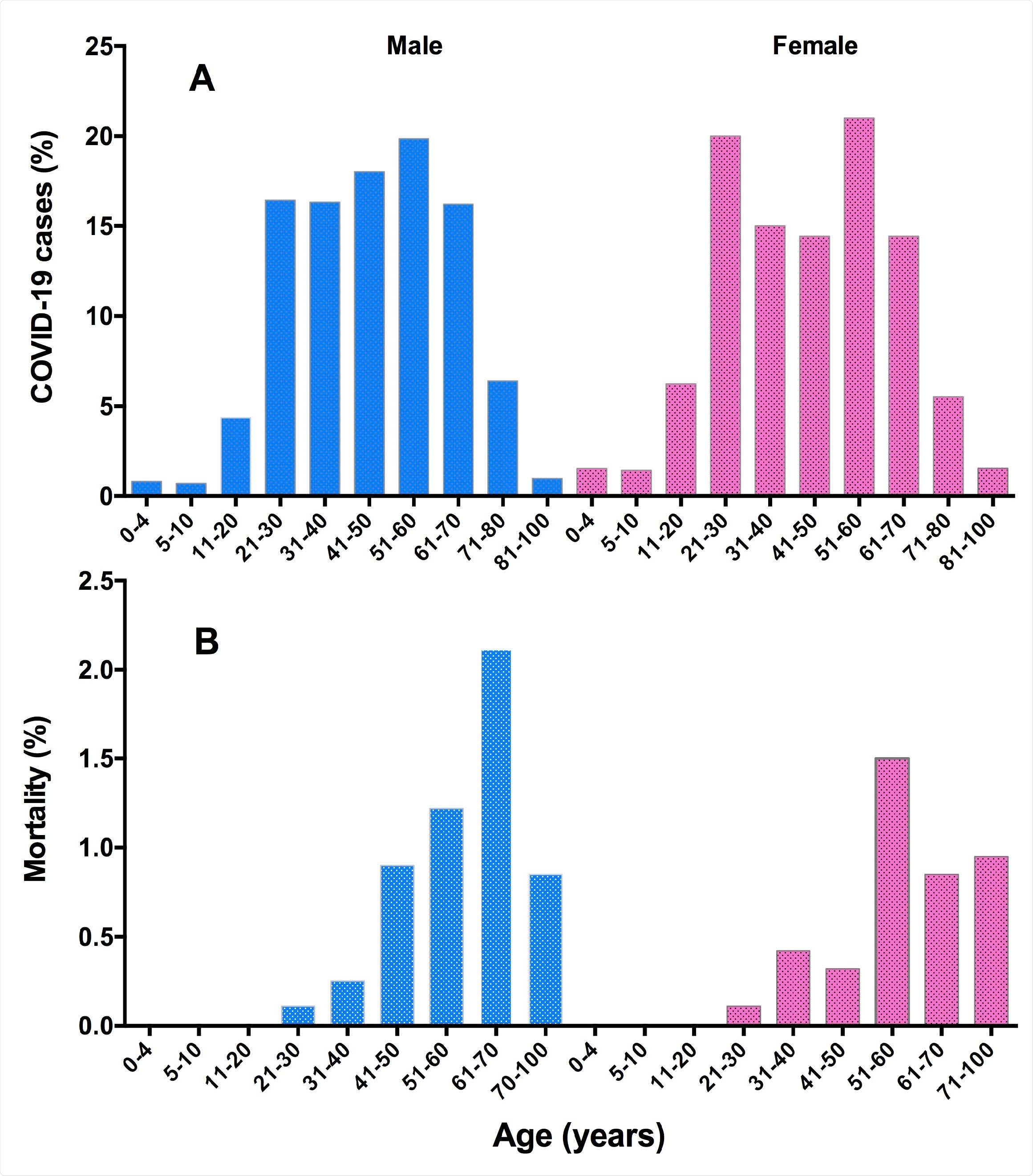
Trend of COVID-19 distribution (A), and mortality proportion (B), in male and female patients of different age groups. A total of 2997 COVID-19 cases (2,030 males and 967 females) were included in this study.

 *Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
*Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
Results show different HICs associated with disease severity and mortality in male and female patients
In the study cohort comprising hospitalized COVID-19 patients, the analysis of HICs showed that hyperferritinemia (odd ratio: 2.9, 95% CI 1.4-6.0), hepatic inflammation (odd ratio: 2.0, 95% CI 0.52-7.40), hematological dysfunctions (odd ratio: 2.10, 95% CI 1.0-4.2), and coagulopathy (odd ratio: 1.5, 95% CI 1.50, 95% CI 0.50-4.60) were more prevalent and severe in male patients with COVID-19.
"Although nearly 30-35% male and female COVID-19 patients had renal inflammation, and ~40% had hyperglycemia, both these criteria were strongly associated with mortality in both male and female COVID-19 patients."
About 86% male to 64% female COVID-19 patients had lymphocytopenia. While cytokinemia (odd ratio: 1.60, 95% CI 0.37 -7.30) and hyperferritinemia (odd ratio: 1.70, 95% CI 0.37-7.43) were strongly linked to mortality in male patients, hematological dysfunctions (odd ratio: 1.70, 95% CI 0.27-10) and coagulopathy (odd ratio: 3.30, 95% CI 0.31-35) were associated with mortality in female patients.
Almost 80% of COVID-19 patients of both genders who died had ≥2 HIS criteria. Chronic renal disease was linked to more deaths in female patients than males (odds ratio: 2.0, 95% CI 0.54 - 7.4).
Although the proportion of mortality was slightly higher in male (6.3%) compared to female (4.5%) COVID-19 patients, survival curves of both genders were not different (hazard ratio: 1.02, 95% CI 0.71-1.40, P = 0. 953).
"Thus, our findings provide experimental validation for the application of various criteria in predicting the risk of severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients as proposed recently."
Findings could help develop gender-based treatment and care for COVID-19 patients
The authors concluded that distinct HICs were associated with disease severity and mortality in male and female COVID-19 patients based on their findings. Coagulopathy and renal dysfunction were specifically harmful to female patients with COVID-19 and the proportion of overall mortality was about 5.3%.
According to the authors, the results suggest that gender differences in severity of COVID-19 and related mortality arise as a result of differences in HICs. They believe that the results could help in the development of gender-based care for COVID-19 patients.
"These findings are in agreement with other studies, which have reported that diabetes/hyperglycemia and renal injury/inflammation substantially increase the risk of mortality in COVID-19 patients."

 *Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
*Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.