A recent study conducted at the Ohio State University, USA, and the Fudan University, China, has revealed that alpha-defensin human neutrophil peptide 1 (HNP1), a cationic antimicrobial peptide, can prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from infecting cells by destabilizing the viral spike protein and disrupting spike-mediated viral envelop – host cell membrane fusion. The study is currently available on the bioRxiv* preprint server.
The induction of adaptive immunity through vaccination is a valuable strategy to combat the current outbreak of COVID-19. Although currently rolling out COVID-19 vaccines have shown good efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptomatic disease, there remains a risk from newly emerging viral variants that may potentially bypass the vaccine-induced immunity by acquiring escape mutations.
Given the fact that a substantial proportion of SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals remain asymptomatic, it can be expected that at least in some conditions, the virus can be eliminated by the innate immune system. Human alpha and beta-defensins are promising members of the innate immune system that show potent antimicrobial efficacy against various pathogens, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), herpes simplex virus, influenza virus, and SARS-CoV.
In the current study, the scientists have evaluated the efficacy of an alpha defensin, human neutrophil peptide 1 (HNP1), and a retrocyclin, RC-101, against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Important observations
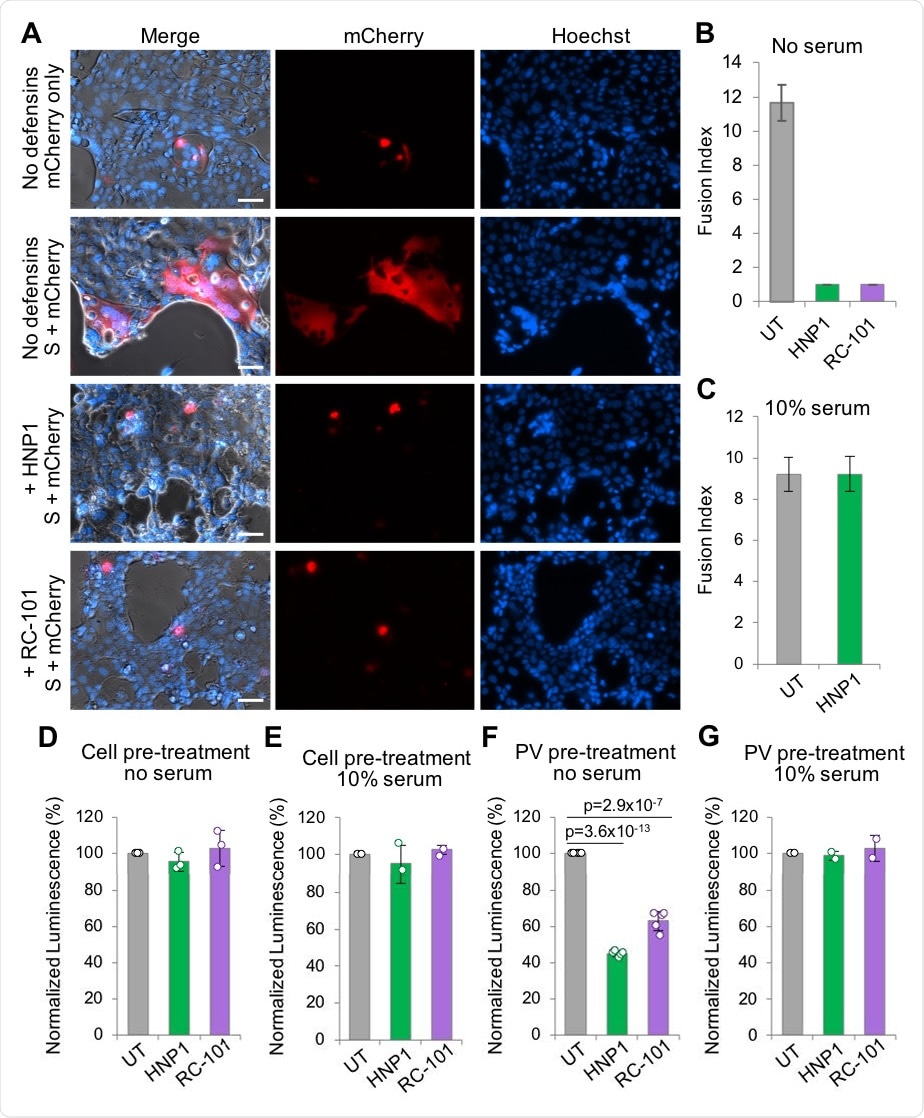
To examine the antiviral efficacy of HNP1 and RC-101, the scientists cocultured two human cell lines stably expressing viral spike protein or human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). By administering HNP1 or RC-101 to the coculture, they observed that in the absence of serum, both HNP1 and RC-101 are capable of completely inhibiting the spike – ACE2 interaction. However, in the presence of serum, the defensin-mediated inhibition was abrogated.
Using a spike-encoding pseudovirus-mediated cell infection model, they observed that preincubation of cells with HNP1 or RC-101 did not influence the infection-creating ability of the virus. However, preincubation of HNP1 or RC-101 with the pseudovirus prior to infection significantly prevented the infection. These findings indicate that rather than influencing host cell molecule ACE2, defensins directly modulate viral particles to inhibit infection.
While studying the mode of action of defensins, they observed that HNP1 directly binds to recombinant spike protein at sub-micromolar concentrations. Since serum inhibited defensin activity, they checked whether HNP1 binds the most abundant serum protein albumin. The findings revealed that HNP1 has a 20-fold lower affinity for serum albumin, highlighting its high selectivity for the viral spike protein.
With further investigation using differential scanning fluorimetry, they observed that both HNP1 and RC-101 can destabilize the spike protein at micromolar concentrations.
To determine whether HNP1 and RC-101 can inhibit infection by genuine SARS-CoV-2 virus, they either preincubated the virus with HNP1 or administered HNP1 to the cell culture medium immediately after adding the virus. In both conditions, HNP1 strongly inhibited the viral infection. Similar to previous experiments, serum inhibited the antiviral efficacy of HNP1 in a dose-dependent manner. However, when used in sufficiently high concentration, HNP1 was capable of inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection even in the presence of 10% serum.
HNP1 and RC101 inhibit SARS-CoV-2 spike-pseudotyped viral infection

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Study significance
The study findings reveal that at sub-micromolar concentrations, defensins including HNP1 and RC-101 are capable of neutralizing SARS-CoV-2. Among defensins, retrocyclins are particularly promising because of their high stability, low toxicity, non-immunogenicity, and resistance to proteolytic degradation. In this context, there is evidence suggesting that retrocyclins can be used as topical antimicrobial agents to prevent sexually transmitted HIV infection.
Although the findings indicate that defensins are less active in the presence of serum, the scientists believe that HNP1 and RC-101 should be regarded as potential anti-COVID-19 agents for topical use.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources