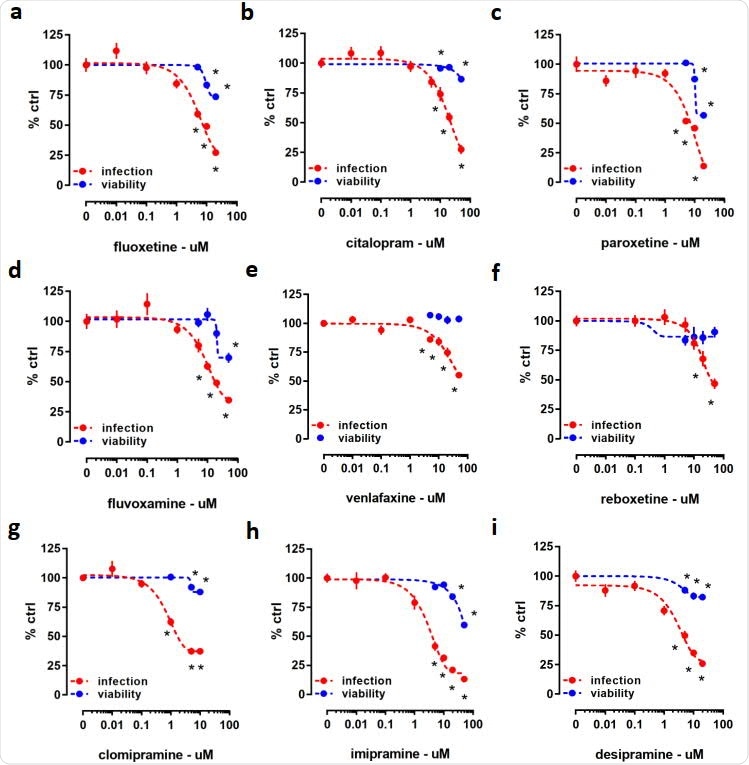
Luciferase reporter activity (infection) and ATP level (viability) in HEK293T-ACE2-TMPRSS2 cells challenged with SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped viruses and pharmacologically diverse antidepressant drugs for 24 h. Treatment with (a) fluoxetine (IC50= 5.992 μM), (b) citalopram (IC50= 27.51μM), (c) paroxetine (IC50= 12.55 μM), (d) fluvoxamine (IC50= 10.54 μM), (e) venlafaxine (IC50= 36.35 μM), (f) reboxetine (IC50= 17.69 μM), (g) clomipramine (IC50= 0.75 μM), (h) imipramine (IC50= 3 μM), and (i) desipramine (IC50= 8.097μM) significantly reduced luciferase reporter activity. At higher concentrations, all the compounds, except (e) venlafaxine and (f) reboxetine reduced ATP levels in the luminescent cell viability assay after 24 h incubation. *p< 0.05 from control group (0). Data represented as mean ± SEM.
Clinically available antidepressants inhibit infection by pseudoviruses without significant impact on cell viability
Several clinically prescribed antidepressants, including citalopram, fluoxetine, imipramine, and reboxetine, as well as antipsychotic compounds such as flupenthixol, chlorpromazine, and pimozide, were found to be capable of inhibiting infection by pseudoviruses with minimal impact on cell viability. The antiviral activity of many of these drugs was tested in Calu-1 cells against the B.1 SARS-CoV-2 lineage.
In contrast, in the pseudovirus model, the anticonvulsant carbamazepine, and antidepressants ketamine and its derivatives as well as MAO and phosphodiesterase inhibitors phenelzine and rolipram, respectively, showed no activity. Moreover, fluoxetine was effective against pseudoviruses with the K417N, N501Y, and E484K spike mutations, and the SARS-CoV-2 variants - VoC-1 (B.1.1.7) and VoC-2 (B.1.351).
Findings show the possibility of using psychoactive compounds as an alternative treatment method for people infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants
These results show the potential of these widely used antidepressants and antipsychotics against infection by SARS-CoV-2 and its new variants. Thermal shift assays and X-ray diffraction studies revealed specific interaction sites for drugs including clomipramine, imipramine, thioridazine, sertraline, and paroxetine, on EBOV glycoprotein.
"It is plausible to argue that antidepressants, as well as related-psychoactive compounds, can be considered as an alternative treatment method for people infected with these variants of SARS-CoV-2."
According to the authors, the findings of the study confirm data from previous studies and expands information on the repurposing of these compounds to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, including the new variants of concern. Overall, this data combined with data from other recent studies show that safe and clinically approved antidepressants might be additional tools in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Similar strategies can be followed to address whether these drugs can bind to SARS-CoV-2 S protein directly."