Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing phytochemicals present in plant families such as Amaryllidaceae, Apocynaceae, Papaveraceae, Asteraceae, and Solanaceae, with potential biological activities and pharmacological effects. Many alkaloids available in human diets are in coffee seeds (caffeine), cacao seeds (theobromine and caffeine), tea leaves (theophylline and caffeine), tomatoes (tomatine), and potatoes (solanine).
Alkaloids are known to be effective in the treatment of various diseases such as neurological disorders, cancer, metabolic disorders, and infectious diseases. These secondary metabolites from plants are also shown to have prominent effects on viruses such as influenza viruses, herpes simplex virus, human immunodeficiency virus, and hepatitis C virus.
To further study these organic compounds, researchers from Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Iran, and Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Chile, reviewed the role of alkaloids as a potential antiviral, specifically against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). They presented the chemistry, plant sources, and antiviral effects of alkaloids and their anti-SARS-CoV-2 effect.
This review is published in the journal, Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
Despite the innumerable efforts to find therapeutic drug candidates for COVID-19 disease, healthcare providers do not have an effective solution to prescribe. To date, SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for over 176 million infections and has claimed over 3.8 million individuals worldwide. An urgent need for a drug to control the disease is the top priority of scientists and physicians the world over.
Despite intense research, the inherent nature of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and its pathogenesis makes it complex and impossible to find an effective drug.
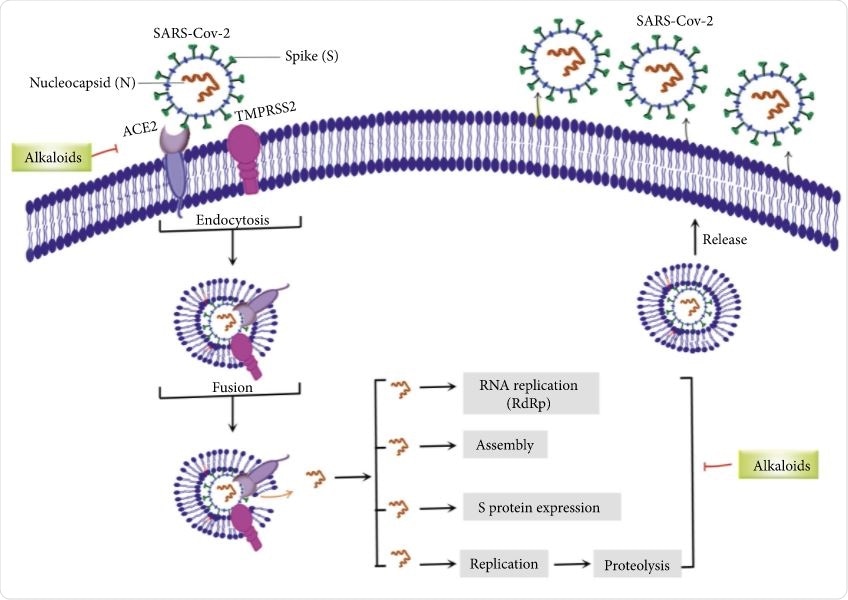
Major targets of alkaloids in combating SARS-CoV-2. ACE2: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, TMPRSS2: transmembrane serine protease 2, and SARS-CoV-2: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2.
Looking in the direction of plant-sourced compounds, the researchers in this review observed that previous in vitro and in silico studies indicated noticeable effects of alkaloids against coronaviruses, especially the SARS-CoV-2. They have summarized all the evidence of antiviral, neuroprotective, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory action of alkaloids.
“The lycorine along with other alkaloids, including tetrandrine, harmine, conessine, and emetine, showed antiviral activities against HCoV such as HCoV-OC43 and HCoV-NL63.”
A list of alkaloids based on in vitro studies and in silico studies with potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity is presented in the review - along with the chemical structure, mechanism of action, type of study, and references.
Alkaloids contain nitrogen atom/atoms in a negative oxidation state at their structures; this is responsible for their alkaline properties associated with therapeutic effects.
While the virus employs different mechanisms such as inhibition of the main protease (Mpro) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), as well as interaction with coronavirus-associated structural proteins, alkaloids interact with the coronavirus structural proteins, as well as the nonstructural angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the cell membrane, and inhibit the RdRp and 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro).
On combating SARS-CoV-2, the researchers discussed the major targets of alkaloids: ACE2, TMPRSS2 (transmembrane serine protease 2), and RNA replication, assembly, S-protein expression and proteolysis.
The researchers noted that several clinical trials are ongoing on alkaloids such as colchicine (NCT04527562, NCT04392141, NCT04375202, NCT04355143, and NCT04360980), berberine (NCT04479202), and tetrandrine (NCT04308317). Many alkaloids have demonstrated high efficacy as anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents.
“According to the antitussive activities of thalimonine and antirhinovirus activities of sophaline D, these alkaloids are promising candidates for COVID-19 treatment.”
In this review, the researchers concluded that alkaloids as a hope for an effective treatment against COVID-19 - due to their simultaneous effects on several therapeutic targets with prominent antiviral effects.
“Hence, marine/plant-derived alkaloids such as berberine, tetrandrine, cepharanthine, lycorine, ergotamine, crambescidin 786, palmatine, noscapine, and quinine with prominent antiSARS-CoV-2 effects along with antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, antitussive and lung injury, immunomodulatory, and protective effects against neurotoxicity, cardiotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and hepatotoxicity could be promising candidates for COVID19 treatment,” the researchers summarized.
Extensive and comprehensive studies on the alkaloids mentioned in the review may be helpful in fighting this pandemic and also the emerging ones.
“Cepharanthine improved the lung injuries, as a critical complication of COVID-19, with the effects on inflammatory signaling pathways. So, cepharanthine could be a promising candidate in combating COVID-19.”